Download the latest CBSE Class 8 Syllabus for Social Science for the 2025-26 academic session. This updated curriculum provides a detailed overview of the Class 8 Social Science course structure, unit and chapter wise weightage and internal assessment guidelines. Class 8 students should refer to this official Social Science syllabus to ensure their preparation is done as per the latest CBSE pattern and books for the current year.
Class 8 Social Science Syllabus and Marks Distribution
We have provided below the official CBSE Class 8 Social Science curriculum issued for the current 2025-26 academic year. It is important for students to study as per the latest Class 8 Social Science curriculum and marks breakup as per important topics. This will help to prepare properly for the upcoming examination.
2025-26 Social Science Syllabus Class 8
Stay updated with the most recent curriculum Class 8 Social Science changes for the 2025-26 session.
CBSE Class 8 Social Science Civics Syllabus
Module – 1 & 2
THE INDIAN CONSTITUTION
Contents:
- Why does a country need a Constitution?
- The Indian Constitution: key features
Activity:
- Download the information about the constitution of Nepal.
Learning Objectives:
- To enable the students to:
- Develop an understanding of the Rule of Law and our involvement with the law.
- To make the students understand the vision and the values of the constitution.
- Develop links between the values/ ideas of democracy and the institutional forms and processes associated with it.
- To develop an appreciation of human rights guaranteed in the Constitution.
Key Terms:
- Dowry Prohibition Act, Untouchability Offences, Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, Republic.
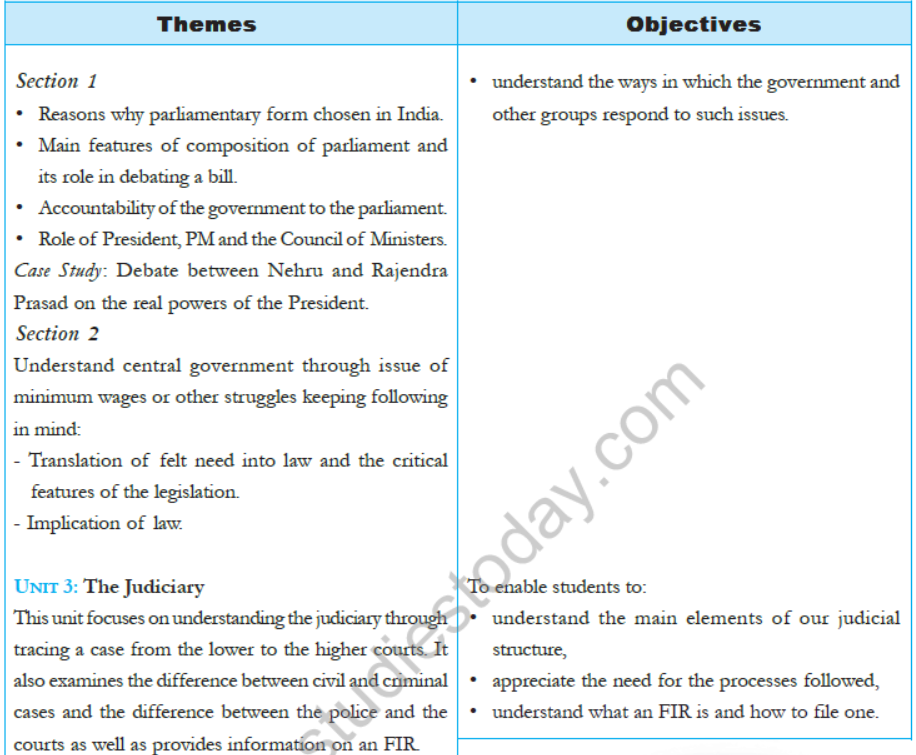
WHY DO WE NEED A PARLIAMENT
Contents:
- Why should people decide?
- People and their representatives.
- The Role of Parliament.
- Who are the people in Parliament?
Learning Objectives:
- To understand why India chose a Parliamentary form of Govt.
- To gain a sense/rationale of the essential elements of the Parliamentary form of Govt.
- Analyse the role of people‟s agency in placing demands for legislation.
- To understand the role of the members of the Parliament.
- To understand the ways in which the Govt. and other groups respond to such issues.
Key Terms:
- Discretionary, Insolvent, Executive, Legislative, Judiciary, Nominate,Summons.
Module – 6, 7 & 8
JUDICIARY
Contents:
- What is the Role of the Judiciary?
- What is an Independent Judiciary?
- What is the structure of courts in India?
- Activity Page 60, 65 of the text book.
- What are the different branches of the legal system?
- Does everyone have access to the courts?
Learning Objectives:
- To enable the students to understand the main elements of our Judicial structure.
- To appreciate the need for the processes followed.
- To distinguish between civil and criminal cases.
- To understand the role of the Public Prosecutor.
Key Terms:
- Appellate Jurisdiction, Writ Jurisdiction, Session Judge, Public Prosecutor.
Module – 9 & 10
Revision For Half Yearly Examination
Module – 11 & 12 (ACTIVITY BASED)
ECONOMIC PRESENCE OF THE GOVERNMENT. PUBLIC FACILITIES
Contents:
- Water and the people of Chennai
- Water as part of the Fundamental Right of life
- The Government‟s Role
- Water supply to Chennai: Is it available to all?
- In search of Alternatives
- Conclusion
Learning Objectives:
- To enable the students to think about the role of government in the economic sphere.
- To see some links between people‟s aspiration or needs and the role of govt.
- To explain how the Govt. is engaged in the developmental activities, especially in the infrastructure and social sectors.
- To explain why we need the Govt., how is the provision done, what is the impact upon the people.
Key Terms:
- Public Sector, Private Sector, Social infrastructure, Literacy.
Module – 13 & 14
UNDERSTANDING MARGINALIZATION
Contents:
- What does it mean to be socially marginalized?
- Who are Adivasis?
- Adivasis and stereotyping.
- Minorities and Marginalized.
Learning Objectives:
- It will enable, the child to learn of about the experiences of inequality of inequality and discrimination faced by certain groups.
- The child to learn about some ways in which groups and individuals challenged existing in equalities.
Key Terms:
- Hierarchy, Ghettoisation, Mainstream, Displaced
Module – 15
UNDERSTANDING MARGINALIZATION
Contents:
- Muslims and Marginalization
- Fundamental Rights.
- Laws for the Marginalized
- Conclusion
Learning Objectives:
This will enable a child to learn that;
- Many marginalized groups like Adivasis, Dalits, Muslims, Women look up to the constitution to address their concerns.
- How rights are translated into laws to protect groups from continued exploitation and the governments efforts to formulate policies to promote the access of these groups to development.
Key Terms:
- Militarized, Malnourished
Module – 16 & 17
CONFRONTING MARGINALIZATION
Contents:
- Protecting the Rights of Dalits and Adivasis.
- The scheduled castes and the scheduled Tribes.
- Adivasi demands and the 1989 Act.
- Conclusion
Learning Objectives:
- To understand what is meant by marginalized group.
- To explain how SC and ST, OBC minorities are a part in it.
- To understand various forms of social inequality.
- To gain an understanding of social and economic injustices.
- To develop skills to analyze an argument from the marginalized point of view.
Key Terms:
- Assertive, Confront, Disposed, Ostracize, Morally Reprehensible, Policy
Module – 18 Revision For Annual Examination
CBSE Class 8 Social Science Geography Syllabus
Module – 1 & 2
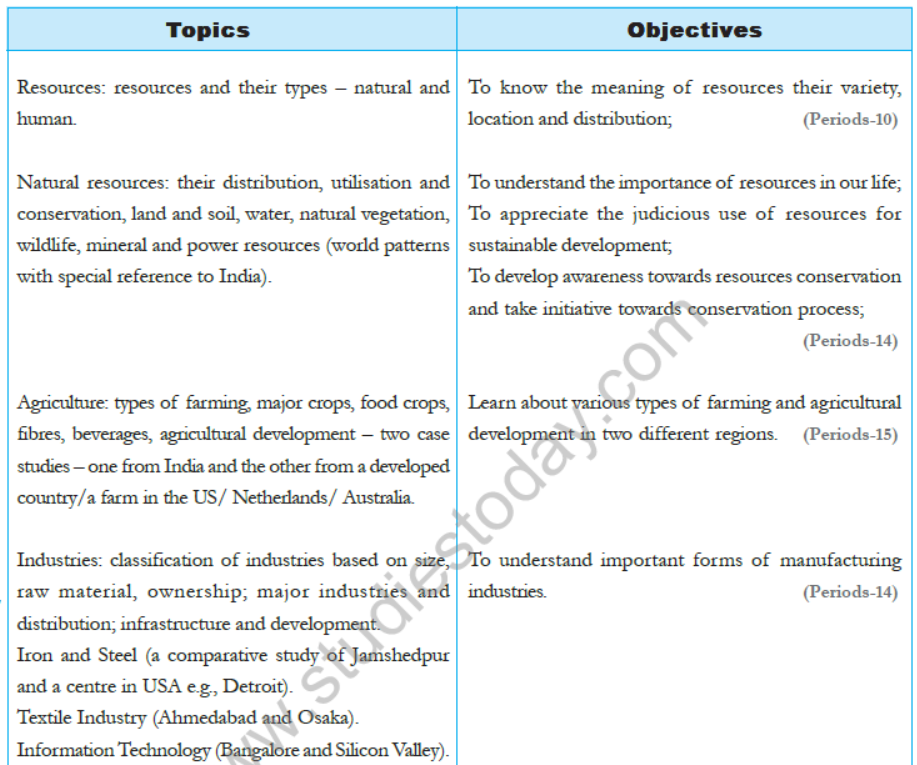
AN INTRODUCTION TO NATURAL RESOURCES
Contents :
I. Resources
II. Types of Resources : Natural, human made & human
III. Classification of Natural Resources :
• Biotic and Abiotic
• Renewable- Non-renewable
• Actual - Potential
• Ubiquitous & Localised
•Conservation of Resources
Learning Objectives :
• Recognize the importance of resources
• Classification based on utility and origin.
• Importance of conservation.
Key Terms :
• Exhaustible and Inexhaustible resources, Sustainable development.
Module – 3
LAND
Contents :
• Land use in selected countries
• Landslides
• Soil, factors of soil formation
• Degradation of soil
• Conservation of soil
Learning Objectives:
• Importance of land for biotic and abiotic community.
• To know land use and causes of land degradation.
• Utility of soils
• Importance of soil conservation.
Key Terms :
• Landslides, Land degradation, Desertification, Khaddar, Bangar, Regur,Leaching, Contour Farming, Crop-rotation, Terrace farming, Shelter belts,Afforestation, Water cycle, Multi-purpose projects.
Module – 4
WATER RESOURCE
Contents :
• Water as renewable resource
• Importance and uses of water
• Problems of water availability
• Conservation of Water resource
Learning Objectives :
• Importance and conservation of water resources.
Key Terms :
• Rain water harvesting, Drip and Sprinkle irrigation.
Module – 5
NATURAL VEGETATION AND WILD LIFE
Contents :
• Natural Vegetation
• Types of forests and wildlife
• Conservation of Forests and Wildlife.
Learning Objectives :
• Location and characteristics of different vegetation types.
• Factors that cause their occurences - mainly climate and relief.
• Importance of conserving natural vegetation - for maintaining an ecological balance.
• How the animal life found in various regions are in tune with the climate,vegetation and relief of that region.
• Animals and their habitat. Special focus on wild life of India.
• Need to conserve wild life.
Key Terms :
• Biosphere, Natural Ecosystem, Deciduous, National Park, Biosphere Reserve,Endangered and Extinct Species
Module – 6
MINERAL AND POWER RESOURCES
Contents :
• Metallic and Non metallic minerals.
• Methods of mining.
• Quality and distribution of minerals in the world and India
Learning Objectives :
• Grades and regions of minerals like Iron, Copper, Gold, Bauxite, Manganese.
• Mining techniques like open cast and deep shaft mining.
Key Terms :
• Open cast mining, shaft mining drilling and quarring
Module – 7
MINERAL AND POWER RESOURCES
Contents :
• Uses and Conservation of minerals
• Power resources Conventional sources, Coal, Petroleum and Natural Gas.
• Power resources in the world.
Learning Objectives :
• Power resources will be studied under two types- Conventional and Non conventional resources. Significance of each will be comprehended.
Key Terms :
• Renewable and Non renewable resources.
Module – 8
MINERAL AND POWER RESOURCES
Contents :
• Hydro Power
• Non-conventional source of energy- Solar, Wind, Nuclear, Geothermal, Tidal and Biogas
Learning Objectives :
Students can differentiate between
• How the non-conventional sources of energy out weigh the conventional ones.
• Distribution of minerals and power resources in the world.
Key Terms :
• Non renewable resources, Nuclear, Geothermal energy, Off shore drilling.
Module – 9
Agriculture
Contents :
• Farm system • Types of farming
Learning Objectives :
Students can differentiate between
• Shifting- Sedentary farming
• Subsistance-Commercial farming
• Intensive- Extensive farming
• Mixed – Plantation Farming
Key Terms :
Jhumming, Truck farming, Granaries of the world.
Module – 10
Revision For Half Yearly Examinations
Module – 11
MAJOR CROPS
Contents :
• Major crops like Rice, Wheat, Millets, Maize, Sugarcane, Cotton, Jute, Tea,Coffee, Rubber
Learning Objectives
• Food crops and Fibre crops have different physical requirements and also grow in different parts of the world. Geographical conditions necessary for the growth of the crops and the regions in which they are cultivated.
Key Terms
• Kharif, Rabi, Ratooning, Retting, Latex.
Module – 12
CASE STUDIES
Contents :
• Case studies of farming practices in India and the USA.
Learning Objectives
• Make a comprehensive study of the agriculture practiced in India -intensive and that in the USA. –extensive.
Key Terms
• Subsistence, Commercial, Green revolution, White revolution, Silos.
Module – 13
INDUSTRIES AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION
Contents :
• Defining the term Industry
• Classification of industries on the basis of
a) Size - large scale Small scale
Cottage industry
b) Ownership- Public sector
Private sector
Joint sector.
c) Raw material- Forest based
Mineral based
Agro based
Pastoral based.
Learning Objectives:
• The word Industry has acquired a new meaning in today‟s world.
• Classification done on different basis.
• Students should be able to give examples for each and also distinguish between them.
Key Terms:
• Cottage industry, Large scale, Small scale, Public, Private and Joint sector
Module – 14
MAJOR INDUSTRIES
Contents :
Factors that influence the location of industries.
• Availability of Raw material
• Availability of Power
• Skilled and Unskilled labour
• Availability of Transport
• Capital
• Market.
Learning Objectives:
• Once the factors responsible for the location of industries are understood, students will appreciate why only a few regions of the world have emerged as industrial areas.
Key Terms:
• Raw-material, Skilled and Unskilled labour, Perishable products.
Module – 15
MAJOR INDUSTRIES
Contents :
Studying basic industries namely:
• Iron & Steel.
• Tata Iron & Steel – Jameshedpur
• Iron & Steel – Pittisburgh
• Cotton Textile Industry – Ahmedabad and Osaka.
• Information Technology
Learning Objectives:
• Why these industries are termed as basic. Significance of these industries in the economic development of a country.
Key Terms:
• Basic industry, Consumer Industry.
Module – 16 & 17
HUMAN RESOURCES
Contents :
• Importance of Human Resource. World density and distribution of population.
• Factors influencing population distribution.
• Growth of population over the century.
• Composition of population(quality of people).
• Indicators like –
Sex ratio.
Age composition.
Rural-Urban distribution.
Literacy level.
Improving Social Structure and Welfare Schemes.
Learning Objectives:
• To realize human beings as the greatest resources by knowing their quantitative and qualitative value.
• To know the reasons for uneven distribution of population and density.
• To understand the important components of population compositions which directly indicate the status of development of a region.
Key Terms:
• Birth rate, Death rate, Growth rate, Life expectancy, Population density,Census, Sex ratio, Dependent population, Literacy, Productive population,Rural-urban divide
Module – 18
Revision For Annual Examination
CBSE Class 8 Social Science History Syllabus
MODULES: HISTORY
Module – 1 & 2
WHEN, WHERE AND HOW
Contents:
•An overview of the period.
•Importance of dates and periodisation
•Sources
Learning Objectives:
•To understand the different ways to periodise Indian history and politics associated with it.
•To evaluate various sources for the modern period in India and problems faced by historians while using certain sources.
Module – 3
FROM TRADE TO TERRITORY (The Company Establishes Power)
Contents:
•East India Company comes east.
•East India Company begins trade in Bengal.
•How trade led to battles.
•The battle of plassey.
•Company officials become „nabobs‟.
•Company rule expands.
Learning Objectives:
•To understand the initial motive of the East India Company in India.
•To understand the way a mere trading company gradually begin to capture territories for more profit in trade.
Key Terms:
•Mercantile, Farman, puppet, „nabobs‟.
Module – 4
FROM TRADE TO TERRITORY (contd.)
Contents:
- Tipu Sultan – The „ Tiger of Mysore‟
- War with the Marathas
- The claim to Paramountcy
- The Doctrine of Lapse
- Setting up a new administration
- The company army
- Slave trade in South Africa
Learning Objectives:
- To explain the resistance and confrontation between the British and the Southern State.
- To explain various means adopted by the British to capture territories in India and expand their rule.
- To understand the reorganization of army and administration by the British in India.
Key Terms:
- Confederacy, qazi, impeachment, Mufti, dharmashastras, Sawar, Matchlock,musket.
Module – 5
RULING THE COUNTRYSIDE
Contents:
- The company becomes the Diwan
- Revenue for the company.
- The need to improve agriculture and problem with it.
- A new system is devised – Permanent Settlement
- The Munro System – Ryotwari settlement.
Learning Objectives:
- To explain the land revenue system of the British.
- To understand the relationship of the British with the peasants.
Key Terms:
- Ryot, talukdar, mahal
Module – 6
RULING THE COUNTRYSIDE (contd.)
Contents:
- Crops for Europe
- Why the demand for Indian indigo?
- Britain turns to India.
- How was indigo cultivated?
- The problem with „nij‟ cultivation.
- Indigo on the land of ryots.
- The Blue Rebellion and after.
Learning Objectives:
- To explain the importance of indigo to the British.
- To understand the plight of the peasants cultivating indigo.
Key Terms:
- Plantation, nij, slaves, Bigha, vat
Module – 7 (ACTIVITY BASED)
TRIBALS, DIKUS AND THE VISION OF A GOLDEN AGE
Contents:
- How did Tribal Groups Live?
- Some were jhum cultivations or hunters and gatherers while some herded animals and some took to settled cultivation.
- How did colonial Rule affect Tribal lives?
- What happened to tribal chiefs, shifting cultivatiors?
- Forest laws and their impact.
- Birsa Munda
Learning Objectives:
- To explain the condition of tribals and their occupations in India.
- To understand the impact of British forest laws on the tribals.
- Form of resistance – case study of Birsa Munda
Key Terms:
- Sleepers, Bewar, fallow
Module – 8
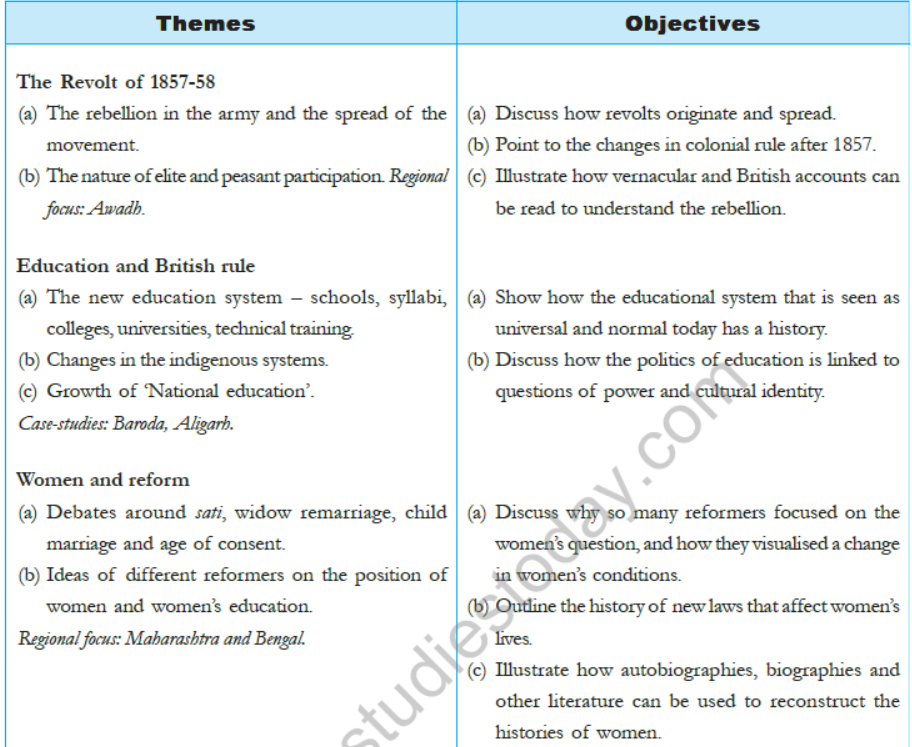
WHEN PEOPLE REBEL (1857 AND AFTER)
Contents:
- Policies and the people.
- Through the eyes of the people.
- A Mutiny becomes a popular rebellion.
Learning Objectives:
- To understand the impact of British exploitative policies on different social groups of India.
- To explain how people perceived the rebellion.
Key Terms:
- Sepoy, mutiny
Module – 9 & 10
WHEN PEOPLE REBEL (contd.)
Contents:
- The company fight back.
- Aftermath
Learning Objectives:
- To explain the suppression of the revolt by the British.
- To understand the administrative and military changes introduced by the British after the Revolt.
Key Terms:
- Sovereign, Paramount, ghazis
Revision For Half Yearly Examinations
Module – 11
COLONIALISM AND THE CITY (The story of an imperial capital)
Contents:
- What happened to cities under colonial Rule?
- How many „Delhis‟ before New Delhi?
- The making of New Delhi.
- Planning a new capital.
Learning Objectives:
- To understand the condition of major cities under the colonial rule.
- To explain the making of the new capital „ New Delhi‟.
- The impact of British rule on the Indian cities.
Key Terms:
- Gulfaroshan, Renaissance, Dargah, Khanqah, Idgah, cut-de-sac, urbanization
Module – 12
COLONIALISM AND THE CITY (contd.)
Contents:
- Life in the time of Partition.
- Inside the old city.
- The decline of havelis.
- The municipality begins to plan.
Learning Objectives:
- To understand the impact of the Partition on the cities.
- To explain the changes occurred in the mughal city during the colonial rule.
- To understand the makeover of the old city into a new modern city.
Key Terms:
- Amir, baoli, Haveli
CIVILIZING THE “NATIVE”, EDUCATING THE NATION
Contents:
- The new education system – schools, syllabi, colleges, universities, technical training.
- Changes in the indigenous system – Growth of national education
- Case studies – Braoda, Aligarh
Learning Objectives:
- To show who the education system that is seen as universal and normal today has a history.
- To discuss how the politics of education is linked to the question of power and cultural identity.
Key Terms:
- Wood‟s Dispatch, Act of 1813
Module – 15 &16
WOMEN AND REFORM
Contents:
- Debates around Sati, Widow remarriage, Child marriage and age of consent.
- Ideas of different reformers on the position of women and women‟s education.
- Regional focus : Maharashtra and Bengal
Learning Objectives:
- To discuss why so many reformers focused on the women‟s question and how they visualized a change in women‟s conditions.
- To outline the history of new laws that affect women‟s lives.
- To illustrate how autobiographies, biographies and other literature can be used to reconstruct the histories of women.
Key Terms:
- Sati, Age of consent
Module – 17 & 18
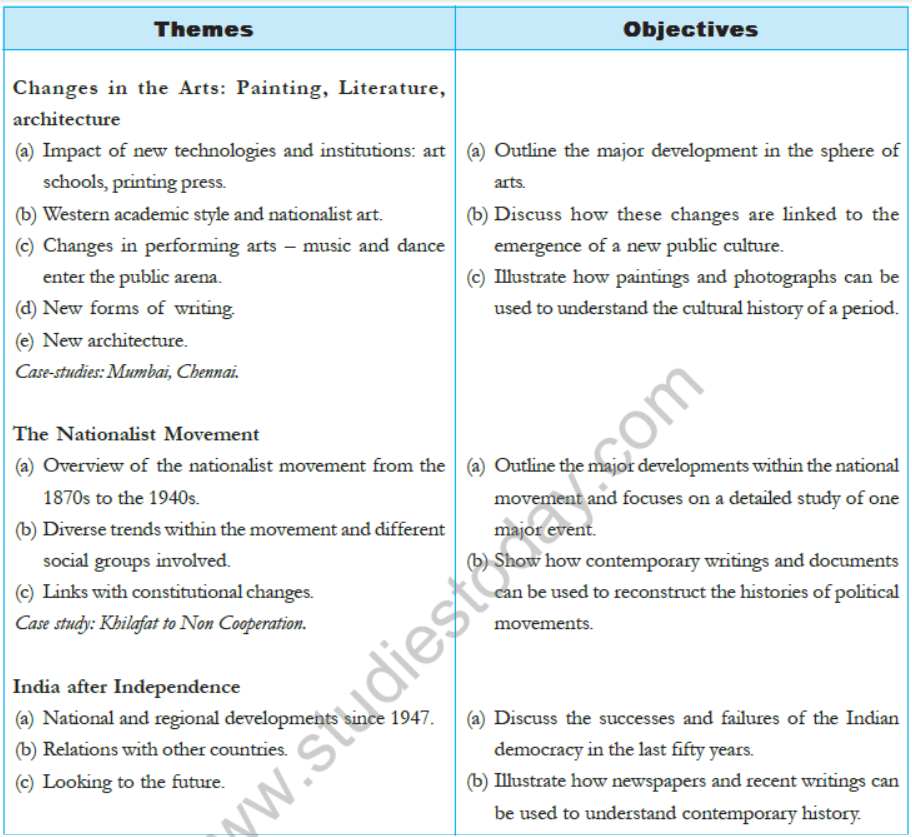
THE MAKING OF THE NATIONAL MOVEMENT : 1870s-1947
Contents:
- Overview of the nationalist movement from the 1870s to the 1940s.
- Diverse trends within the movement and different social groups involved.
- Links with constitutional changes.
- Case study : Khilafat to Non-cooperation.
Learning Objectives:
- To outline the major developments within the national movement and focus on a detailed study of one of the major events.
- To show how contemporary writings and documents can be used to reconstruct the histories of political movements.
Key Terms:
- Non-cooperation, Civil Disobedience, Khilafat
Module – 19
Revision For Annual Examination


VCLASIS VIIII
RULE OF LAW AND SOCIAL JUSTICE
Rationale
The theme of law and social justice for Class VIII attempts to connect constitutional values and vision to the reality of contemporary India and to look at the constitution as an inspiring and evolving document. Some provisions of the constitution relating to fundamental rights, parliamentary form of government, role of the judiciary and economic role of government are the topics discussed in this light. The attempt is to move from listing rules and functions to discussing some of the key ideas underlying the working of these institutions. The role of people as desiring and striving for a just society and hence responding and evolving laws and structures that govern us is brought forth.
Objectives
The specific objectives of the course, where it is not clear from the rationale of the approach, are indicated beside the themes to be taught in the course.




Important Practice Resources for Class 8 Social Science
The complete and updated syllabus for Class 8 Social Science for the 2025-26 academic session is available on StudiesToday.com with detailed chapter-wise marks issued by CBSE.
Yes, several topics have been rationalized to reduce the academic load on Class 8 students. The Social Science syllabus highlights the deleted topics section and is as per 2026 Exam format.
For Class 8 Social Science, the evaluation is split into an 80-mark theory paper and a 20-mark internal assessment (Project/ASL).
The Class 8 Social Science curriculum focuses on 50% competency-based questions.
We have provided the Class 8 Social Science curriculum in a bilingual format where applicable for 2026 session.
Our team has carefully updated all resources based on the latest circulars from the official CBSE website. The Class 8 Social Science syllabus is 100% authentic and aligned with the 2025-2026 academic calendar.


