Exercise 6.1
Question 1: Write the fraction representing the shaded portion:
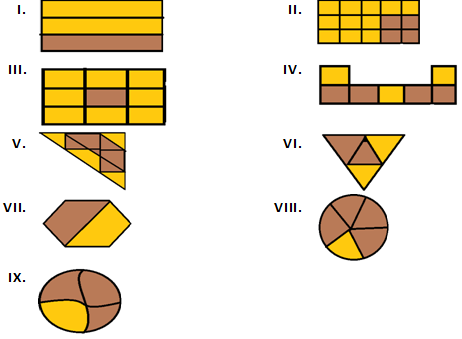
Solution 1:
As we know :
Fraction of the shaded portion = (Number of shaded parts)/(Total number of parts)
(i) Number of total parts = 3
Number of Shaded parts = 2
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 2/3
(ii) Number of total parts = 15
Number of Shaded parts = 11
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 11/15
(iii) Number of total parts = 9
Number of Shaded parts = 8
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 8/9
(iv) Number of total parts = 7
Number of Shaded parts = 3
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 3/7
(v)Number of total parts = 9
Number of Shaded parts = 4
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 4/9
(vi) Number of total parts = 4
Number of Shaded parts = 2
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 2/4 = 1/2
(vii) Number of total parts = 2
Number of Shaded parts = 1
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 1/2
(viii) Number of total parts = 5
Number of Shaded parts = 1
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 1/5
(ix) Number of total parts = 4
Number of Shaded parts = 1
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 1/4
Question 2: Write the fraction representing the shaded parts:
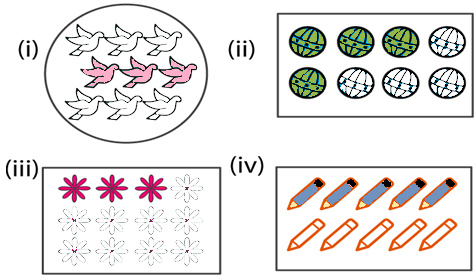
Solution 2:
As we know:
Fraction of the shaded portion = (Number of shaded parts)/(Total number of parts)
(i) Number of total parts = 9
Number of Shaded parts = 3
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 3/(9 ) =1/3
(ii) Number of total parts = 8
Number of Shaded parts = 4
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 4/8 =1/2
(iii) Number of total parts = 12
Number of Shaded parts = 3
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 3/12 =1/4
(iv) Number of total parts = 10
Number of Shaded parts = 5
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 5/10 =1/2
Question 3: Write the fraction representing the shaded portion:
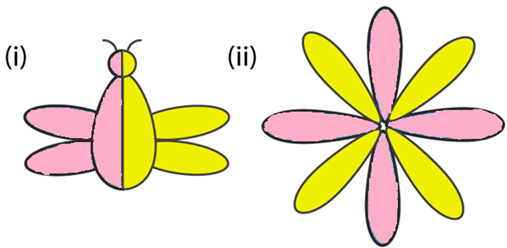
Solution 3:
As We know :
Fraction of the shaded portion = (Number of shaded parts)/(Total number of parts)
(i) Number of total parts = 2
Number of Shaded parts = 1
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 1/2
(ii) Number of total parts = 8
Number of Shaded parts = 4
So, Fraction of the shaded portion = 4/8 =1/2
Question 4: Colour the part according to the fraction given:
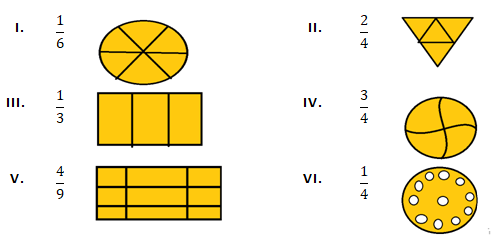
Solution 4:

Question 5: What fraction of an hour is 20 minutes?
Solution 5:
As we know:
There are 60 Minutes in an hour.
So, 20 minutes of an hour = 20/60 = 1/3
Hence, 1/3 of an hour is 20 minutes.
Question 6: Write the natural numbers from 2 to 12. What fraction of them are prime numbers?
Solution 6:
As we know that the natural numbers from 2 to 12 are:
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12.
The prime numbers from 2 to 12 are
2, 3, 5, 7 and 11.
So, there are 5 prime numbers are among the 11 numbers.
Hence, 5/11 of them are prime numbers.
Question 7: Write the natural numbers from 102 to 113. What fraction of them are prime numbers?
Solution 7:
As we know that the natural numbers from 102 to 113 are:
102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112 and 113
The prime numbers from 102 to 113 are
103, 107, 109 and 113
So, there are 4 prime numbers are among the 12 numbers.
Hence, 4/12 =1/3 fraction of them are prime numbers.
Question 8: Mukesh has a box of 24 pencils. He gives half of them to Sunita. How many does Sunita get? How many does Mukesh still have?
Solution 8:
Mukesh has pencils box = 24
He gives half of pencils box to Sunita = 24/2 = 12 pencils box
So, the number of pencils box Mukesh still has = 24 – 12 = 12
Hence, Mukesh gives 12 pencils box to Sunita and still has 12 pencils box.
Question 9: Kavita has 44 cassettes. She gives 3/4 of them to Sonia. How many does Sonia get? How many does Kavita keep?
Solution 9:
Kavita has cassettes = 44
She gives 3/4 of them to Sonia = 3/4 /44 = 33
So, the number of cassettes Kavita keeps = 44 – 33 = 11
Hence, Kavita gives 33 cassettes to Sonia and still have 11 cassettes.
Question 10: Shikhas has three frocks that she wears when playing. The material is good, but the colours are faded. Her mother buys some blue dye and uses it on two of the frocks. What fraction of all of the Shikha play frocks did her mother dye?
Solution 10:
Number of frocks of Shikha = 3
Number of frocks Shikha’s mother dyed = 2
So, the fraction of dyed frocks = 2/3
Hence, Shikha’s mother dyed 2/3 fraction of all of Shikha’s play frocks. 2/5
Exercise 6.2
Question 1: Represent on a number line.
Solution 1: The fraction of is represented on a number line as given below:
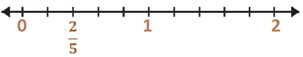
Question 2: Represent 0/10,1/10,5/10 and 10/10 on a number line.
Solution 2:
The fraction of 0/10,1/10,5/10 and 10/10 are represented on a number line as given below:
Question 3: Represent 2/7,5/7,and 6/7 on a number line.
Solution 3:
The fraction of 2/7,5/7,and 6/7 are represented on a number line as given below:
Question 4: How many fractions lie between 0 and 1.
Solution 4:
Number of Fractions which are lie between 0 and 1 are Infinite.
This can be done by taking numerator less than denominator in a fraction.
Question 5: Represent 0/8 and 8/8 on a number line.
Solution 5:
The fraction of 0/8 and 8/8 are represented on a number line as given below:
Exercise 6.3
Question 1: Write each of the following divisions as fractions:
(i) 6 ÷ 3
(ii) 25 ÷ 5
(iii) 125 ÷ 50
(iv) 55 ÷ 11
Solution 1:
(i) 6 ÷ 3 = fraction can be written as 6/3.
(ii)25 ÷ 5 = fractions can be written as 25/5.
(iii) 125 ÷ 50 = fractions can be written as 125/50.
(iv) 55 ÷ 11 = fractions can be written as 55/11.

Exercise 6.4
Question 1: Convert each of the following into a mixed fraction:
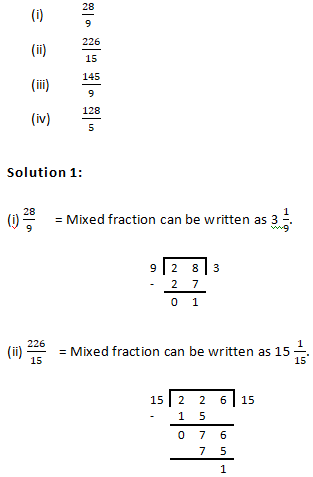
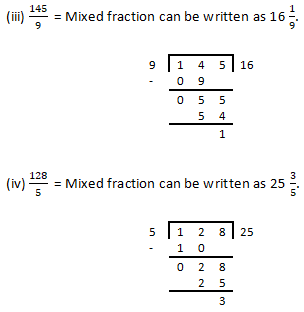
Question 2: Convert each of the following into an improper fraction:
(i) 7 ¼
(ii) 8 5/7
(iii) 5 3/10
(iv) 12 7/15
Solution 2:

Exercise 6.5
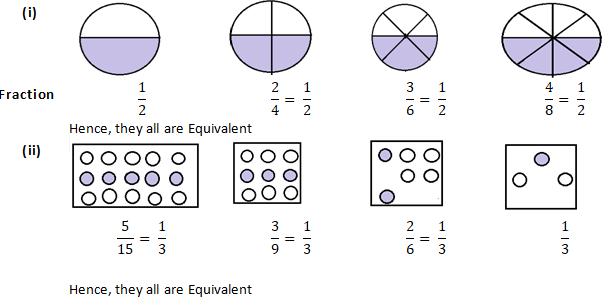
Question 1: Write the fractions and check whether they are equivalent or not:
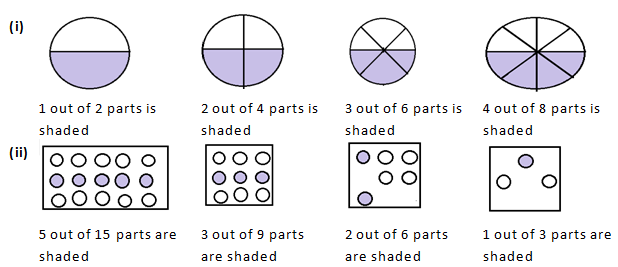
Solution 1:
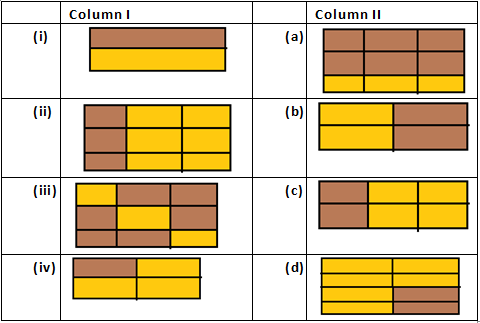
Question 2: Write the fractions and match fractions in Column I with the equivalent fractions in Column II.
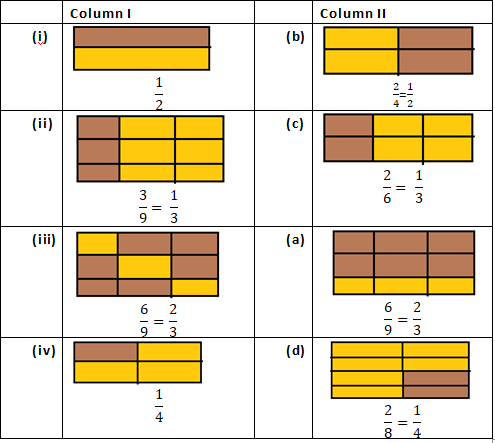
Solution 2:
Question 3: Replace ☐ in each of the following by the correct number:

Solution 3:

Question 4: Find the equivalent fraction of 3/5 having:
(i) Numerator 9
(ii) Denominator 30
(iii) Numerator 21
(iv) denominator 40
Solution 4:
(i) Given fraction is 3/5
If we consider numerator = 9
As we know: 3 × 3 = 9
So, we will Multiply the numerator and denominator of the 3/5 by 3
3/5× 3/3 = 9/15
(ii) Given fraction = 3/5
If we consider denominator = 30
As we know: 5 × 6 = 30
So, we will Multiply the numerator and denominator of the 3/5 by 6
3/5× 6/6= 18/30
(iii) Given fraction = 3/5
If we consider numerator = 21
As we know: 3 × 7 = 21
Multiply the numerator and denominator of the 3/5 by 7
3/5× 7/7 = 21/35
(iv) Given fraction = 3/5
If we consider denominator = 40
As we know: 5 × 8 = 40
Multiply the numerator and denominator of the 3/5 by 8
3/5× 8/8= 24/40
Question 5: Find the fraction equivalent to 45/60, having:
(i) Numerator 15
(ii) Denominator 4
(iii) Denominator 240
(iv) Numerator 135
Solution 5:

Question 6: Find the fraction equivalent of 35/42, having:
(i) Numerator 15
(ii) Denominator 18
(iii) Denominator 30
(iv) Numerator 30
Solution 6:


Question 7: Check whether the given fractions are equivalent:

Solution 7:
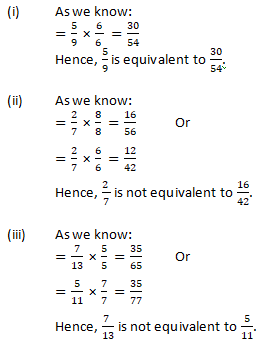
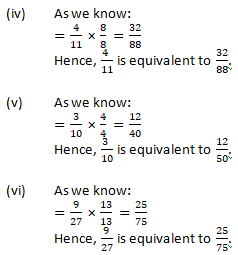
Question 8: Match the equivalent fractions and write another 2 for each:

Solution 8:
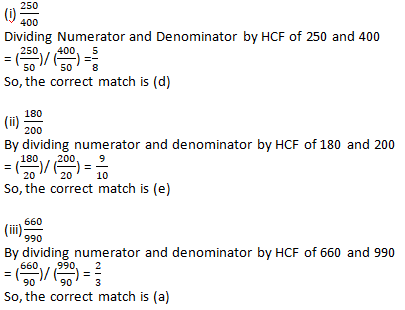

Question 9: Write some equivalent fractions which contain all digits from 1 to 9 once only.
Solution 9: There are those equivalent fractions which contain all digits from 1 to 9 once only are:
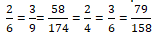
Question 10: Ravish had 20 pencils, Shikha had 50 pencils and Priya had 80 pencils. After 4 months, Ravish used up 10 pencils, Shikha used up 25 pencils and Priya used up 40 pencils. What fraction did each use up? Check if each has used up an equal fraction of their pencils?
Solution 10:
Number of pencils Ravish had = 20 pencils
Number of pencils Ravish used = 10 pencils
We take HCF of 10 and 20 by dividing the numerator and denominator
We get the fraction of pencils used = (10 ÷ 10)/ (20 ÷ 10) = 1/2
Number of pencils Shikha had = 50
Number of pencils used by Shikha = 25
We take HCF of 25 and 50 by dividing the numerator and denominator
We get the fraction of pencils used = (25 ÷ 25)/ (50 ÷ 25) = 1/2
Number of pencils Priya had = 80
Number of pencils used by Priya = 40
We take HCF of 40 and 80 by dividing the numerator and denominator
We get the fraction of pencils used = (40 ÷ 40)/ (80 ÷ 40) = 1/2
Yes, Ravish, Shikha and Priya has used an same fraction of their pencils.
Exercise 6.6
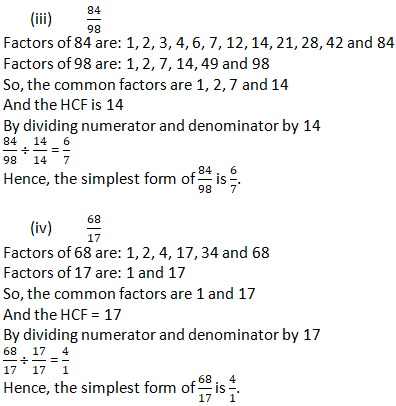
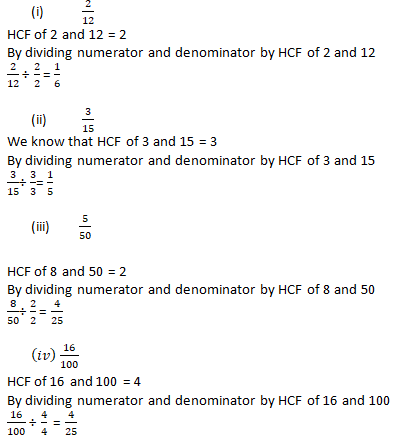
Question 1: Reduce each of the following fractions to its lowest term (simplest form):

Solution 1:



Question 2: Simplify each of the following to its lowest term:
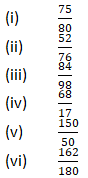
Solution 2:


Exercise 6.7
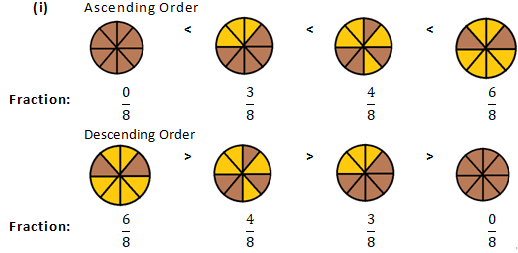
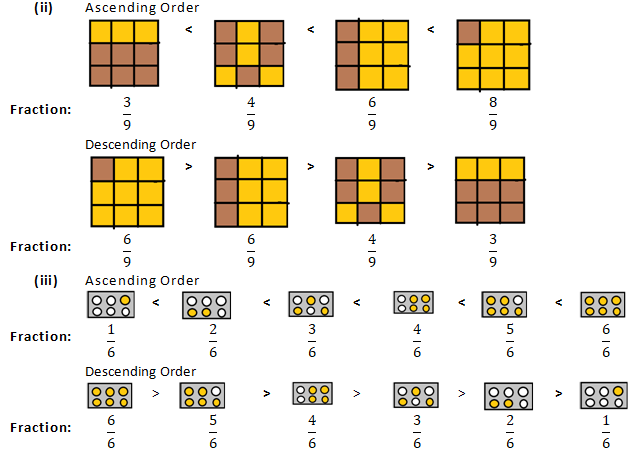
Question 1: Write each fraction. Arrange them in ascending and descending order using correct sign <, =, > between the fractions:

Solution 1:




Question 5: The following fractions represent just three different numbers. Separate them in to three groups of equal fractions by changing each one to its simplest form:
Solution 5:



Question 6: Isha read 25 pages of a book containing 100 pages. Nagma read ½ of the same book. Who read less?
Solution 6: Number of pages in the book = 100

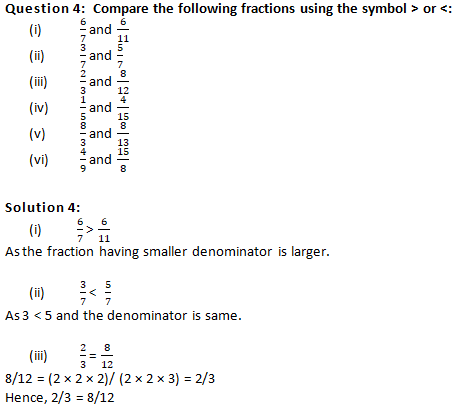
Question 7: Arrange the following fractions in the ascending order:

Solution 7:


Question 8: Arrange in descending order in each of the following using the symbol >:

Solution 8:

Question 9: Find answers to the following. Write and indicate how you solved them.
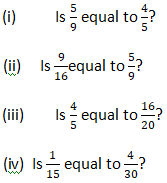
Solution 9:
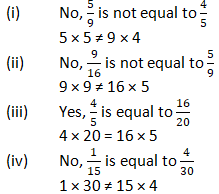
Exercise 6.8
Question 1: Write these fractions appropriately as additions or subtractions:

Solution 1:
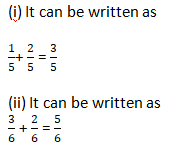
Question 2: Solve:
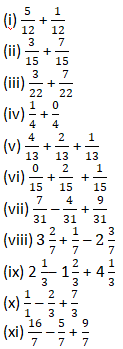
Solution 2:
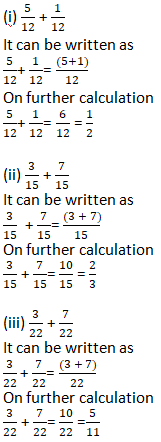


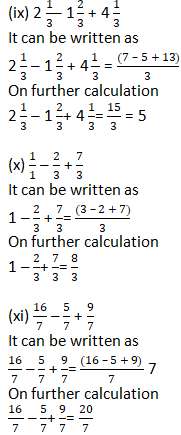
Question 3: Shikha painted 1/5 of the wall space in her room. Her brother Ravish helped and painted 3/5 of the wall space. How much did they paint together? How much the room is left unpainted?
Solution 3:

Question 4: Ramesh bought 2 ½ kg sugar whereas Rohit bought 3 ½kg of sugar. Find the total amount of sugar bought by both of them.
Solution 4:
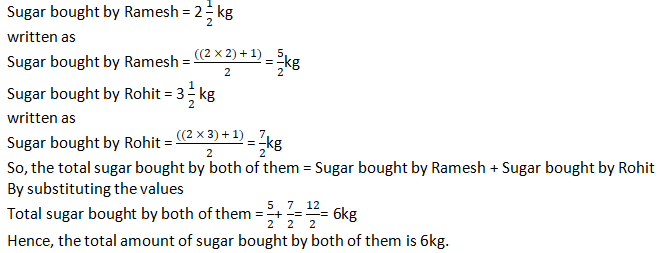


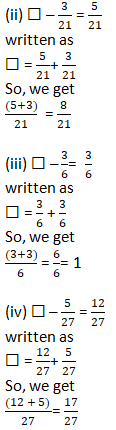

















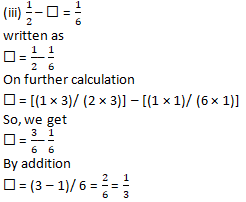
Question 7: Savita bought 2/5 m of ribbon and Kavita 3/4 m of the ribbon. What was the total length of the ribbon they bought?
Solution 7:
Length of ribbon Kavita bought = 3/4 m
Length of ribbon Savita bought = 2/5 m
So, the total length of ribbon Kavita and Savita bought = 2/5 + 3/4
We know that the LCM of 5 and 4 is 20
So, we get
= [(2 × 4)/ (5 × 4)] + [(3 × 5)/ (4 × 5)]
On further calculation
= 8/20 + 15/20
We get
= (8 + 15)/20 = 23/20 m
Hence, the total length of the ribbon Kavita and Savita bought is 23/20 m.
Question 8: Ravish takes 2 1/5 minutes to walk across the school ground. Rahul takes 7/4 minutes to do the same. Who takes less time and by what fraction?
Solution 8:
Time taken by Ravish = 2 1/5 minutes = 11/5 minutes
Time taken by Rahul = 7/4 minutes
By comparing 11/5 and 7/4 minutes
We know that LCM of 4 and 5 is 20
In order to convert fraction into equivalent fraction having 20 as denominator
[(11 × 4)/ (5 × 4)], [(7 × 5)/ (4 × 5)]
44/20 > 35/20
So, Rahul takes less time
written as
44/20 – 35/20= (44 – 35)/20 = 9/20minutes
Hence, Rahul takes less time by 9/20 minutes.
Question 9: A piece of a wire 7/8 meters long broke into two pieces. One piece was 1/4 meter long. How long is the other piece?
Solution 9:
Given:
Length of wire = 7/8 m
Length of first piece = 1/4 m
Consider x m as the length of second piece
It can be written as
Length of wire = Length of first piece + Length of second piece
By substituting the values
7/8 = 1/4 + x
On further calculation
x = 7/8 – 1/4
We know that the LCM of 8 and 4 is 8
x = [(7 × 1)/ (8 × 1)] – [(1 × 2)/ (4 × 2)]
We get
x = 7/8 – 2/8
By subtraction
x = (7 – 2)/ 8 = 5/8 m
Hence, the length of second piece of wire is 5/8m.
Question 10: Shikha and Priya have bookshelves of the same size Shikha’s shelf is 5/6full of book and Priya’s shelf is 2/5full. Whose bookshelf is more full? By what fraction?
Solution 10:
Fraction of Shikha’s shelf filled with books = 5/6
Fraction of Priya’s shelf filled with books = 2/5
We know that LCM of 5 and 6 is 30
In order to convert fraction into equivalent fraction having 30 as denominator
= [(5 × 5)/ (6 × 5)], [(2 × 6)/ (5 × 6)]
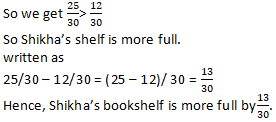
Question 11: Ravish’s house is 9/10 km from his school. He walked some distance and then took a bus for 1/2 km up to the school. How far did he walk?
Solution 11:
Given:
Distance of Ravish’s house from his school = 9/10 km
Distance covered by bus = 1/2 km
written as
Distance between house and school = Distance covered by walking + Distance covered by bus
So, we get
Distance covered by walking = Distance between house and school – Distance covered by bus
Exercise 6.10
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
Question 1: Which of the following is a proper fraction?
(a) 4/3
(b) 3/4
(c) 13/4
(d) 21/5
Solution 1: The correct answer is (b).
We know that in a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator.
Question 2: Which of the following is an improper fraction?
(a) 1/2
(b) 3/7
(c) 7/3
(d) 3/15
Solution 2: The correct answer is (c).
We know that in an improper fraction, the numerator is more than the denominator.
Question 3: Which of the following is a fraction equivalent of 2/3?
(a) 4/5
(b) 8/6
(c) 10/25
(d) 10/15
Solution 3: The correct answer is (d).
10/15 = 2/3
By cross multiplication
10 × 3 = 2 × 15
We get
30 = 30
Question 4: A fraction equivalent to 3/5 is
(a) (3+2)/(5+2)
(b) (3-2)/(5-2)
(c) (3×2)/(5 ×2)
(d) None of these
Solution 4: The correct answer is (c).
We know that by dividing the numerator and denominator by 2, we obtain 3/5.
Question 5: If 5/12 is equivalent of x/3, then x =
(a) 5/4
(b) 4/5
(c) 5/3
(d) 3/5
Solution 5: The correct answer is (a).
Consider 5/12 = x/3
By cross multiplication
5 × 3 = 12 × x
So we get
x = (( 5 × 3))/12 = (( 5 × 3))/((4 ×3)) = 5/4
Question 6: Which of the following are like fractions?
(a) 3/5, 3/7, 3/11 , 3/16
(b) 5/11, 7/11, 15/11 , 2/11
(c) 2/3, 3/4 , 4/5, 6/7
(d) None of these
Solution 6: The correct answer is (b).
We know that like fractions are the fractions with the same denominator.
Question 7: If 11/4 =77/x, then x =
(a) 28
(b) 77/28
(c) 44
(d) 308
Solution 7: The correct answer is (a).
11/4 =77/x
By cross multiplication
11 × x = 77 × 4
x = (77 × 4)/ 11 = (7 × 11 × 4)/ 11
Dividing both the numerator & denominator by 11, we obtain 28.



Question 11: Which of the following fractions is the smallest?
1/2, 3/7, 3/5, 4/9
(a) 4/9
(b) 3/5
(c) 3/7
(d) 1/2
Solution 11: The correct answer is (c).
We know that the LCM of numerator is 12
By converting each fraction to an equivalent fraction having 12 as numerator
We know that if the denominator is same the fraction having larger numerator is the greatest.
Hence, 7/8 is the greatest fraction.
Question 13: What is the value of a+b/ a−b, If a/b=4?
(a) 3/5
(b) 5/3
(c) 4/5
(d) 5/4
Solution 13: The correct answer is (b).
It is given that a/b = 4
We can write it as a = 4b
By substituting the value of a in a+b/a-b
a+b/a-b = 4b+b/4b-b = 5b/3b
Dividing numerator and denominator by b, the value is 5/3.
Question 14: If a/b = 4/3, then the value of 6a+4b/ 6a-5b is
(a) −1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Solution 14: The correct answer is (c).
It is given that a/b = 4/3
We can write it as a = 4b/3
By substituting the value of a in 6a+4b/6a-5b
Question 17: If 45/(60) is equivalent to 3/x, then x =
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 20
Solution 17: The correct answer is (b).
Given:
45/60 = 3/x
By cross multiplication
45 × x = 3 × 60
x = (3 × 60)/45 = 180/45
Dividing the fraction by HCF
(180 ÷ 45)/(45÷45) = 4

