Practice NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs provided below. The MCQ Questions for NTSE Geometry Mathematics with answers and follow the latest NTSE/ NCERT and KVS patterns. Refer to more Chapter-wise MCQs for NTSE NTSE Mathematics and also download more latest study material for all subjects
MCQ for NTSE Mathematics Geometry
NTSE Mathematics students should review the 50 questions and answers to strengthen understanding of core concepts in Geometry
Geometry MCQ Questions NTSE Mathematics with Answers
Question: In the adjoining figure, it is given that D and E the mid points of AB and AC respectively.
If
- a) 1200
- b) 1600
- c) 700
- d) 1150
Answer: 1200
Question: In the given figureIn the given figure
If BF = 4 cm, FD = 6 cm and BE = 8 cm, then BC =______
- a) 12 cm
- b) 15 cm
- c) 25 cm
- d) None of these
Answer: 25 cm
Question: In the given figure
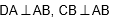 and
and 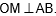
If AP = 5.4 cm, OC = 7.2 cm and BO = 6 cm, then the length of DO is :
- a) 4.5 cm
- b) 4 cm
- c) 5 cm
- d) 6.5 cm
Answer: 4.5 cm
Question: ABCD is a quadrilateral piece of land in which DC = 30 m. The land has been divided into three parts as shown in the figure. If
GH = 8 m and HB = 12 m then the length of DE =
- a) 3 m
- b) 4 m
- c) 5 m
- d) 6 m
Answer: 6 m
Question: The number of triangles with any three of the lengths 1, 4, 6 and 8 cms consider is
- a) 1
- b) 2
- c) 3
- d) 4
Answer: 1
Question: In a right triangle ABC, AD = AE, and CF = CE and shown in fig. If
= x then the value of x equals.
- a) 30°
- b) 45°
- c) 60°
- d) 75°
Answer: 45°
Question: In the figure given sum of all the angles is equal to
- a) 10 right angles
- b) 12 right angles
- c) 14 right angles
- d) 16 right angles
Answer: 16 right angles
Question: If three lengths are given a = 537 cms, b = 139 cms and c = 181 cms, then with these sides
- a) One triangle can be constructed
- b) No triangle can be constructed
- c) Two triangles can be constructed
- d) None of these
Answer: No triangle can be constructed
Question: Two circles touch each other externally, the number of common tangents to the circles is
- a) 1
- b) 2
- c) 3
- d) 4
Answer: 3
Question: If two circles touch each other internally then the distance between their centers is equal to
- a) Sum of their radii
- b) Difference of their radii
- c) Product of their radii
- d) Larger of the two radii
Answer: Difference of their radii
More Questions........................
Question: PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral and RS is a diameter. If
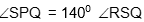 is equal to
is equal to
- a) 300
- b) 500
- c) 600
- d) 800
Answer: 500
Question: In the given figure, AB and AC are produced to P and Q respectively. The bisectors of  and
and 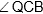 intersect at O.
intersect at O. 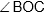 equal to
equal to
- a) 100
- b) 300
- c) 500
- d) 600
Answer: 500
Question: ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral. AB is the diameter of the circle through points A, B, C and D. If 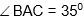 ,the
,the  is equal to
is equal to
- a) 750
- b) 1100
- c) 1250
- d) 1350
Answer: 1250
Question: In the figure given below
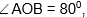 arc AC = arc BC, then
arc AC = arc BC, then  is equal to
is equal to
- a) 600
- b) 700
- c) 800
- d) 900
Answer: 700
Question: ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral inscribed in a circle with the centre O. Then 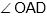 is equal to
is equal to
- a) 300
- b) 400
- c) 500
- d) 600
Answer: 600
Question: ABCD is a parallelogram inscribed is a circle, then it is a
- a) Rhombus
- b) Square
- c) Rectangle
- d) Trapezium
Answer: Rectangle
Question: Two concentric circle of radius 3 cm and 4 cm, intersect in
- a) One paints
- b) Two points
- c) Three points
- d) None of these
Answer: None of these
Question: AB and CD are diameters of a circle,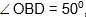 the
the  is equal to
is equal to
- a) 400
- b) 500
- c) 700
- d) 800
Answer: 800
Question: A square, whose side is 2cm, has its corners cut away so as to form an octagon with all sides equal. Then the length of each side of the octagon, in meters, is
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In the Fig. AMN, APQ, QRM and PRN are all straight lines.
The value of α + β is .
- a) 700
- b) 550
- c) 900
- d) 750
Answer: 700
Question: The areas of three adjacent faces of a cuboids are x, yz. If the volume is V, then V2 will be equal to
- a) xy/z
- b) yz/x2
- c) x2y2/z2
- d) xyz
Answer: xyz
Question: If ABC is a quarter circle and a circle is inscribed in it and if AB = 1 cm, find radius of smaller circle.
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)
Answer:
Question: In the diagram given below,
If AB : CD = 3 : 1, the ratio of CD PQ is
- a) 1 : 0.69
- b) 1 : 0.75
- c) 1 : 0.72
- d) None of the above
Answer: 1 : 0.75
Question: In the right-angled triangle QPR given below, PS is the altitude to the hypotenuse. The figure is followed by three possible inferences.
I. Triangle PQS and Triangle RPS and similar.
II. Triangle PSQ and Triangle RSP are congruent.
III. Triangle PSQ and Triangle RPQ are similar.
- a) I and II are correct
- b) I and III are correct
- c) Only II is correct
- d) All three are correct
Answer: I and III are correct
Question: In the adjoining figure DP is parallel to AC; then the ratio of area of triangle PCB and quadrilateral ABCD is
- a) 1 : 1
- b) 1 : 2
- c) 1 : 4
- d) 2 : 3
Answer: 1 : 1
Question: In a triangle ABC, the internal bisector of the angle A meets BC at D. If AB = 4, AC = 3 and 
- a) 2√3
- b)
- c)
- d) None of these
Answer:
Question: In the figure below, AL is perpendicular to BC and CM is perpendicular to AB. If CL = AL = 2BL, find MC/AM.
- a) 2
- b) 3
- c) 4
- d) Cannot be determined
Answer: 3
Question: In the triangle ABC shown below DE is parallel to BC such that D divides AB in the ratio 1 : 3.
In the area of triangle ADE is 5 cm2. What is the area of the triangle EFC ?
- a) 12 cm2
- b) 14.4 cm2
- c) 15 cm2
- d) 20 cm2
Answer: 12 cm2
Question: In the figure given below, PC is tangent to the circle from the point P and B is a point of the circle such that PB = CB. Find 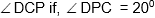
- a) 1200
- b) 1400
- c) 1200
- d) 1000
Answer: 1400
Question: PQRS is a parallelogram and PA, SB, RC, QD are angle bisectors. If PQ = QD = 6 units find m 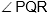
- a) 300
- b) 600
- c) 1200
- d) Indeterminate
Answer: 1200
Question: In the below diagram, ABCD is a rectangle with AE = EF = FB. What is the ratio of the areas of 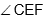 and that of the rectangle ?
and that of the rectangle ?
- a) 1/6
- b) 1/8
- c) 1/9
- d) None of these
Answer: 1/6
Question: In the below figure, ABC is a right-angled triangle. CD is the altitude. Circles are inscribed within the 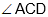 and
and 
P and Q are the centers of the circles. The distance PQ is
- a) 5
- b) √50
- c) 7
- d) 8
Answer: √50
Question: In the adjoining figure, chord ED is parallel to the diameter AC of the circle. If 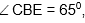 then what is the value of
then what is the value of 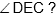
- a) 350
- b) 550
- c) 450
- d) 250
Answer: 250
Question: In the adjoining figure, the chords XY and SR are produced to meet outside the circle at P. The chords XR and YS meet inside the circle at T. If x = x0 and 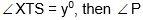 is equal to
is equal to
- a) (x + y)0
- b) (y - x)0
- c) 2(y - x)0
- d) (y - 2x)0
Answer: (y - 2x)0
Question: In the given figure, ABC is a right angled triangle. Also  and AG = GE = EB. If De = 12 cm, then the measure of BC is
and AG = GE = EB. If De = 12 cm, then the measure of BC is
- a) 12 cm
- b) 18 cm
- c) 24 cm
- d) 30 cm
Answer: 18 cm
Question: In the figure AE : EB = 1 : 2 and BD : DC = 5 : 3 Find EG : GC.
- a) 5 : 9
- b) 2 : 3
- c) 3 : 2
- d) Cannot be determined
Answer: 5 : 9
Question: In the above diagram O1 and O2 are the centers of the circles 1 and 2 respectively and O1 lies on the smaller circle. Radius of the smaller circle is r. Given than
Find the value of O1 P in terms of r.
- a) 1. 2r
- b) r
- c) 0.8r
- d) Cannot be determined
Answer: 1. 2r
Question: A circle is touching the side BC of ΔABC at ‘T’ and touching AB and AC produced at Q and R respectively, then the value of AQ is
- a) QR
- b)
- c) AB + BC + AC
- d) None of these
Answer:
Question: In the figure
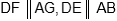 AB = 15, CD = 8, AD = x, DE = 10, FG = y and CG = 6. The ratio x : y equal to
AB = 15, CD = 8, AD = x, DE = 10, FG = y and CG = 6. The ratio x : y equal to
- a) 1 : 2
- b) 1 : 3
- c) 2 : 1
- d) 3 : 2
Answer: 2 : 1
Question: In the figure
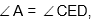 CD = 8 cm CE = 10 cm, BE = 2cm, AB = 9, AD = b and DE = a. The value of a + b is
CD = 8 cm CE = 10 cm, BE = 2cm, AB = 9, AD = b and DE = a. The value of a + b is
- a) 13 cm
- b) 15 cm
- c) 12 cm
- d) 9 cm
Answer: 13 cm
Question: In the figure, AB is a diameter of the circle. TD is a tangent. If 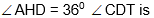
- a) 1200
- b)1160
- c) 1060
- d) 1260
Answer: 1260
Question: In the figure given above, A and B are the centres of the two congruent circles with radius 17 units. If AB = 30 units, the length of the common chord DC is
- a) 25 units
- b) 18 units
- c) 10 units
- d) 16 units
Answer: 16 units
Question: Let X be any point on the side BC of a triangle ABC. If XM, XN are drawn parallel to BA and CA Meeting CA, BA in M, N respectively ; MN meets CB produced in T. Then -
- a) TB2 = TX × TC
- b) TC2 = TX × TX
- c) TX2 = TB × TC
- d) TX2 = 2(TB × TC)
Answer: TX2 = TB × TC
Question: In figure, D and E are the mid-points of sides AB and AC respectively of 
- a) 1100
- b) 1200
- c) 700
- d) 800
Answer: 1100
Question: The exterior angle of a regular is 1/5 of its interior angle. Find the number of sides of the polygon
- a) 12
- b) 10
- c) 7
- d) 8
Answer: 12
Question: The exterior angle of a regular is 1/5 of its interior angle. Find the number of sides of the polygon
- a) 12
- b) 10
- c) 7
- d) 8
Answer: 12
Question: The difference between an exterior angle of n - 1 sided regular polygon and exterior angle of n + 2 sided regular polygon is 60. Find the value of n.
- a) 13
- b) 12
- c) 7
- d) 10
Answer: 13
Question: ABCD is a parallelogram inscribed is a circle, then it is a
- a) Rhombus
- b) Square
- c) Rectangle
- d) Trapezium
Answer: Rectangle
Question: The exterior angle of a regular is 1/5 of its interior angle. Find the number of sides of the polygon
- a) 12
- b) 10
- c) 7
- d) 8
Answer: 12
Question: The difference between an exterior angle of n - 1 sided regular polygon and exterior angle of n + 2 sided regular polygon is 60. Find the value of n.
- a) 13
- b) 12
- c) 7
- d) 10
Answer: 13
| NTSE Mathematics Arithmetic Progression and Geometric Progression MCQs |
| NTSE Mathematics Commercial Mathematics MCQs Set A |
| NTSE Mathematics Commercial Mathematics MCQs Set B |
| NTSE Mathematics Commercial Mathematics MCQs Set C |
| NTSE Mathematics Coordinate Geometry MCQs |
| NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs |
| NTSE Mathematics Modern Mathematics MCQs |
| NTSE Mathematics Statistics MCQs |
More free study material for Mathematics
MCQs for Geometry Mathematics NTSE
Students can use these MCQs for Geometry to quickly test their knowledge of the chapter. These multiple-choice questions have been designed as per the latest syllabus for NTSE Mathematics released by NTSE. Our expert teachers suggest that you should practice daily and solving these objective questions of Geometry to understand the important concepts and better marks in your school tests.
Geometry NCERT Based Objective Questions
Our expert teachers have designed these Mathematics MCQs based on the official NCERT book for NTSE. We have identified all questions from the most important topics that are always asked in exams. After solving these, please compare your choices with our provided answers. For better understanding of Geometry, you should also refer to our NCERT solutions for NTSE Mathematics created by our team.
Online Practice and Revision for Geometry Mathematics
To prepare for your exams you should also take the NTSE Mathematics MCQ Test for this chapter on our website. This will help you improve your speed and accuracy and its also free for you. Regular revision of these Mathematics topics will make you an expert in all important chapters of your course.
You can get most exhaustive NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs for free on StudiesToday.com. These MCQs for NTSE Mathematics are updated for the 2025-26 academic session as per NTSE examination standards.
Yes, our NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs include the latest type of questions, such as Assertion-Reasoning and Case-based MCQs. 50% of the NTSE paper is now competency-based.
By solving our NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs, NTSE students can improve their accuracy and speed which is important as objective questions provide a chance to secure 100% marks in the Mathematics.
Yes, Mathematics MCQs for NTSE have answer key and brief explanations to help students understand logic behind the correct option as its important for 2026 competency-focused NTSE exams.
Yes, you can also access online interactive tests for NTSE Mathematics Geometry MCQs on StudiesToday.com as they provide instant answers and score to help you track your progress in Mathematics.

