Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Biology Our Environment Management Of Natural Resources Worksheet Set A. Students and teachers of Class 10 Science can get free printable Worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment in PDF format prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination pattern in your schools. Class 10 students should practice questions and answers given here for Science in Class 10 which will help them to improve your knowledge of all important chapters and its topics. Students should also download free pdf of Class 10 Science Worksheets prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this academic year and solve important problems with solutions on daily basis to get more score in school exams and tests
Worksheet for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following printable worksheet in Pdf for Chapter 15 Our Environment in Class 10. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 10 will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 10 Science Worksheet for Chapter 15 Our Environment
• Environment means everything which surrounds us. It may include living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components. So, it may include besides all creatures, water & air also.
• Environmental science can be defined as the study of organisms in relation to their surrounding
• Human activities related to livelihood and welfare generate waste. All wastes are pollutants, and they create pollution in one way or another. Air, land and water surroundings are affected due to
improper disposal of wastes which create an imbalance in the environment.
POLLUTION: Any undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, land and water that affect human life adversely is called pollution.
POLLUTANT: A substance released into the environment due to natural or human activity which affects adversely the environment is called pollutant. e.g., Sulphur-di-oxide, carbon-monoxide, lead, mercury, etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF WASTES:
Bio–degradable wastes- Substances that are broken down by biological process of biological or microbial action are called bio-degradable waste. e.g., wood, paper and leather.
Non–bio-degradable wastes- Substances that are not broken down by biological or microbial action are called non-bio- degradable wastes. e.g., Plastic substances and mineral wastes.
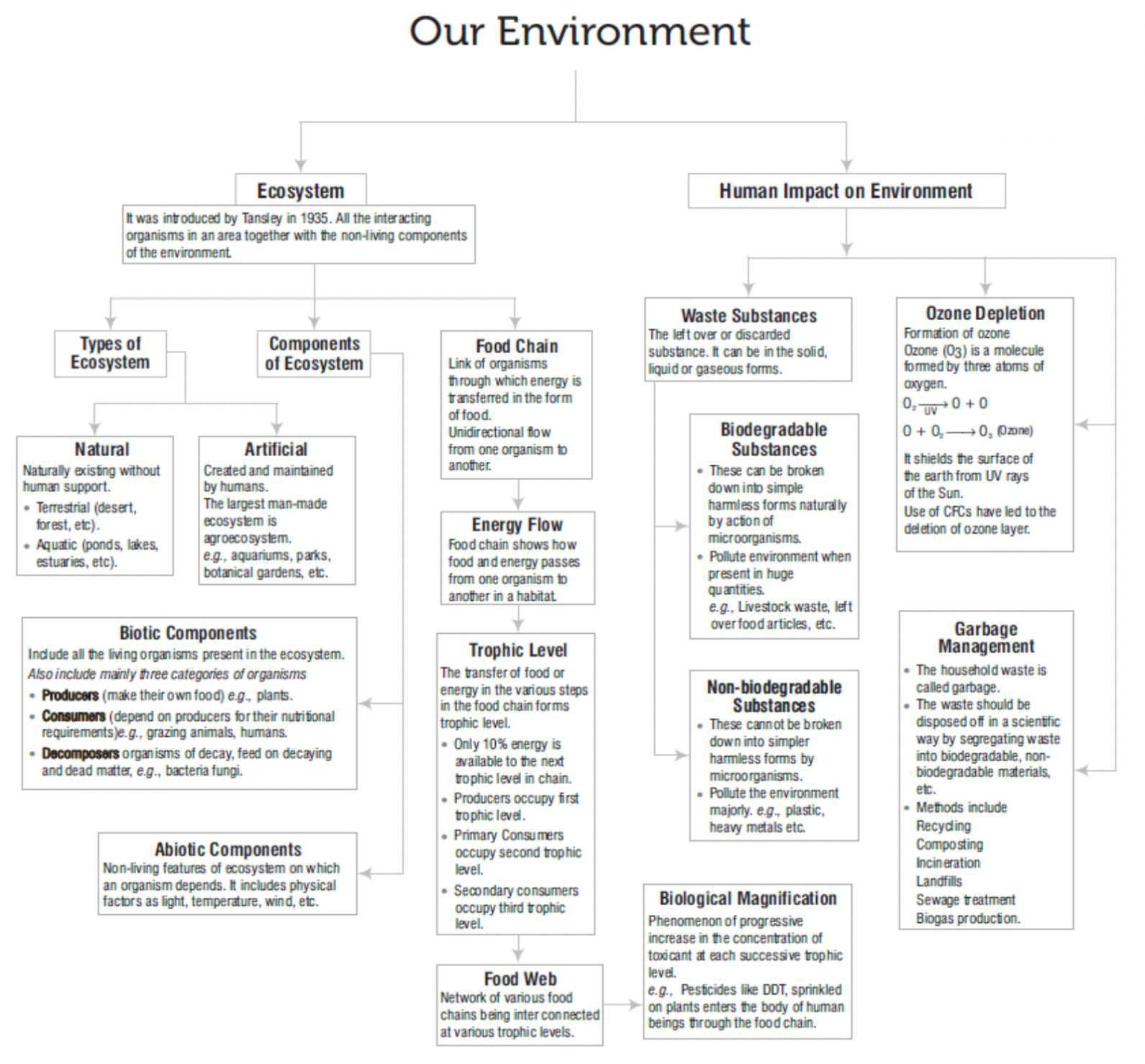
ECO-SYSTEM — WHAT ARE ITS COMPONENTS?
A community of organisms that interact with one another and with the physical environment is called an ecosystem. An ecosystem has two types of components, viz. biotic component (living creatures) and abiotic components like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil etc.
All living organisms are classified on the basis of the manner in which they survive in the Ecosystem.
These groups include: -
PRODUCERS– All green plants, blue green algae can produce their food (Sugar & starch) from in organic substance using light energy (Photosynthesis).
CONSUMERS– Include organisms which depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for their sustenance. In other word consumers consume the food produced by producers.
DECOMPOSERS– Decomposers include micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi that obtain nutrients by breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals. They help in the breakdown of organic matter or biomass from the body of dead plants and animals into simple inorganic raw materials such as Carbon dioxide , water and some nutrients.
FOOD CHAIN AND FOOD WEB
FOOD CHAIN (i) A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another.
(ii) The ultimate source of this energy is the sun.
(iii) Producers like green plants trap solar energy and convert it into the chemical energy of food.
When a primary consumer eats the producer, a part of this energy is passed on to it.
(iv) The primary consumer is then eaten by a secondary consumer.
(v) And the secondary consumer may be eaten by a tertiary consumer, and so on.
(vi) In this way energy gets transferred from one consumer to the next higher level of consumer.
• In a forest ecosystem, grass is eaten by a deer, which in turn is eaten by a tiger. The grass, deer and tiger form a food chain. In this food chain, energy flows from the grass (producer) to the deer (primary consumer) to the tiger (secondary consumer) [see figure (a)].
• A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks [see figure (b)].
• In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond, the organisms in the food chain include algae, small animals, insects and their larvae, small fish, big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal [see figure (c)].
A food chain always begins with producers. Herbivores (plant-eaters) come next in the chain.
They are consumed by carnivores (flesh-eaters). A few food chains can be long and may extend to the fourth, fifth or even sixth order of consumers.
Some common food chains are mentioned below:
Plants → Deer → Lion
Plants → Worm→ Bird → Cat
Plants→ Grasshopper→ Frog→ Snake→ Hawk
Algae→ Small→ animal → Small fish → Big fish —> Bird
FOOD WEB
Food webs consist of many interconnected food chains and are more realistic representation of consumption relationships in ecosystems.
TROPHIC LEVEL
The levels of a food chain (food pyramid) are called Trophic levels. The trophic level of an organism is the level it holds in a food pyramid.
• The producers (plants) represent the first trophic level.
• Herbivores (primary consumers) present the second trophic level.
• Primary carnivores (secondary consumers) represent the third trophic level
• Top carnivores (tertiary consumers) represent the fourth or the last level.
TEN PERCENT LAW
• The Ten percent law was given by Lindemann (1942).
• This law states that when the energy is passed on from one trophic level to another, only 10 percent of the energy is passed on to the next trophic level, remaining 90℅ energy is always used up by the organism in performing living processes such as reproduction etc or as body heat.
BIO-MAGNIFICATION
• Biomagnification refers to the accumulation of toxic substances in the food chain.
• The toxic chemicals that are released into the environment are absorbed by the lower organisms such as plants, earthworms, etc.
• These chemicals are then transferred to different trophic levels when lower organisms are eaten by other organisms.
• The pesticides and chemicals such as DDT, and mercury released into the lakes and rivers are ingested by the aquatic organisms. These get accumulated in their body tissues and are transferred to other organisms that feed on them.
• Since the pesticides are industrially processed, they contain traces of heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, cadmium, etc. These metals have been found in the bodies of animals and humans and are believed to have an adverse effect on them.
OZONE LAYER DEPLETION
• Oxygen is a molecule formed by 3 atoms of oxygen while O2 which we normally refer to as oxygen is essential for all aerobic forms of life.
• Ozone is a deadly poison.
• However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere (in stratosphere), ozone performs an essential function.
• FUNCTION OF OZONE- It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
• Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen molecule. The higher energy UV radiation split apart some molecular oxygen into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown—
REASON OF OZONE DEPLETION: Excessive use of CFCs (Choro Flouro Carbon) a synthetic, inert chemical E.g., Freon which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers, caused Ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere. A single chlorine atom can destroys1,00,000 Ozone molecules. U.N.E.P. (United Nation Environment Programme) did an excellent job in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels (KYOTO Protocol) by all countries.
HOW TO PROTECT US FROM THESE HAZARDOUS WASTES : Industrialization and rise in demand of consumer goods have created a major problem in the form of wastes/garbage accumulation and its disposal especially in urban area. The different methods of solid wastes disposal commonly used around the world are.
(i) Open dumping: A conventional method in which solid wastes dumped in selected areas of a town. It actually causes pollution.
(ii) Land fillings: Wastes are dumped in low living area and are compacted by rolling with bulldozers. There are permanent storage facilities in secured lands for military related liquid and radioactive waste materials. High level radioactive wastes are stored in deep underground storage.
(iii) Composting: Organic wastes are filled into a compost pit (2m x 1m x 1m). It is then covered with a thin layer of soil. After about three months the same garbage filled inside the pit changes into organic manure.
(iv) Recycling: The solid wastes is broken down into its constituent simpler materials. These materials are then used to make new items. Even non-biodegradable solid wastes like plastic, metal can be recycled.
(v) Reuse: A very simple conventional technique of using an item again & again. For E.g., paper can be reused for making envelops etc.
(vi) Incineration: The burning of materials is called incineration. Hazardous bio-medical wastes are usually disposed of by means of incineration. Human anatomicsssal wastes, discarded medicines, toxic drugs, blood, pus, animal wastes, microbiological and bio-technological wastes etc., are called bio-medical wastes.
(vii) Deep well injection: It involves drilling a well into dry porous material below ground water.
Hazardous waste liquids are pumped into the well. They are soaked into the porous material and made to remain isolated indefinitely.
Objective Questions
Question. When is the World Environment Day celebrated?
(a) 16 June
(b) 5 December
(c) 5 June
(d) 5 July
Answer. C
Question. Which of these is a greenhouse gas?
(a) Hydrogen Sulphide
(b) Methane
(c) Ozone
(d) Carbon monoxide
Answer. B
Question. The transfer of Energy in a food chain is always:
(a) Unidirectional
(b) Methane
(c) Bi-directional
(d) Random
Answer. A
Question. If a grasshopper is eaten by frog, then the energy transfer will be from:
(a) producers to decomposers
(b) producer to primary consumer
(c) primary consumer to secondary consumer
(d) secondary consumer to primary consumer
Answer. C
Question. The % of solar radiation absorbed by all green plants for photosynthesis is about ———–.
(a) 1%
(b) 5%
(c) 8%
(d) 10%
Answer. A
Question. In a given food chain if the amount of energy at the fourth trophic level is 6 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level?
(a) 6000 kJ
(b) 20 kJ
(c) 60 kJ
(d) 600 kJ
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following is biodegradable waste ?
(a) DDT
(b) Aluminium can
(c) Plastic bag
(d) Cow dung
Answer. D
Question. Which of the following is the best way for disposal of vegetable and fruit peels?
(a) Landfill
(b) Recycling
(c) Composting
(d) Burning
Answer. C
Question. Accumulation of non-biodegradable pesticides in the food chain in increasing amount at each higher trophic level is known as:
(a) Eutrophication
(b) Pollution
(c) Biomagnifications
(d) Accumulation
Answer. C
Question. In an ecosystem, the 10% of energy available for transfer from one trophic level to the next is in the form of :
(a) heat energy
(b) light energy
(c) chemical energy
(d) mechanical energy
Answer. C
Question. In the given Figure the various trophic levels are shown in a pyramid. At which trophic level is maximum energy available?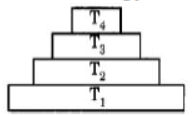
(a) T4
(b) T2
(c) T1
(d) T3
Answer. C
Question. Which of the statements is incorrect?
(а) All green plants and blue green algae are producers
(b) Green plants get their food from organic compounds
(c) Producers prepare their own food from inorganic compounds
(d) Plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
Answer. B
Question. What will happen if Deer is missing in the food chain given below? Grass → Deer → Tiger
(а) The population of tiger increases
(b) The population of grass decreases
(c) Tiger will start eating grass
(d) The population of tiger decreases and the population of grass increases
Answer. D
Question. What provides the energy which then flows through a food chain ?
(a) glucose
(b) oxygen
(c) respiration
(d) sunlight
Answer : D
Question. Which pollutant released into the air during refrigeration and airconditioning is the greatest contributor to
the depletion of ozone layer ?
(a) BHC
(b) DDT
(c) CFC
(d) UNEP
Answer : C
Question. In the food chain given below, if the amount of energy available at fourth trophic level is 5 kJ, what was the energy available at the producer level ?
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
(a) 500 kJ
(b) 50 kJ
(c) 5000 kJ
(d) 5 kJ
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain ?
(a) insufficient food supply from producer level
(b) decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(c) increase in the number of organisms at higher trophic levels
(d) accumulation of harmful chemicals at higher trophic levels
Answer : B
Question. What percentage of sun’s energy falling on the leaves of green plants is utilised by the plants in the process of photosynthesis and stored as chemical energy of food ?
(a) 99 per cent
(b) 10 per cent
(c) 1 per cent
(d) 20 per cent
Answer : C
Question. The depletion of ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is mainly due to the emission of :
(a) unburnt hydrocarbons
(b) chlorofluorocarbons
(c) greenhouse gases
(d) ultraviolet radiations
Answer : B
Question. In an ecosystem, the ten per cent energy available for transfer from one trophic level to the next is in the form of :
(a) heat energy
(b) light energy
(c) chemical energy
(d) mechanical energy
Answer : C
Question. The flow of energy in an ecosystem is always :
(a) unidirectional
(b) bidirectional
(c) cyclic
(d) multidirectional
Answer : A
Question. The excessive exposure of humans to ultraviolet rays results in :
(i) damage to immune system (ii) damage to lungs
(iii) skin cancer (iv) peptic ulcers
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following gets the minimum energy through the food chain in an ecosystem ?
(a) carnivore
(b) large carnivore
(c) producer
(d) herbivore
Answer : B
Question. A food chain comprises of cat, seed-eating bird, plants, and dog. The organism which will have the maximum concentration of harmful pesticides coming through the food chain is most likely to be :
(a) cat
(b) plants
(c) dog
(d) seed-eating bird
Answer : C
Question. An aquatic food chain comprises of the organisms like tadpoles, weeds, fish and water beetles. The organism which gets the minimum energy through this food chain is :
(a) water beetles
(b) tadpoles
(c) weeds
(d) fish
Answer : D
Question. Most of the water surface of a lake is covered with algae. This algae is part of the food chain which also includes small fish, bird, larvae and big fish. Which of the following will obtain the maximum energy ?
(a) big fish
(b) bird
(c) larvae
(d) small fish
Answer : C
Question. If the energy available at the producer level in a food chain is 150 J, how much energy will be transferred to : tertiary consumer ?
(a) 15 J
(b) 10 J
(c) 1.50 J
(d) 0.15 J
Answer : D
Question. If the energy transferred to a tertiary consumer in a food chain is 10 J, how much energy was available to the primary consumer ?
(a) 100 J
(b) 500 J
(c) 1000 J
(d) 5000 J
Answer : C
Question. In addition to wheat plants, a crop field ecosystem has organisms such as snake, peacock, eagle and mice. If the wheat plants are sprayed with pesticides periodically, which of the following will have the minimum concentration of pesticides in the body ?
(a) snake
(b) eagle
(c) mice
(d) peacock
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is the best method to dispose of biological wastes from hospitals ?
(a) landfill
(b) recycling
(c) incineration
(d) composting
Answer : C
Question. In an ecosystem :
(i) the flow of energy is unidirectional
(ii) the flow of materials is unidirectional
(iii) the flow of materials is cyclic
(iv) the flow of energy is cyclic.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer : D
Question. The ten per cent law is associated with
(a) transfer of energy from various trophic levels to decomposers in a food chain
(b) transfer of ATP energy into muscular energy
(c) transfer of chemical energy from one organism to another
(d) transfer of sun’s energy to the organisms called producers.
Answer : C
Question. The harmful chemical which is accumulating in human beings through food chain is :
(a) benzenehexachloride
(b) dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
(c) chlorofluorocarbon
(d) abscisic acid
Answer : B
Question. O2 is converted into O3 by the action of :
(a) infrared radiations
(b) ultraviolet radiations
(c) gamma radiations
(d) cosmic radiations
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following cannot be added in a composting pit to prepare compost ?
(a) sunflower plants
(b) fruit and vegetable peels
(c) flowers of plastic
(d) red worms
Answer : C
Question. If a grasshopper is eaten by a frog, then the energy transfer will be from :
(a) producer to decomposer
(b) producer to primary consumer
(c) primary consumer to secondary consumer
(d) secondary consumer to tertiary consumer
Answer : C
Question. An ecosystem includes :
(a) all living organisms
(b) non-living objects
(c) both living organisms and non-living objects
(d) all living organisms and input of sun’s energy
Answer : C
Question. The decomposers in an ecosystem :
(a) convert inorganic material to simpler forms
(b) convert organic material to inorganic forms
(c) convert inorganic material into organic compounds
(d) do not break down organic compounds
Answer : B
Question. What will happen if deer is missing in the food chain given below ?
Grass → Deer → Tiger
(a) The population of tigers increases
(b) The population of grass decreases
(c) Tigers will start eating grass
(d) The population of tigers decreases and the population of grass increases.
Answer : D
Question. Organisms which synthesise carbohydrates from inorganic compounds by using radiant energy are called :
(a) decomposers
(b) producers
(c) herbivores
(d) carnivores
Answer : B
Question. Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a number of lower trophic levels constitute the :
(a) ecosystem
(b) food web
(c) ecological pyramid
(d) food chain
Answer : B
Question. In the following groups of materials, which group/groups contain only non-biodegradable materials ?
(i) wood, paper, leather (ii) polythene, detergent, PVC
(iii) plastic, detergent, grass (iv) plastic, bakelite, DDT
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
(a) all green plants and blue green algae are producers
(b) green plants get their food from readymade organic compounds
(c) producers prepare their own food from inorganic compounds
(d) plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following group of organisms are not constituents of a food chain ?
(i) grass, lion, rabbit, wolf (ii) plankton, man, fish, grasshopper
(iii) wolf, grass, snake, tiger (iv) frog, snake, eagle, grass, grasshopper
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer : C
Question. In the figure given alongside, the various trophic levels are shown in the form of a pyramid. At which trophic level the maximum energy is available ?
(a) T4
(b) T2
(c) T1
(d) T3
Answer : C
Question : A food chain always starts with:
a. Respiration
b. Decomposition
c. Photosynthesis
d. Nitrogen fixation
Answer : C
Explanation: A food chain in an ecosystem always starts with photosynthesis.
The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers.
Question : Organisms which synthesise carbohydrates from inorganic compounds using radiant energy are called:
a. Decomposers
b. Producers
c. Herbivores
d. Carnivores
Answer : B
Question : An ecosystem includes:
a. All living organisms
b. Non-Living objects
c. Both Living and Non-living objects
d. sometimes living and sometimes non-living
Answer : C
Question : Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
a. Grass, flowers and leather
b. Grass, wood and plastic
c. Fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice
d. Cake, wood and grass
Answer : A,C,D
Question : Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
a. Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
b. Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
c. Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter
d. All of the above
Answer : D
ASSERTION REASON TYPE OF QUESTIONS
(a) If both Assertion and reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion
(c) If Assertion is true but the Reason is false
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Question. Assertion: Polythene bags and plastic containers are non-biodegradable substances.
Reason: They can be broken down by microorganisms in natural simple harmless substances
Answer. B
Question. Assertion - Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level
Reason - Autotrophs or producers are the first trophic level in the ecosystem
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - Green plants harvest the solar energy directly and convert light energy into chemical energy
Reason - Food transfer in the ecosystem takes place through food chain and food web
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - The length and complexity of food chain vary greatly in an ecosystem
Reason - There is a reduction of energy when it transfers from one trophic level to other by eating and being eaten
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - There is generally greater number of individuals at the lower trophic levels of an ecosystem
Reason - Green plants are the producers in an ecosystem
Answer. B
Question. Assertion - Ozone is formed by three atoms of oxygen
Reason - UV rays are needed to form ozone molecule
Answer. A
Question. Assertion – Substances that are broken down by biological process are said to be Biodegradable
Reason- Some Pesticides and chemicals are Non- biodegradable
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - More and more things we use becoming disposable, changes in packaging have resulted in much of our waste becoming Non-biodegradable
Reason - Biodegradable materials are environment friendly and easily degraded by the microbes in nature
Answer. A
Question. Assertion-Enzymes are very essential for digestion of food materials in our body. Specific enzymes are needed for the breakdown of a particular substance
Reason - We will not get energy if we try to eat coal
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - Water, soil, temperature, light, minerals are the abiotic factors in the ecosystem
Reason - Biotic factors interact with abiotic factors in an ecosystem to sustain
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - Ozone layer is seen at the Stratosphere of atmosphere, which is harmful to plants and animals.
Reason - The Ozone layer that is found in the troposphere of atmosphere is good to the plants and animals
Answer. D
Question. Assertion - A sparrow when feeds on seeds, it is a primary consumer, but when it feeds on an insect, it belongs to secondary consumer.
Reason - The ecological pyramids (trophic levels) are not always reliable
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - Only the green plants can prepare their own food by means of photosynthesis
Reason - Some Bacteria derive their nutrition by autotrophic means
Answer. B
Question. Assertion - Forests, Grass lands, Rivers, Meadows, Estuaries are natural ecosystems
Reason - Artificial ecosystems are manmade ecosystems
Answer. A
Question. Assertion - In Sea waters the number of Primary Producers is more than that of Primary consumers
Reason - In Sea water the Primary consumers are more than that of Primary Producers
Answer. B
Very Short Answer Questions
Question : If all the waste we generate is bio-degradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer : If all the waste we generate is bio-degradable and is managed in such a way that it is allowed to decompose then it will have no impact on the environment.
Question : The first tropic level in a food chain is always a green plant. Why?
Answer : Because only plants can utilise the radiant energy of the sun and transform it to chemical form during photosynthesis.
Question : Write any two consequences if decomposers are removed from the ecosystem?
Answer : (i) Dead organisms will pile up.
(ii) There will be no replenishment of soil.
Question. What is the functional unit of the environment comprising of the living and non-living components called ?
Answer : Ecosystem
Question. Name the organisms belonging to the second and the fourth trophic levels in the food chain comprising the following : Frogs, Plants, Snakes, Hawk, Insects
Answer : Second trophic level : Insects ; Fourth trophic level : Snakes
Question. What are the various steps of food chain called ?
Answer : The various steps of a food chain are called trophic levels.
Question. Construct a food chain comprising the following : Snakes, Hawk, Rats, Plants
Answer : A food chain refers to the order of events in an ecosystem, where one living organism eats another organism, and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism. The flow of nutrients and energy from one organism to another at different trophic levels forms a food chain .Plants → Rats → Snakes → Hawks
Question. Name two natural ecosystems and two artificial ecosystems.
Answer : Two natural ecosystems are the pond ecosystem and the forest ecosystem. Two artificial ecosystems are the crop field ecosystem and the aquarium ecosystem.
Question. What are planktons ?
Answer : The tiny herbivorous plants and animals present in water are known as plankton. Plankton are classified as phytoplankton (plants) and zooplankton (animals).
Question. State whether the following statements are true or false :
(a) In biology, human beings are called producers.
(b) Secondary consumers and tertiary consumers, both are carnivores.
Answer : (a) False (b) True
Question. Which category of organisms forms the starting point of a food chain ?
Answer : Producers
Question. Which of the following belong to the same trophic level ? Goat ; Spider ; Plants ; Hawk ; Rat
Answer : Goat and Rat (both are herbivores)
Question. Which one of the following is not a terrestial ecosystem ? Forest, Grassland, Aquarium, Desert
Answer : Aquarium
Question. Why are plants called producers ?
Answer : Plants are known as producers because they prepare their food themselves by the process of photosynthesis.
Question. What name has been given to those organisms which break down the complex organic compounds present in dead animals and plants ?
Answer : decomposers
Question. Which of the following belong to the same trophic level ? Tree ; Frog ; Snake ; Grass ; Lizard
Answer : Tree and Grass (both are producers)
Question. Write an aquatic food chain.
Answer : Food chain existing in the aquatic ecosystem often starts with algae or phytoplankton as producers, then zooplankton, which feed on them. Zooplankton are then eaten by small fish and crustaceans, which in turn get consumed by large fish, sharks and whales.
Phytoplankton→Zooplankton→small fish →large fish
Question. Arrange the following in a food chain : Fish, Algae, Small animals, Big Fish
Answer : Algae → Small animals → Fish → Big fish.
Question. Which organisms belong to third and fourth trophic levels in the food chain comprising the following ? Rats, Plants, Hawk, Snakes
Answer : Snakes belong to the third trophic level and hawks belong to the fourth trophic level in the food chain.
Question. Which one term in the following includes the others ? air, flora, fauna, environment, water, sunlight, soil
Answer : Environment
Question. A food chain represents a unidirectional flow of X. What is X ?
Answer : A food chain represents a unidirectional flow of energy. X is energy.
Short Answer Questions
Question. What is natural and artificial ecosystem? Give one example each
Answer. Natural ecosystem: Self-sustaining ecosystem formed by the interaction of living and non living things in an area. Eg: Forest or pond
Artificial ecosystem: An ecosystem which is formed or modified by human intervention. Crop field or aquarium.
Question. Define ecosystem and name its components.
Answer. The living and non-living components of an area interact with each other to form an ecosystem. Components of ecosystem are: Biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living)
Question. What is the full form of CFCs and UNEP?
Answer. CFC=Chlorofluorocarbons UNEP = United Nations Environment Programme
Question. What is the ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem? Which process helps to trap this energy in producers?
Answer. Sun is the ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem. Photosynthesis helps to trap this energy in producers.
Question. Define trophic level in a food chain? The first trophic level in a food chain is always a green plant. Why?
Answer. Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level. The autotrophs or the producers are the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for the heterotrophs or consumers. The first tropic level in a food chain is always a green plant because only plants can utilize the radiant energy of the sun and transform it to chemical form during photosynthesis.
Question. Food web increases the stability of an ecosystem. Justify.
Answer. Food web shows food relationship in an ecological community. It consists of many food chains. Thus, if any one organism becomes endangered or extinct, the one dependent in it has an alternative option available to him for survival. In this way food web increases stability in the ecosystem.
Question. What is food chain? Construct an aquatic food chain showing four trophic levels.
Answer. Food chain is formed by a series of organisms feeding on one another.
Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small fish → Bird.
Question. List two causes of depletion of ozone layer. Mention any two harmful effects of depletion of this layer.
Answer. Two causes of depletion of ozone layer are as follows:
a. Use of CFC’s
b. Use of Halogens
Harmful effects of ozone depletion:
a. Due to depletion of ozone UV radiation reaches the earth. This UV radiation causes skin cancer, damage to eyes and immune system.
b. Ozone depletion may also lead to variation in global rainfall, ecological disturbances and wildling of global food supplies.
Question. What are decomposers? Write any two consequences of decomposers are removed from the ecosystem?
Answer. Decomposers are organisms that live on dead and decaying matter. They convert complex organic material into simple materials and mix with soil. Eg: fungi, bacteria
Some of the consequences if decomposers are removed from soil are
a. Dead organisms will pile up.
b. There will be no replenishment of soil.
Question : Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer : The impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level will be same. If the organisms of any trophic level be removed it will certainly damage the ecosystem.
For example,
Grass → Grass hopper → Frog → Snake → Peacock
In this if all grasshoppers are killed/removed frogs will strive and grass will reproduce in abundance.
If snakes are removed then the number of frogs will increase which will disturb the entire ecosystem.
Question : What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable waste that we generate?
Answer : (i) As the non-biodegradable waste cannot be broken down into simpler forms hence they keep on accumulating in nature causing pollution.
(ii) They cause diseases.
(iii) It also causes biological magnification.
Question : Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer : Ozone layer in the strastosphere is very helpful in shielding harmful UV rays. In absence of ozone layer heavy damage to organism may occur. It may cause diseases like skin cancer, cataract, reduced crop production etc.
The damage is limited by UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme), it has forged an agreement to freeze for CFC production in 1986.
CFC– Chlorofluorocarbons used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
Question : How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Suggest any three methods.
Answer : Methods to reduce the problem of waste disposal:
(1) Segregation of waste should be done by separating biodegradable waste substances from non-biodegradable substances.
(2) By recycling solid wastes like paper, plastic and metals etc, i.e., they are reprocessed or melted and remoulded to make new articles.
(3) By composting biodegradable domestic wastes such as fruit and vegetable peels, leaves of potted plants can be converted into compost and used as a manure.
(4) By reducing and reusing of Non Biodegradable substances.
Question : Explain some harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment.
Answer : Harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment:
(1) Fertilizer added to soil not only changes the chemistry of the soil but also kills many useful microbes.
(2) Pesticides sprayed over crops reach water bodies and persistent pesticides undergo bio-magnification proving harmful to higher organisms.
(3) Extensive cropping on a particular piece of land causes the loss of soil fertility.
(4) Continuous use of ground water in agriculture has resulted in lowering of water table at most of the places
(5) Natural ecosystems and habitats have been damaged because of clearing of land for agriculture.
(6) Excessive cutting down of trees for agricultural purposes causes deforestation and can lead to soil erosion.
(7) Synthetic fertilizers and pesticides used in the field during rainfall are washed away to rivers and other bodies, which cause water pollution.
Question : (A) Construct a terrestrial food chain comprising four trophic levels.
(B) What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
(C) Calculate the amount of energy available to the organisms at the fourth trophic level if the energy available to the organisms at the second trophic level is 2000 J.
Answer : (A) A terrestrial food chain comprising of fourt trophic levels: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake
(B) If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level the transfer of food energy to next level will stop. Organisms of previous trophic level will also increase. For example: If all herbivores in an ecosystem are killed: There will be no food available for the carnivores of that area. Consequently they will also die or will shift to other areas. Populations of producers will also increase in absence of herbivores causing imbalance in the ecosystem.
(C) Consider the same food chain as we have made in 1% (a): Grass → Grass hopper → Frog → Snake In this food chain, second trophic level is grass hopper and the energy available at this trophic level is 2000 j. According to 10% law, 10% of energy will be available to frog (Third trophic level) which is 200 j. The energy available to the snakes will be available as 10% of 200 j. Thus, the energy available to the snake is 20 %. Explanation: 10% law states that during transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level, only about 10% energy is available to the higher trophic level. To summarise: Grass → Grass hopp
Question : What are the advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping?
Answer : Advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping are as follows:
(1) Cloth bags are more durable and thus can be used again and again.
(2) They are strong and thus capable of carrying more things.
(3) They are biodegradable in nature.
Question : Food web increases the stability of an ecosystem. Justify.
Answer : Food web shows feeding connection in an ecological community. It consists if many food chains. Thus, if any one organism becomes endangered or extinct, the one dependent in it has an alternative option available to him for its survival. In this way food web increases stability in the ecosystem.
Question : Pesticides like DDT which are sprayed to kill pests on crops to kill pests on crops are found to be present in the soil, groundwater, water bodies etc. Explain. How do they reach these places?
Answer : Soil: Pesticides are used to protect plants from insects. They consequently get settled into soil particles, when used on plants.
Groundwater: Through irrigation in the fields, these pesticides present in soil pass into lower layers of soil and reach groundwater.
Water bodies: When the wastewater or other agricultural waste is thrown in water bodies like river, canals, ponds, etc. the pesticides affect water bodies.
Question : (a) “Energy flow in a chain is unidirectional”. Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
(b) What is an ecosystem? List two main components.
Answer : (a) Because the energy moves progressively through the various trophic levels and is no longer available to the previous trophic level. The energy captured by autotrophs does not revert back to the solar input.
* Pesticides, used for crop protection when washed down into the soil/water body, are absorbed by the plant along with water and minerals
* Being non-biodegradable, these chemicals get accumulated progressively in the food chain and into our body
(b)A self-sustaining functional unit consisting of living and non-living component is called an ecosystem.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) List any two characteristics of a good fuel.
(b) What are non-renewable resources of energy? Give two examples of such resources.
Answer : a) Characteristics of a good fuel:
• It should have a high calorific value.
• It should bum without giving out any smoke or harmful gases.
• Its ignition temperature should neither be too low nor too high.
• After burning it should not leave much ash behind.
(b) Those sources of energy which have accumulated in nature over a very very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted, are called non-renewable sources of energy.
Example: Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and nuclear fuels (uranium) are nonrenewable sources of energy
Question. List the products of combustion of fossil fuels. What are their adverse effects on the environment?
Answer : When fossil fuels are burnt, the products of combustion are – carbon dioxide, water, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. If combustion takes place in an insufficient supply of air then carbon monoxide is produced. All these products are harmful and create some adverse effects on the environment.
• Sulphur dioxide dissolves in rainwater making it acidic. The acid rain thus produced damages trees, plants, buildings and metal structures.
• Nitrogen oxide also causes acid rain.
• Carbon monoxide is a greenhouse gas which traps Sun’s heat energy falling on the earth. The increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes increased greenhouse effects leading to global warming.
Question. List any two disadvantages of using fossil fuels for the production of energy.
Give two examples each of the following:
(i) Renewable sources of energy; (ii) Non-renewable sources of energy.
Answer : (a) Disadvantages of using fossil fuels are:
1. Fossil fuels are non-renewable source of energy.
2. Elements like carbon, nitrogen and sulfur are present in fossil fuels. When fossil fuels are burnt, these elements react with oxygen of air to produce oxides which are acidic in nature. This leads to acid rain which adversely affects the quality of water and soil.
3. CO2 is a gas which produces greenhouse effect. This leads to global warming.
4. CO produced is a toxic gas that causes respiratory problems.
(b) (i) Examples of renewable sources of energy:
1. Solar energy
2. Tidal energy
3. Hydel power
(ii) Examples of non-renewable sources of energy:
1. Diesel
2. Petrol
3. CNG
Question. (a) What is an ecosystem? List its two main components.
(b) We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Explain.
Answer : (a) An ecosystem is a self-contained unit of living things (plants, animals and decomposers) and their non-living environment (soil, air and water). An ecosystem needs only the input of sunlight energy for its functioning.
The two main components of an ecosystem are:
1. Abiotic component. It includes all non-living components like soil, water, air temperature, light, pressure, etc.
2. Biotic component. It includes all living components like plants, animals, decomposers, etc.
(b) A pond is a self sufficient or independent unit in nature. It contains all the components of the ecosystem. In this ecosystem, producers (hydrophytes) trap the solar energy and then provide the basic food or energy for all other life in the pond. When the producers and
consumers die, the decomposers present in the pond act on their dead bodies to return the various elements back to the nutrient pool. On the other hand, in an aquarium there are not any producers and nutrient pool to trap solar energy, therefore the fishes living in an aquarium need to be nourished. Moreover due to absence of decomposers the excreta of the fishes cannot be decomposed. Therefore the aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly.
Question. “Our foodgrains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues.” State the reason to explain how and why it happens?
Answer : Pesticides are poisonous chemical substances which are sprayed over crop plants to protect them from pests and diseases. These pesticides mix up with soil and water and are then absorbed by growing plants along with water and other minerals.
Thus pesticides enter the food chain at the producer level (plant level) and in the process of transfer of food through food chains these harmful chemicals get concentrated at each trophic level. These chemicals are non-biodegradable, so they get accumulated at each trophic level. Pesticides present in wheat grains, fruits vegetables and meat cannot always be removed by washing, etc.
Question. (a) Create a food chain of the following organisms.
Insect, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog
(b) Name the organism at the third trophic level of the created food chain.
(c) Which organism of this food chain will have the highest concentration of non- biodegradable chemicals?
(d) Name the phenomenon associated with it.
(e) If 10,000 Joules of energy is available to frogs, how much energy will be available to snakes in this food chain?
Answer : (a) Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake → Hawk
(b) Frog is present in the above created food chain.
(c) Hawk is the top consumer of the food chain, so, it will have high concentration of nonbiodegradable chemicals.
(d) Biological magnification
(e) As per 10% law of flow of energy in an ecosystem, only 10% of energy is received by the
next trophic level. Hence, in the given food chain, if 10,000 Joules of energy is available to frog, then the energy available to snakes will be 1000 Joule.
Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake → Hawk
10,00000 J 10,0000 J 10,000 J 1000 J 100 J
Question. “Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional.” Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
Answer : “Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional.” In the ecosystem energy flows from one trophic level to the next trophic level of the food chain. Energy flows from producers i.e., green plants to the consumers. It does not flow from the last consumer to its previous consumer and so on. Thus the energy does not flow back from consumers to the producers. So we say that flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional.
Entry of pesticides in a food chain: Some harmful chemicals like pesticides, when absorbed by the plants through soil and water, get transferred from first trophic to the last trophic level of the food chain. As these chemicals are non-degradable, their concentration in the bodies of living organisms at each trophic level progressively increases. Their increase in the concentration of harmful chemicals in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification. The level of concentration of chemicals is maximum for human beings as they are at the highest trophic level
Question. Subhash has started the project of constructing his building. His architect suggested that he should add a system of rain water harvesting in his building. He thought by adopting water harvesting in his project he can solve his water crisis problem in the years to come. Is Subhash correct in his approach? Support your answer.
Answer : Rainwater collected on the roof is not allowed to go into the drain. It is allowed to percolate under the ground by a specially made passage so as to recharge the ground-water.
This process is called rainwater harvesting.
Advantages of rainwater harvesting:
• Rainwater stored as underground water does not evaporate.
• The water stored in ground does not promote breeding of mosquitoes.
• It is protected from contamination by human and animal waste.
• This water recharges wells.
Question. Human body is made up of five important components of which water is the main component.
Food as well as potable water are essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture. Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields. These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
Why is the maximum concentration of pesticides found in human beings?
Answer : The pesticides are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. As human beings occupy the topmost level in food chain, their concentration becomes maximum in our bodies
Question. (a) What is meant by biodegradable waste materials ? Give two examples of biodegradable wastes.
(b) Which of the following materials are non-biodegradable ?
Aluminium wire, Tea leaves, Synthetic fibre, Wool
Answer : (a) The waste material that can be easily broken down into non-poisonous substances that can be decomposed and recycled easily is called biodegradable waste. Example: Kitchen waste, paper bits, etc.
(b) Aluminium wire and synthetic fiber are non-biodegradable.
Question. (a) What is meant by non-biodegradable waste materials ? Give two examples of non-biodegradable wastes (b) Which of the following materials are biodegradable ?
Animal bones, Iron nails, Plastic mugs, Leather belts, Silver foil
Answer : a The waste materials which cannot be broken down into non-poisonous or harmless substances in nature are called non-biodegradable waste materials. Example – D.D.T and Plastics.b Animal Bones and Leather Belts.
Question. (a) Define an ecosystem. Give examples of any two ecosystems.
(b) List the biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem.
Answer : (a) An ecosystem is a self-sustained unit of living things (plants, animals and decomposers) and their non-living environment (air, water and soil).
Examples: A pond is an ecosystem that includes the aquatic life (aquatic animals and plants) that live in the pond water.
A forest is an example of a terrestrial ecosystem that includes the physical environment of the forest along with the plants and animals that live in that forest.
(b) The biotic components of an ecosystem are the plants, animals and decomposers present in it.
The abiotic components of an ecosystem are air, water and soil. The abiotic components also include physical factors such as light, temperature, pressure and humidity. Inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus are also abiotic components of an ecosystem.
Question. (a) What is a food chain ? Give one example of a simple food chain.
(b) What is a ‘food web’ ? Show its formation.
Answer : (a) The sequence of living organisms in a community in which one organism consumes another organism to transfer food energy is called a food chain. An example of a simple food chain is that operating in a grassland:
Grass (Producer) ⟶Deer(Herbivore)⟶Lion(Carnivore)
(b) The inter-connected food chains operating in an ecosystem that establish a network of relationships among various species comprise a food web.
A food web is formed by many food chains operating together. A food web operating in a grassland is shown in the figure.
Question. (a) What is meant by ‘environment’ ?
(b) What type of substances are the major pollutants of the environment ? Name two such substances.
(c) Name the organisms whose uncontrolled activities are damaging the environment.
(d) Explain why, it is better to use paper bags than plastic bags.
Answer : (c) Humans
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases And Salts Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Metals And Non Metals Worksheet Set A |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Metals And Non Metals Worksheet Set B |
| CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sources Of Energy Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sustainable Management of Natural Resources Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Revision Worksheet Set D |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Collection Of Important Questions Worksheet |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Physics Worksheet Set A |
More Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment Worksheet
We hope students liked the above worksheet for Chapter 15 Our Environment designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in the above worksheet for Class 10 Science on a daily basis. All the latest worksheets with answers have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better scores in their class tests and examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Class 10 students to get all the latest study material free of cost.
Worksheet for Science CBSE Class 10 Chapter 15 Our Environment
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to the NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 worksheet. If you download the practice worksheet for one chapter daily, you will get higher and better marks in Class 10 exams this year as you will have stronger concepts. Daily questions practice of Science worksheet and its study material will help students to have a stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them experts on all scoring topics. You can easily download and save all revision worksheet for Class 10 Science also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the worksheet which have been developed as per the latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers
Chapter 15 Our Environment worksheet Science CBSE Class 10
All worksheets given above for Class 10 Science have been made as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. The students of Class 10 can be rest assured that the answers have been also provided by our teachers for all worksheet of Science so that you are able to solve the questions and then compare your answers with the solutions provided by us. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Science in the worksheet so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. All study material for Class 10 Science students have been given on studiestoday.
Chapter 15 Our Environment CBSE Class 10 Science Worksheet
Regular worksheet practice helps to gain more practice in solving questions to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of Chapter 15 Our Environment concepts. Worksheets play an important role in developing an understanding of Chapter 15 Our Environment in CBSE Class 10. Students can download and save or print all the worksheets, printable assignments, and practice sheets of the above chapter in Class 10 Science in Pdf format from studiestoday. You can print or read them online on your computer or mobile or any other device. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Science MCQ Test for the same chapter.
Worksheet for CBSE Science Class 10 Chapter 15 Our Environment
CBSE Class 10 Science best textbooks have been used for writing the problems given in the above worksheet. If you have tests coming up then you should revise all concepts relating to Chapter 15 Our Environment and then take out a print of the above worksheet and attempt all problems. We have also provided a lot of other Worksheets for Class 10 Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Science
You can download the CBSE Printable worksheets for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the links above and download Printable worksheets in PDFs for Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 for Science
Yes, the Printable worksheets issued for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment have been made available here for latest academic session
You can easily access the links above and download the Class 10 Printable worksheets Science Chapter 15 Our Environment for each chapter
There is no charge for the Printable worksheets for Class 10 CBSE Science Chapter 15 Our Environment you can download everything free
Regular revision of practice worksheets given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 15 Our Environment can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, studiestoday.com provides all latest NCERT Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 Science test sheets with answers based on the latest books for the current academic session
Yes, studiestoday provides worksheets in Pdf for Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 Science in mobile-friendly format and can be accessed on smartphones and tablets.
Yes, worksheets for Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 Science are available in multiple languages, including English, Hindi

