Please refer to CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Globalization and the Indian Economy. Download HOTS questions and answers for Class 10 Social Science. Read CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy below and download in pdf. High Order Thinking Skills questions come in exams for Social Science in Class 10 and if prepared properly can help you to score more marks. You can refer to more chapter wise Class 10 Social Science HOTS Questions with solutions and also get latest topic wise important study material as per NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and pattern for Class 10
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science HOTS
Class 10 Social Science students should refer to the following high order thinking skills questions with answers for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy in Class 10. These HOTS questions with answers for Class 10 Social Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
HOTS Questions Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Summary
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Question : WTO is dominated by countries like ___ .
(a) U.S. and U.K.
(b) China and France
(c) India and Japan
(d) Ireland and Germany
Answer : A
Question : What was the idea behind developing Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India?
(a) To attract foreign companies to invest in India
(b) To earn foreign exchange
(c) To make India financially stable
(d) To make India a developed country
Answer : A
Question : What are the investments made by MNCs called?
(a) Foreign investments
(b) International investments
(c) Multi National investments
(d) None of these
Answer : A
Question : Rajiv has a textile firm. For carrying out production, Rajiv spent money on procuring thread from traders, buying machine and equipment and built a warehouse to store the cloth produced. The expenditure incurred by Rajiv for conducting the production process is termed as _____.
(a) investment
(b) profits
(c) equity
(d) interest
Answer : A
Question : ____________ is a major benefit of joint production between a local company and a Multi-National Company.
(a) MNCs can bring latest technology in the production
(b) MNCs can control the increase in the price
(c) MNCs can buy the local company
(d) MNCs can sell the products under their brand name
Answer : A
Question : Indian government felt the need for removing barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment in ____________.
(a) 1991
(b) 1951
(c) 1991
(d) 1971
Answer : C
Question : ___________refers to all those different economic reforms or policy measures and changes which aim at increasing the productivity and efficiency by creating an environment of competition in the economy.
(a) New economic policy
(b) Public sector reforms
(c) Five year plans
(d) None of the above
Answer : A
Question : The past two decades of globalisation have seen rapid movements in:
(a) goods, services, technology and investments between countries.
(b) goods, services and people between countries.
(c) goods, investments and people between countries.
(d) none of the above
Answer : A
Question : Globalisation has led to improvement in living conditions:
(a) of all the people.
(b) of people in developed countries.
(c) of workers in the developing countries.
(d) none of the above.
Answer : C
Question : Why did the government decide to remove barriers on foreign trade and foreign competitors?
(a) Because the government wanted to earn the foreign exchange.
(b) Because the government felt that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers in the world market.
(c) Because the government wanted to maintain good relations with other countries.
(d) All of the above.
Answer : D
Question : It creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. What does it refer to?
(a) Technology
(b) Investments
(c) Trade barriers
(d) Globalisation
Answer : D
Question : What is the full form of WTO?
(a) World Transactions Organisation
(b) Wealth Trade Organisation
(c) World Trade Organisation
(d) None of the above
Answer : C
True / False
Question : Joint production helps in bringing the latest technology by MNC's, thus improving the value of the product. (True/False)
Answer : True
Question : A consumer gets greater choices of goods because of entry of MNC's, increase in foreign trade and free trade regulated by international organisation.
Answer : True
Assertion and Reasoning Based Questions
Mark the option which is most suitable :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Question : Assertion : Globalisation leads to increased competition in international and domestic markets.
Reason : Globalisation also makes the consumers better off as they have a wider variety of goods to choose from at lower prices.
Answer : (b) Globalisation leads to increased competition in international and domestic markets as there is free movement of goods, services, labour and funds across countries. Also, consumers are better off as they get better quality and increased variety of goods at lower prices.
Question : Assertion : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets.
Reason : Foreign trade expands the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
Answer : (b) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets and thus expands the choices available for consumers.
Question : Assertion : Local businesses may set up joint production process with MNCs and earn higher profits.
Reason : MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
Answer : (a) At times, MNCs set up production jointly with some of the local companies of the host countries. The benefit to the local company from such joint production is two-fold as MNCs can provide for additional investments and can bring in newer technology of production that result in fast-paced production.
Question : Assertion : Foreign trade and foreign investment results in disintegration of production across countries.
Reason : MNCs disrupt the production processes in domestic country.
Answer : (d) The result of greater foreign investment and greater foreign trade has been greater integration of production and markets across countries. When MNCs conduct joint business processes with local companies, the benefit to local companies is massive as they receive investment funds and exposure to different production techniques.
Question : Assertion : Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process.
Reason : Developing countries are likely to become at par with developed countries in terms of technological development due to globalisation.
Answer : (b) Since globalisation leads to movement of goods, services, people and technology across nations, developing countries are likely to become at par with developed countries in terms of technological development.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question : Assertion : A tax on imports makes the market for imported goods lucrative in terms of earning higher profits.
Reason : Taxes are imposed to regulate trade between nations. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
Answer : (d) A is false, but R is true
Question : Assertion : Globalisation leads to increased competition in international and domestic markets.
Reason : Globalisation also makes the consumers better off as they have a wider variety of goods to choose from at lower prices.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Foreign trade and foreign investment results in disintegration of production across countries.
Reason : MNCs promote the production processes in domestic country.
Answer : (d) A is false, but R is true
Question : Assertion : Tax on exports is an important barrier on foreign trade.
Reason : Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease foreign trade.
Answer : (d) A is false, and R is true
Question : Assertion : (MNCs) is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation.
Reason : MNCs is not only sell their finished products globally, but more importantly, the goods and services are produced globally.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all, and also ensure that the benefits of globalization are shared better.
Reason : Globalisation has benefited well-off consumers and also producers with skill, education and wealth.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question : Assertion : Global production has a complex structure.
Reason : Production of one good may take place in different parts of the world. For instance, an equipment may be formed by combining components produced in different countries.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Very Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Question : Why do MNCs set up their offices and factories in those regions where they get cheap labour and other resources?
Answer : To minimise the cost of production and maximise profit earning, MNCs set up their offices and factories in region where they get cheap labour and other resources.
Question : What is Liberalisation ?
Answer : Liberalisation is the process of removing barriers or restrictions to trade and investment limits set by the government.
Question : Correct the following statement and rewrite:
The most common route for investments by MNCs in countries around the world is to form partnerships with local government.
Answer : The most common route for investments by MNCs in countries around the world is to form partnerships with local companies.
Question : Why are the MNCs spreading their production to other countries ?
Answer : Expanded markets, lower cost, proximity to other markets are some of the reasons for MNCs spreading their production to other countries.
Question : What benefits do the containers provide ?
Answer : Containers have led to huge reduction in port handling costs and increased the speed with which exports can reach to the markets quickly.
Question : Give an example of trade barrier.
Answer : Tax on imports is an example of trade barrier.
Question : What is the objective of WTO ?
Answer : The main aim of World Trade Organisation (WTO) is to liberalise international trade.
Question : Match the following items given in column A with those in column B. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

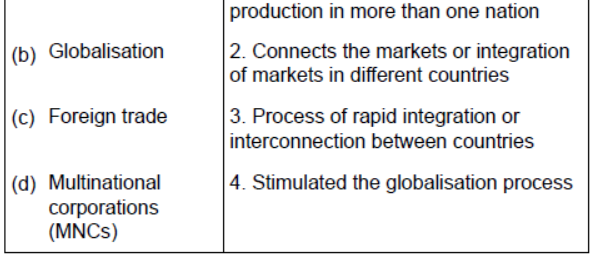
(A) (a) 4, (b) 3, (c) 2, (d) 1
(B) (a) 1, (b) 2, (c) 3, (d) 4
(C) (a) 3, (b) 1, (c) 4, (d) 2
(D) (a) 2, (b) 4, (c) 1, (d) 3
Answer : (A) (a) 4, (b) 3, (c) 2, (d) 1
Question : What is globalisation?
Answer : Globalisation is this process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
Question : What is the main aim of foreign trade?
Answer : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries.
Question : The Indian government removed barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment to a large extent. What does this mean?
Answer : This means that goods could be imported and exported easily and also foreign companies could set up factories and offices here.
Question : Why had the Indian Government put barrier to foreign trade and foreign investment after independence? State any one reason.
Answer : The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment because this was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition.
Question : Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crossed the boundaries of these countries?
Answer : There were raw materials, food stuff and finished products.
Question : What is an MNC?
Answer : An MNC (Multi-National Corporation) is a company that owns and controls production in more than one nation.
Question : Where do MNCs set up offices and factories for production?
Answer : MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get cheap labour and other resources.
Question : For which purpose can government use trade barriers?
Answer : Government can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of each, should come into the country.
Question : What is the aim of World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
Answer : Its aim is to liberalise international trade.
Question : How are Mexico and Eastern Europe useful for the MNCs?
Answer : In these two countries are close to the markets in the US and Europe.
Short Questions for Class 10 Social Science Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Question : What values worked behind the restrictions on foreign trade in India after independence?
Answer : After India became independent, the Indian government put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. The values that worked behind this are:
(i) It was essential at that time to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to emerge.
(ii) Since industries were newly born during that period, it was necessary to make their foundation strong by providing them opportunities to flourish first within the country, then across the country.
(iii) The restrictions on foreign trade for a certain period proved to be a boon for domestic producers in the sense that they became self-sufficient. This self sufficiency made them able to face competitions.
Question : What would happen of Government of India parts heavy tax on import of Chinese toys? Explain any three points.
Answer : (i) Those who wish to import Chinese toys would have to pay tax on this.
(ii) Because of the tax, buyers will have to pay a higher price on imported toys.
(iii) Chinese toys would no longer be so cheap in the Indian markets and imports from China will automatically reduce.
(iv) Indian toy makers will prosper.
Question : Differentiate between foreign trade and foreign investment.
Answer :
Question : What is the impact of globalisation on the well-off sections in the urban areas of India?
Answer : Due to globalisation there is greater choice before the people belonging to welloff sections. They now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier.
Question : “Information and communication technology has played a major role in spreading out products and services across countries.” Support the statement.
Answer : (i) In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, internet has been changing rapidly
(ii) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
(iii) Computers have now entered almost every field of activity. Through the use of internet, one can communicate across the world at negligible costs.
(iv) These devices help us in various ways, transfer of money across the countries has become easy. We can place order for a variety of things through the phone or the internet, and goods are delivered at our home.
Question : How is information technology connected with globalisation?
Answer : Information and communication technology is closely connected with globalisation. In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, internet has been changing rapidly.
(i) Telecommunications facilities such as telegraph, telephone including mobiles, fax have brought the world closer. Now people can contact around the world easily. These developments are used to access the information instantly and communicate in the remote areas.
(ii) Computer and internet have entered in almost all the fields. Internet allows one to share information on almost everything. We can send instant e-mail and talk through voice-mail across the world at almost negligible cost.
Question : “Globalisation and competition among producers has been of advantage to the consumers.” Give arguments in support of this statement.
Answer : (i) There is greater choice available to the consumers in goods.
(ii) The quality of goods has been improved.
(iii) Prices of goods are lower.
(iv) Consumers are now able to enjoy a better life.
Question : ‘Barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent in India since 1991.’ Justify the statement.
OR
Why did the Government of India remove trade barriers ? Explain the reasons.
Answer : (i) Due to this, imports and exports could easily flow between different countries.
(ii) It allowed the local producers to compete with products at global level, so that they could improve the quality of their product.
(iii) Global MNCs could set up their production units, they brought latest technology of production into the country.
Question : Who has benefitted the most by the globalisation?
Answer : Globalisation has not provided benefits to everyone in equal proportion. People with education, skill and wealth have made the better use of the new opportunities in comparison to those with less education, skills and wealth.
Question : Write a short note on WTO.
Answer : World Trade Organisation (WTO) is an institution whose aim is to liberalise international trade. WTO is a regulating and monitoring authority which establishes rules regarding international trade, and sees that these rules are obeyed. About 160, nearly 165 countries of the world are members of the WTO.
Question : What are the ways in which MNCs interact with local producers ?
Answer : MNCs interact with local producers in the following ways :
(i) By setting up partnerships with local companies.
(ii) By using the local companies for supplies.
(iii) By closely competing with the local companies.
Question : ‘‘How can the Government of India play a major role to make globalisation more fair? Explain with examples.
Answer : Fair globalisation would create equal opportunities for all and would ensure that the benefits of globalisation are shared better. The government can play a major role in making this possible. The policies of the government must protect the interests of all the people of the country, and not only of the rich and powerful. Hence, the government can play a significant role in bridging the gap between the two. The government must ensure that the labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights. Support to the domestic and smaller producers must be ensured for making them strong enough to enter the competitive global market.
It is necessary for the developing countries to have stronger trade and investment rules. They should negotiate at the WTO for fairer rules and regulations.
Question : What kind of opportunity is created by foreign trade for producers?
Answer : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country, but they can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world.
Question : ‘‘Globalisation and greater competition among producers has been advantageous to consumers.’’ Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Globalisation and greater competition among producersboth local and foreign, has been of advantage to consumers in the following ways :
(i) Companies have invested in new technology to enhance their production quality to compete with the MNCs, thus, ensuring that consumers get better quality products and be satisfied.
(ii) Indian companies have collaborated with MNCs to produce more functional and advanced products, thus, benefitting the consumers.
(iii) Consumer can enjoy improved quality at lower prices for several products. This has led to higher standard of living.
(iv) There is a greater choice available to the consumers of goods.
(v) The quality of goods has improved.
(vi) Due to competition, the prices of various products has come down.
Question : Describe the contribution of technology in promoting the process of globalisation.
Answer : The technology has contributed immensely in promoting the process of globalisation. Visible improvements in this field are:
(i) Past fifty years have seen several improvements in transportation technology.
(ii) This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at cheaper costs.
(iii) In recent times, technology in the areas of telecommunication, computers, internet, mobiles has been changing rapidly.
(iv) Technology has facilitated the use of satellite communication devices.
(v) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world at any time. The facility of video conferencing or one-to-one video calling has become common.
(vi) Internet also allows us to send instant electronic mail (email), and talk (voice mail) across the world at negligible costs.
Question : What kind of opportunity is created by foreign trade for consumers?
Answer : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the buyers to import goods produced in another country. This is one of the ways to expand the choice of goods and services for the consumers which goes beyond what is domestically available.
Question : How has globalisation affected the life of Indians? Explain with examples.
Answer : Globalisation has contributed in the development of the Indian economy in the following ways:
(i) Greater competition among producers resulting from globalisation is a great advantage to consumers as there is a greater choice regarding every product before them.
(ii) Due to globalisation, many MNCs have increased their investments in India, this has not only helped in the inflow of capital, but has also helped largely in employment generation.
(iii) Local companies supplying raw materials to the industries that have been set as a result of the globalisation, have prospered leaps and bounds.
(iv) Large Indian companies have emerged as multinational companies. This has helped our country to increase our contacts around the world. Globalisation has helped increase our GDP and per capita income, thus making the living standards better across the globe.
Question : Rapid improvement in technology has been a major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. Explain.
OR
Explain the role of technology in stimulating globalisation process.
OR
‘‘Technology has stimulated the globalisation process’’. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Rapid improvement in technology has been one of the major factors that has stimulated the globalisation process. For instance, in the past seven decades, we have seen several improvements in transportation and communication technology. The rapid improvement in the transportation facilities has led to much faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower costs. Even more remarkable developments have taken place in communication technology. Communication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) have changed the pace of information sharing. Now it is very easy to access information, send and receive information etc. Now, the information even to the remote areas can also be shared. It has also changed the way of doing business. Production technologies have also become such that they have not remained confined to only few specific territories. This has led to the expansion of MNCs.
Question : What are the various ways in which MNCs set up, or control, production in other countries?
Answer : MNCs set up factories and offices for production. At times, MNCs set up production jointly with some of the local companies of these countries. But the most common route for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and then to expand production. MNCs with huge wealth can quite easily do so. Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers. Garments, footwear, sports items are examples of industries where production is carried out by a large number of small producers around the world. These products are then supplied to the MNCs, which sell these products under their own brand names to the customers.
Question : would flexibility in labour laws help companies?
Answer : Companies nowadays are facing intense competition. This competition is compelling them to provide the consumers more value for their money. This may happen only when they reduce their cost. Salary and wages are the significant part of their cost. Hiring people for a flexible time duration will help the companies to manage their hiring costs because in the busy period they may hire more labour while in lean period they may reduce manpower, thus reducing their operational costs. Without flexibility in labour laws, companies will not be able to hire and remove people easily which may hamper their production plans.
Question : Why is a trade-barrier called a barrier ? What does it do ?
Answer : It is called a barrier because some restriction on the trade has been set up. Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and in what quantities should come into the country.
Question : Explain by giving examples that Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are spreading their productions in different ways.
Answer : MNCs spread their production in the following ways :
(i) They set up production facility jointly with local companies. They provide money for additional investment like buying new machines for faster production.
(ii) MNC may buy up local companies and then expand production. For example : Cargil Foods, a very large MNC (from USA), has bought smaller Indian companies such as Parakh Foods.
(iii) The MNCs provide efficient managerial and advanced technology for faster production and efficient use of resources.
(iv) Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers. Examples are garments, footwear, sports items etc. The products are supplied to the MNCs, which then sell these under their own brand names to the customers.
(v) MNCs procure raw materials for their production from local producers which has helped the latter to prosper and grow.
Question : How are multinational corporations (MNCs) controlling and spreading their productions across the world? Explain.
OR
Explain by giving examples that MNCs are spreading their production in different ways.
Answer : The most common strategy of a multinational corporation is to first buy a local company and then to expand its production. Depending on the product, MNCs adopt another strategies also. In labour intensive products like garments, the MNCs are setting up partnerships with local companies. MNCs are using the local companies for supply of raw material or accessories. MNCs are closely competing with the local companies. MNCs are taking over local companies with immense money power. Thus, MNCs are exerting a strong influence on production at distant locations.
Question : How are local companies benefitted by joining hands with MNCs for production?
Answer : At times, MNCs set up production jointly with some local companies. The benefit to the local companies of such joint production is two-fold.
(i) MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
(ii) MNCs might bring with them the latest technology for production.
Question : What is the impact of flexible labour laws on workers?
Answer : Flexibility in labour laws has badly affected the workers. MNCs employ them on a temporary basis in order to cut costs. They do not pay throughout the year. During peak seasons, workers are made to work for long hours and in night shifts. They are also not given fair wages. This forces them to lead a very hard and highly insecured life.
Long Questions for Class 10 Social Science Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Question : How are MNCs spreading their production across countries? Explain with an example.
Answer : Various ways in which MNCs control production in other countries:
(i) By setting up partnerships with local companies — At Times MNCS set up production jointly with some of the local companies. The benefit to the local company of such joint production is two bold. First MNCS can provide φ money for additional investments, the like buying new machines for faster production. Second, MNCS might bring with them the latest technology for production.
(ii) By closely competing with local companies or buying them up. The most common route for MNC investments is to buy up local companies and to expand production. With their huge wealth they can easily do so.
(iii) By using local companies for supply—Large MNCs in developed countries place orders for production with small producers. E.g. garments, footwear, sports item etc. The products are supplied to MNCs which then sell these under their own brand names to the customers. These large MNCs have great power to determine price, quality, delivery and labour conditions for these distant producers.
Question : What is globalisation? How does globalisation help in interconnection among different countries? Explain with examples.
Answer : Globalisation: integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries under conditions of free flow of trade, capital and movement of persons across borders.
Globalisation interconnect different countries by:
• Foreign trade. It leads to integration of markets across countries due to which the latest models of goods like digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions etc. are available in one country.
• Foreign investment. MNCs invest capital in different countries by
• jointly producing with local companies.
• buying the local companies.
• placing orders for production like garments footwear, sports goods etc. with small producers of other countries.
Question : How has globalisation benefited India? Explain with five examples.
Answer : The impact of globalisation on India are:
• It has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as MNCs such as Tata Motors, Infosys.
• It has also created new opportunities for companies providing services like information technology.
• Greater competition among producers has been of special advantage particularly to the welloff sections of consumers in the urban areas. They have greater choice and enjoy improved quality and lower prices for various products. Thus, they are enjoying a higher standard of living.
• In these industries and services, new jobs have been created and also the companies supplying raw materials to these industries have prospered.
• Several of the top Indian companies have been able to benefit from the increased competition. They have invested in new technology and production methods and raised the standard of their products. Some of them have gained from successful collaboration with foreign companies.
Question : How is foreign trade inter-connecting the markets in different countries? Explain with examples.
Answer : Foreign trade is the main channel which connects the markets of various countries.
It leads to integration of markets across the countries in following ways:
• It creates opportunities for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets or the markets of their own countries such as Tata Motors and Ranbaxy of India have emerged as multinational corporations.
• Import of goods from various countries provides choice of goods for consumers beyond the goods that are produced domestically. Availability of foreign goods like television, mobiles etc. has increased the choice of the consumers.
• Producers of different countries compete with each other although they are thousands of miles away.
• It results in bringing down the prices of commodities which further leads to increase in production and supply. Thus, people have access to cheap products which were costlier earlier.
Question : What is the main aim of World Trade Organisation? Explain its functions.
Answer : The main aim of World Trade Organisation is to liberalise international trade. It says that all barriers to foreign trade and investment are harmful. There should be no barriers.
The main functions of World Trade Organisation are:
• It establishes rules regarding international trade and sees that they are obeyed.
• It provides a platform to member countries to decide future strategies related to trade.
• It administers the rules and processes related to dispute settlement.
• It ensures optimum utilisation of world resources. .
• It assists international organisations such as IMF and 1BPD for establishing coherence in Universal Economic Policy determination.
Question : What is trade? Explain the importance of international trade.
Answer : The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as trade.
The international trade is important because:
• It helps in exchange of surplus goods with those of deficit countries through foreign trade.
• It helps in improving the quality of domestic goods.
• It contributes to the economic growth of the country by raising income level of the people and increasing foreign exchange reserves.
• It enables a country to import advanced technology of other countries to improve its own production.
Question : Explain four ways in which globalisation and pressure of competition has changed the lives of workers substantially.
Answer : Globalisation and pressure of competition has affected the workers in following ways:
• Casual workers are hired oh contract when demand is high and laid off when demand declines.
• There is no job security among workers.
• They have long working hours and work in the night shifts on a regular basis during peak seasons.
• They are not given any benefits of pension, overtime, medical leaves etc.
Question : How has transportation technology stimulated the globalisation process? Explain with suitable examples.
Answer : Transportation technology has stimulated the globalisation process in the following ways:
• Faster trains connecting every nook and corner of a country and faster planes that cover the distance within a few hours have enabled the faster delivery of goods.
• Improvements done in transportation technology in the past fifty years have also helped in the quick movement of goods. For example, containers carrying goods have led to huge reduction in port handling costs and an increased speed, with which exports can reach markets.
• Reduced cost of air transport has enabled much greater volumes of goods being transported by airlines.
Question : How do large companies often manipulate the markets? Explain with an example.
Answer : The large companies manipulate the market in the following ways:
• Sometimes false information is passed on through media and other sources to attract consumers. For example, a company selling powder milk for babies as the most scientific product claiming it to be better than mother’s milk which although was a false claim.
• Some food items were consumed in India for many years although it is very harmful for the health of people. But through attractive and convincing advertisements in media, it was able to control the market such as Maggie noddles manufactured by Nestle was found harmful after testing in India in May 2015.
• They may also hide the essential information about the product like expiry date, contents, terms and conditions etc. to keep the consumers in dark.
• Sometimes, the expired products are packed in a new packing and again released in the market.
• It has also been evident that artificial scarcity is created by the producers and the product is hoarded for sale in future at a high price.
Question : Describe any five factors that promote the Multinational Corporations (MNCs to set up their production units in a particular place.
Answer : The factors that MNCs take into consideration to set up their production units in a particular place are:
• where it is close to the markets.
• where the skilled and unskilled labour at low costs is available.
• where the favourable government policies looking after their interest are , present.
• where the other factors of production such as raw materials, water, electricity and transport are available.
• where there are standard safety measures for assured production.
Question : Explain the role of information technology in globalisation.
Answer : Information and communication technology has stimulated the globalisation process as:
• In recent years, technology in the areas of computers, telecommunication and internet has been changed rapidly.
• Telecommunication facilitates including telegraph, telephone, mobile phone, fax are used to contact one another around the world and to get information instantly and to communicate from remote areas.
• All this has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
• Computers and internet have enabled people to obtain and share information on any subject.
Question : What role can the government play in order to ensure a fair globalisation?
Or
Explain how globalisation can be made fairer.
Answer : The government can play a major role in ensuring a fair globalisation in India:
(i) Its policies must protect the interests, not only of the rich and the powerful, but all the people in the country.
(ii) The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights.
(iii) It can support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete.
(iv) If necessary, the government can use trade and investment barriers.
(v) It can negotiate at the WTO for ‘fairer rules’.
(vi) It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
Question : In recent years, how our markets have been transformed? Explain with examples.
Answer : Transformation of markets in recent years:
(i) The advent of globalisation and the policy of liberalisation has opened the market to the world players. The economy of our country has rapidly grown with the onset of LPG. i.e., Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation reforms in 1991.
(ii) MNCs play a vital role in the world market and as a result foreign trade and investment in the country has increased. MNCs are playing a major role in the market by introducing exchange of technology between countries.
(iii) Foreign trade affects the integration of domestic markets in different countries.
(iv) Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those dealing in IT.
(v) Better job opportunities for people have given rise to migration.
(vi) Also, globalisation has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals themselves. Tata Motors (automobiles), Infosys (IT), Ranbaxy (medicines) are some Indian companies which are spreading their operations worldwide.
Question : What factors have enabled globalisation?
Answer : Following are the various factors that have promoted globalisation:
(i) Technology : Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. For instance, in the past seven decades, we have seen several improvements in transportation and communication technology. This has led to much faster delivery of goods across long distances at lower costs. Similarly, communication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) have changed the pace of information sharing. It has also changed the way of doing business.
(ii) Liberalisation policies : Starting around 1991, the Indian government had the realisation that in order to improve the functioning of the Indian economy, the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe. It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country since they would have to improve their quality. Thus, barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent and foreign trade and investments were liberalised.
(iii) World Trade Organisation : The liberalisation of foreign trade and investment in India was supported by some very powerful international organisations. These organisations were of the view that all barriers to foreign trade and investment are harmful and they supported free trade. World Trade Organisation (WTO) was one such organisation which supported free trade and investment in the country.
Question : Since globalisation is now a reality, how can it be made more ‘fair’ for all the countries ?
Answer : Globalisation is a reality in present. It is a phenomenon which has advanced so much that it is now impossible for any country or organisation to turn it over. So each country has to adopt it for its betterment. Now every effort must be made by all the countries individually and collectively to make it "Fair" for everyone. Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all, and also ensure that the benefits of globalisation governments can play a major role in making this possible. Its policies must protect the interests of all the people in the country whether rich or poor. Following are some of the possible steps that the government can take to make globalisation "Fair" for everyone :
(i) The government must support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete. The government can use trade and investment barriers till that time.
(ii) It must support the agriculturists of the country so that they are not eliminated by cheaper imports. This happened in Kerala where due to cheaper imports of coconuts from Sri Lanka, the coconut farmers were put in problems.
(iii) The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights.
(iv) It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
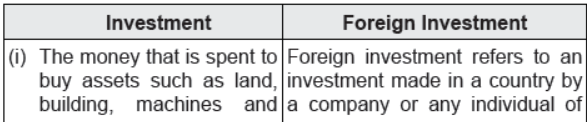
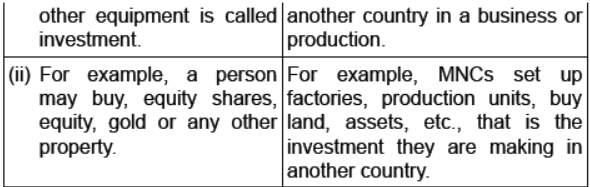
Question : Differentiate between Investment and Foreign Investment.
Answer :
Question : How can globalisation be an integrating force ?
Answer : Globalisation is an integrating force that integrates the economies of the nations. This integration takes place through foreign trade, foreign investment and movement of people. Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. The producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. When the goods travel from one market to another, prices of similar goods in the two markets tend to become equal. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country expands their choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced. So the choice of goods in the markets rises. This has also raised their standard of consumption at par with their counterparts in other countries. Foreign investments through MNCs play a major role in the integration process. More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries. This has led to the profitability of MNCs getting affected by their performance in other countries. There is one more way in which the countries are getting connected i.e., through the movement of people between countries who move from one country to another in search of better income, better jobs or better education. This leads to the sharing of culture between the people.
Question : How can globalisation be an integrating force?
Answer : Globalisation is an integrating force that integrates the economies of the nations. This integration takes place through foreign trade, foreign investment and movement of people.
Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. The producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country, but they can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. When the goods travel from one market to another, prices of similar goods in the two markets tend to become equal. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
Similarly, for buyers, import of goods produced in another country expands their choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced. So, the choice of goods in the markets increases. This has also increased their standard of consumption at par with their counterparts in other countries.
Foreign investments through MNCs play a major role in the integration process. More and more goods and services, investments and technology are moving between countries. This has led to the profitability of MNCs getting affected by their performance in other countries.
There is one more way in which the countries are getting connected. This is through the movement of people between countries who move from one country to another in search of better income, better jobs or better education. This leads to the sharing of culture between the people.
Question : Why do you think that the Chinese toys are more popular in Indian market? What would happen if Indian government impose heavy import duties on Chinese toys?
Answer : Chinese toys are more popular in Indian markets because they are cheaper in comparison to Indian toys. Other reasons for Chinese toys' popularity are their better make and design. Now almost all the toy shops are selling Chinese toys in large numbers. It seems that Chinese toys have almost replaced the Indian toys. This is a very serious situation for Indian toys manufacturers in terms of their income and employment.
If the Indian government imposes heavy import duty on Chinese toys, it will increase their cost and hence the prices in the Indian market. This will decrease their demand in the market. This will lead to more demand of Indian toys and fall in the imports of Chinese toys. This will happen only when their prices become higher than the prices of Indian toys due to import duties. So, if even after imposing the import duty, the Chinese products remain cheaper in comparison to Indian toys than their imports will not fall.
Question : What is WTO ? Why it has been formed ?
Answer : World Trade Organisation (WTO) is the only International Organisation that deals with the global rules of trade between nations. Its main role is to help producers of goods and services, exporters and importers protect and manage their businesses better. It was established in 1995 and its headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland. At its heart are the WTO agreements, negotiated and signed by the bulk of the World's trading nations and ratified in their parliaments. Its purpose is to monitor WTO trade agreements, facilitate trade negotiations, mediate trade disputes, monitor international trade policies and provide assistance to developing economies.
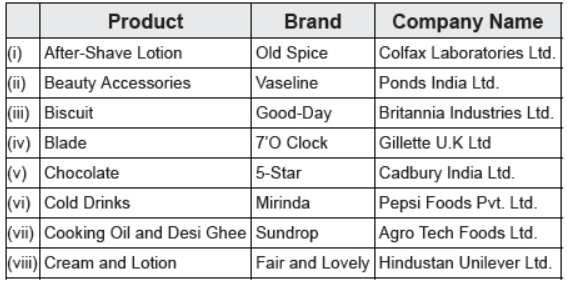
Question : Take some branded products that we use everyday (soaps, toothpaste, garments, electronic goods, etc.). Check which of these are produced by MNCs.
Answer :
Question : How do Multi-National Corporations (MNCs) interlink their production across countries? Explain with examples.
Answer : Multi-National Corporations (MNCs) control their production across countries in various ways:
(i) MNC is a company that owns and control production in more than one nation. MNCs set up offices and factories for production in regions where they can get cheaper labour and other resources. This is done so that the cost of production may be low and the MNCs may earn greater profits.
(ii) The MNCs are not only selling their finished products globally, but more importantly, these goods and services are produced globally.
(iii) The production process is divided into small parts and spread out across the globe. In the above example, China provides the advantage of being a cheap manufacturing location.
(iv) The most common route for MNCs investments is to buy up local companies and then to expand production. For example, Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC bought over Indian company Parakh Foods which had a large marketing network in various parts of India and also a good reputation. With this advantage, Cargill has now become the largest producer of edible oil in India.
(v) There is another way in which MNCs control production. Large MNCs in developed countries place order for production with small producers of cheaper countries. Garments, footwear, sport items come in this category and MNCs, after quality check, put their brand name on these items.
(vi) As a result, production in these widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
Source/Extract Based Questions
Question : "Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. Similarly, for the buyers, imports of goods produced in other country are one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced. In general, with the opening of trade, goods travel from one market to another. Choice of goods in the markets rises. Prices of similar goods in the two markets tend to become equal. And, producers in the two countries now closely compete against each other even though they are separated by thousands of miles. Foreign trade thus results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries."
(i) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the :
(a) Consumers
(b) Producers
(c) Manufacturers
(d) None of these
Answer : (b) Producers
(ii) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to :
(a) reach beyond their expectations.
(b) go beyond the domestic markets.
(c) go beyond the foreign markets.
(d) none of the above.
Answer : (b) go beyond the domestic markets.
(iii) Fill in the blank :
___________ results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
Answer : Foreign trade
(iv) Assertion : Producers can sell their produce in markets located in other countries of the world.
Reason : Foreign trade results in connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(v) What is the one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced?
(a) Export of goods
(b) Import of goods
(c) Exim trade
(d) None of these
Answer : (b) Import of goods
Read the source given below and answer the following questions.
Ford Motors, an American company, is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 26 countries of the world. Ford Motors came to India in 1995 and spent ` 1700 crore to set up a large plant near Chennai. This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of jeeps and trucks. By the year
2004, Ford Motors was selling 27,000 cars in the Indian markets, while 24,000 cars were exported from India to South Africa, Mexico and Brazil. The company wanted to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
Question : The passage given above relates to which of the following options?
(a) Increased employment
(b) Foreign investment
(c) Foreign collaboration
(d) International competition
Answer : (b) Foreign investment.
Question : According to the given passage, Ford Motors can be termed as a Multinational Company based on which of the following options?
(a) Production of different types of automobiles
(b) Largest automobile manufacturer in the world
(c) Because of large scale exports of cars across globe
(d) Industrial and commercial ventures across globe
Answer : (d) Industrial and commercial ventures across globe.
Question : By setting up their production plants in India, Ford Motors wanted to—
(a) Collaborate with a leading Indian Automobile company
(b) Satisfy the demands of American, African and Indian markets
(c) Tap the benefits of low-cost production and a large market
(d) Take over small automobile manufacturing units in India
Answer : (c) Tap the benefits of low-cost production and a large market.
Question : ‘Ford Motors’ wish to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe is an evidence of—
(a) Promoting local industries of India
(b) Merging trade from different countries
(c) Supplying jobs to factory workers in India
(d) Interlinking of production across countries
Answer : (d) Interlinking of production across countries.
Question : Read the sources given below and answer the question that follows :
Source A – Chinese toys in India
Chinese manufactures learn of an opportunity to export toys to India where toys are sold at a high price. Chinese toys become more popular in the Indian markets because of the cheaper prices and new toy shops have replaced Indian toys with Chinese toys.
Source B – Using IT in globalisation
A news magazine published for London readers is to be designed and printed in Delhi. The text of the magazine is sent through Internet to the Delhi office. The designers in the Delhi office get orders on how to design the magazine from the office in London using telecommunication facilities. The designing in done on computer. After printing, the Magazines are sent by air to London to a bank in Delhi instantly through e-banking.
Source C – Route for MNC investment
According to sources, The most common is to buy up local companies and then to expand production. MNCs with huge wealth can quite easily do so.
Question : Source A – Why Chinese toys are becoming more popular in Indian markets ?
Answer : Chinese toys are becoming more popular in Indian markets because of the cheaper prices and new designs.
Question : Source B – How is information technology connected with globalisation ?
Answer : Information technology is connected with globalisation with the help of e-banking, telecommunications, internet, computer etc.
Question : Source C – Give example for the mentioned sources.
Answer : Cargill foods an American MNC has bought over smaller Indian companies such as Parakh foods which had built a large marketing network in various parts of India.
Read the following extract and answer the questions that follows :
Ford Motors, an American company, is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with productions spread over 26 countries of the world. It came to India in 1995 and spent ` 1700 crore to set up a large plant near Chennai. This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra a major Indian manufacturer of Jeeps and trucks.
Question : Would you say Ford Motors is a MNC ? why ?
Answer : Yes, it is a MNC as it is operating in more than one country.
Question : What is foreign investment ? How much did Ford Motors invest in India ?
Answer : It means the investment made by the MNCs. Ford Motors investmented ` 1700 crore in India.
Question : Ford Motors belongs to which country :
Answer : America.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions.
Chinese manufacturers learn of an opportunity to export toys to India, where toys are sold at a high price.
They start exporting plastic toys to India. Buyers in India now have the option of choosing between Indian and the Chinese toys. Because of the cheaper prices and new designs, Chinese toys become more popular in the Indian markets. Within a year, 70 to 80 per cent of the toy shops have replaced Indian toys with Chinese toys. Toys are now cheaper in the Indian markets than earlier.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question : Which one of the following suits best title for the above paragraph?
(a) Ease of Global Trade
(b) People likes value for money products
(c) Effect of foreign trade
(d) Toys are hot selling products in India
Answer : (c) Effect of foreign trade
Question : Which one of the following statements, proves that foreign products harm Indian manufacturings?
(a) Chinese manufacturers learn of an opportunity to export toys to India.
(b) 70 to 80 per cent of the toy shops have replaced Indian toys with Chinese toys
(c) Toys are now cheaper in the Indian markets than earlier.
(d) Buyers in India now have the option of choosing between Indian and the Chinese toys.
Answer : (b) 70 to 80 per cent of the toy shops have replaced Indian toys with Chinese toys
Question : The Chinese toys attract Indian customers, because ________ .
(a) They are cheaper and have latest design.
(b) They are more durable and environment friendly.
(c) Have high reselling price.
(d) It boosts Indian trade with China.
Answer : (a) They are cheaper and have latest design.
Question : Chinese manufacturers could easily expand their toys market in India. Chinese manufactures—
(a) Understand the demand of Indian market.
(b) Could successfully beat the Indian quality and design.
(c) Provide the toys at cheaper price.
(d) All of them
Answer : (d) All of them.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
There are a variety of ways in which the MNCs are spreading their production and interacting with local producers in various countries across the globe. By setting up partnerships with local companies, by using the local companies for supplies, by closely competing with the local companies or buying them up, MNCs are exerting a strong influence on production at these distant locations. As a result, production in these widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
Question : Which of the following best describes an MNC?
(a) An MNC is a company that controls production of good and services in multiple nations.
(b) An MNC is a government organized body that controls the distribution of resources in a country.
(c) An MNC is an organization that ensures new technology is used by the farming sector of a country.
(d) An MNC is a conglomerate of domestic companies that control production of goods and services in the domestic region.
Answer : (a) An MNC is a company that controls production of good and services in multiple nations.
Question : Which of the following is an advantage of globalization to multinational companies?
(a) Multinational companies do not have to procure raw materials from other countries as globalization leads to self-sufficiency of companies.
(b) Spreading out production across international borders can help in lowering the cost of production.
(c) When multinational companies expand production across the world, they do not have to pay taxes as they help in generating employment.
(d) Multinational companies can easily put the burden of increased cost of production on global consumers and continue to earn high profits.
Answer : (b) Spreading out production across international borders can help in lowering the cost of production.
Question : Rajiv has a textile firm. For carrying out production,Rajiv spent money on procuring thread from traders,buying machine and equipment and built a warehouse to store the cloth produced. The expenditure incurred by Rajiv for conducting the production process is termed as …………
(a) investment
(b) profits
(c) equity
(d) interest
Answer : (a) investment.
Question : Which of the following can be a benefit to local businesses if they conduct business with MNCs?
(a) Local businesses do not have to invest in the business as MNCs do all the investment.
(b) MNCs provide cheap labour to local businesses.
(c) MNCs can bring advanced techniques of production.
(d) Local businesses earn higher profits as their cost of production becomes nil.
Answer : (c) MNCs can bring advanced techniques of production.
Question : Arrange the following according to their establishment year :
(i) Sony (ii) Ranbaxy
(iii) Nokia (iv) IBM
(a) i-iv-ii-iii
(b) ii-iv-i-iii
(c) iv-ii-i-iii
(d) i-ii-iii-iv
Answer : (d) i-ii-iii-iv
Question : Which of the following option best describe the ‘Globalisation’ ?
(a) The process of removing international borders by countries.
(b) The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
(c) The process of abolishing own government and letting United Nation govern.
(d) The process of abolishing own currency and adopting dollar as only recognised currency.
OR
Which of the following cannot be used as collateral?
(a) Land titles
(b) Deposits with banks
(c) Godown taken on rent
(d) Livestock
Answer : (b) The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
OR
(c) Godown taken on rent.
Question : Which of the following is an example of globalization?
(a) Indians consuming good produced abroad.
(b) Indians becoming self-sufficient in terms of production of goods and services.
(c) Indians moving across different states in domestic territory.
(d) Indians producing huge amount of agricultural produce.
Answer : (a) Indians consuming good produced abroad.
Question : Which of the following best describes an MNC?
(a) An MNC is a company that controls production of good and services in multiple nations.
(b) An MNC is a government organized body that controls the distribution of resources in a country.
(c) An MNC is an organization that ensures new technology is used by the farming sector of a country.
(d) An MNC is a conglomerate of domestic companies that control production of goods and services in the domestic region.
Answer : (a) An MNC is a company that controls production of good and services in multiple nations.
Question : The investment made by MNCs is called ______.
(a) foreign investment
(b) foreign trade
(c) foreign demand
(d) foreign supply
Answer : (a) foreign investment
Question : When was this organisation established ?
(a) January 1, 1995
(b) April 1, 1995
(c) January 1, 1990
(d) April 1, 1990
Answer : (a) January 1, 1995
Question : Which of the following is an advantage of globalization to multinational companies?
(a) Multinational companies do not have to procure raw materials from other countries as globalization leads to self-sufficiency of companies.
(b) Spreading out production across international borders can help in lowering the cost of production.
(c) When multinational companies expand production across the world, they do not have to pay taxes as they help in generating employment.
(d) Multinational companies can easily put the burden of increased cost of production on global consumers and continue to earn high profits.
Answer : (b) Spreading out production across international borders can help in lowering the cost of production.
(b) Improvements and modernization of technology.
(iii) Can you think of any other step that the government could take?
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Resources and Development |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Resources and Development in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Forest and Wildlife Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Water Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Water Resources in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Agriculture |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Agriculture in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Minerals & Energy Resources |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Minerals & Energy Resources in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Manufacturing Industries |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Manufacturing Industries in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Lifelines of National Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Geography HOTs Lifelines of National Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Power Sharing |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Power Sharing in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Federalism |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Federalism in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Democracy and Diversity in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Democracy and Diversity |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Gender Religion and Caste |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Gender Religion and Caste in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Popular struggles and Movements in hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Popular Struggles and Movements |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Political Parties in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Political Parties |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Outcomes of Democracy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Outcomes of Democracy |
| CBSE Class 10 Civics HOTs Challenges to Democracy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Challenges to democracy |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Rise of Nationalism in Europe in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Nationalism in India in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Nationalism in India |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs The Making of a Global World in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Making of a Global World |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs The Age of Industrialization in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs The Age of Industrialization |
| CBSE Class 10 History HOTs Print Culture and the Modern World in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Print culture and the Modern World |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Development in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Development |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Sectors of the Indian Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Sectors of the Indian Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Money and Credit |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Money and Credit in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Globalisation and the Indian Economy in Hindi |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Globalization and the Indian Economy |
| CBSE Class 10 Social Science HOTs Consumer Rights |
| CBSE Class 10 Economics HOTs Consumer Rights in Hindi |
More Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy HOTS
We hope students liked the above HOTS for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Social Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the High Order Thinking Skills Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Social Science HOTS Questions on daily basis. All latest HOTS with answers have been developed for Social Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics that the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Studiestoday is the best portal for Class 10 students to get all latest study material free of cost.
HOTS for Social Science CBSE Class 10 Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Social Science to develop the Social Science Class 10 HOTS. If you download HOTS with answers for the above chapter daily, you will get higher and better marks in Class 10 test and exams in the current year as you will be able to have stronger understanding of all concepts. Daily High Order Thinking Skills questions practice of Social Science and its study material will help students to have stronger understanding of all concepts and also make them expert on all critical topics. You can easily download and save all HOTS for Class 10 Social Science also from www.studiestoday.com without paying anything in Pdf format. After solving the questions given in the HOTS which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science designed by our teachers
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy HOTS Social Science CBSE Class 10
All HOTS given above for Class 10 Social Science have been made as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. The students of Class 10 can refer to the answers which have been also provided by our teachers for all HOTS of Social Science so that you are able to solve the questions and then compare your answers with the solutions provided by us. We have also provided lot of MCQ questions for Class 10 Social Science in the HOTS so that you can solve questions relating to all topics given in each chapter. All study material for Class 10 Social Science students have been given on studiestoday.
Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy CBSE Class 10 HOTS Social Science
Regular HOTS practice helps to gain more practice in solving questions to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy concepts. HOTS play an important role in developing an understanding of Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy in CBSE Class 10. Students can download and save or print all the HOTS, printable assignments, and practice sheets of the above chapter in Class 10 Social Science in Pdf format from studiestoday. You can print or read them online on your computer or mobile or any other device. After solving these you should also refer to Class 10 Social Science MCQ Test for the same chapter
CBSE HOTS Social Science Class 10 Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy
CBSE Class 10 Social Science best textbooks have been used for writing the problems given in the above HOTS. If you have tests coming up then you should revise all concepts relating to Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy and then take out print of the above HOTS and attempt all problems. We have also provided a lot of other HOTS for Class 10 Social Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Social Science.
You can download the CBSE HOTS for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the link above and download topic wise HOTS Questions Pdfs for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 for Social Science
Yes, the HOTS issued by CBSE for Class 10 Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy have been made available here for latest academic session
You can easily access the link above and download the Class 10 HOTS Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy for each topic
There is no charge for the HOTS and their answers for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 CBSE Social Science you can download everything free
HOTS stands for "Higher Order Thinking Skills" in Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science. It refers to questions that require critical thinking, analysis, and application of knowledge
Regular revision of HOTS given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Social Science Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy can help you to score better marks in exams
Yes, HOTS questions are important for Understanding Economic Development Chapter 4 Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Social Science exams as it helps to assess your ability to think critically, apply concepts, and display understanding of the subject.

