Download CBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effects of Electric Current Notes in PDF format. All Revision notes for Class 8 Science have been designed as per the latest syllabus and updated chapters given in your textbook for Science in Class 8. Our teachers have designed these concept notes for the benefit of Class 8 students. You should use these chapter wise notes for revision on daily basis. These study notes can also be used for learning each chapter and its important and difficult topics or revision just before your exams to help you get better scores in upcoming examinations, You can also use Printable notes for Class 8 Science for faster revision of difficult topics and get higher rank. After reading these notes also refer to MCQ questions for Class 8 Science given on studiestoday
Revision Notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Class 8 Science students should refer to the following concepts and notes for Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current in Class 8. These exam notes for Class 8 Science will be very useful for upcoming class tests and examinations and help you to score good marks
Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Notes Class 8 Science
CBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effect of Current Chapter Notes. Learning the important concepts is very important for every student to get better marks in examinations. The concepts should be clear which will help in faster learning. The attached concepts made as per NCERT and CBSE pattern will help the student to understand the chapter and score better marks in the examinations.
CHEMICAL EFFECT OF CURRENT
INTRODUCTION
Your parents and teachers always warn you not to touch the electrical switches with wet hands, as you are likely to get a severe electric shock. It is just possible that a drop of water may trickle inside the electric switch and make contact with electric wire. The water on our hands always contains small amount of salt dissolved in it. This makes the water good conductor of electricity. Thus, the electric current from the switch flows through the water and enters your body. The flow of electric current in your body gives an electric shock.
CAUTION : Do not touch the electric switch with wet hands, just for the fun or to check the above statement. It can be highly dangerous.
Let us perform the following activities to find out which of liquids conduct electricity and which of them do not conduct electricity.
ACTIVITY
To find out whether distilled water conducts electricity or not.
Materials required :
A dry cell. *Three insulated copper wires A, Band C with bare ends* a 1 volt bulb fixed in a bulb holder * a beaker * distilled water * cellotape.
Method : Half fill the beaker with distilled water. Connect the bare ends of the copper wires A, B and C through a bulb with the help of cellotape. Touch the bare ends of the wires B and C with one another. We will observe that bulb glows, thereby showing that all the parts of circuit are conducting electricity.
Dip the bare ends of the wires B and C in the distilled water. We will observe that the bulb does not glow. Thus, the activity clearly proves that distilled water does not conduct electricity
ACTIVITY
To show that the addition of salts, acids or alkalis, make the distilled water a conductor of electricity.
MATERIALS REQUIRED : All materials as in activity 1 and * common salt * sulphuric acid * sodium hydroxide.*a glass rod and a dropper.
METHOD: Proceed as in Activity 1 and confirm that distilled water does not conduct electricity. Now take a spoonful of common salt and add it into distilled water. Dissolve the common salt by stirring it with a glass rod. Dip the bare ends of the wires B and C in the above solution. You will observe that bulb lights up. Thus, the activity proves that addition of common salt in water makes it a conductor of electricity. Pour off the common salt solution and rinse the beaker with distilled water. Half fill the beaker with distilled water and add to it about 10 drops of sulphuric acid. On dipping the bare ends of wire B and C in the above solution you will observe that bulb lights up. This proves that acids on dissolving in distilled water make it a conductor of electricity.
Similarly, if we repeat the activity by adding 10 drops of sodium hydroxide solution in distilled water, the bulb will light up, thereby proving that alkalis on dissolving in distilled water make it conductor of electricity.
ACTIVITY
To find electrically conducting liquids and non-conducting liquids.
Materials required : *A dry cell * three insulated copper wire A, Band C with bare ends. *cellotape * 1 volt bulb fixed in a bulb holder. *100 cc beaker containing distilled water.*tap water *common salt solution. *vinegar solution *lemon juice solution. *alcohol petrol.*kerosene oil *mustard oil and dilute hydrochloric acid solution.
Method : Set up the apparatus as in Activity 1 or 2. Dip the bare ends of the wires Band C in the above mentioned solutions one by one, and record in which solutions the bulb lights up and in which solutions the bulb does not light up. We will observe that bulb lights up in case of tap water, common salt solution, vinegar solution, lemon juice solution and dilute hydrochloric acid solution. Thus, these liquids conduct electricity. We will also observe that bulb does not light up in case of distilled water, alcohol, petrol, kerosene oil and mustard oil. Thus, these liquids do not conduct electricity.
To find electrically conducting liquids and non-conducting liquids.
Materials required :
• A dry cell.
• three insulated copper wire A, Band C with bare ends.
• cellotape • 1 volt bulb fixed in a bulb holder. • 100 cc beaker containing distilled water. • tap water
• common salt solution. • vinegar solution • lemon juice solution. • alcohol petrol. • kerosene oil •mustard oil and dilute hydrochloric acid solution.
Method : Set up the apparatus as in Activity 1 or 2. Dip the bare ends of the wires Band C in the above mentioned solutions one by one, and record in which solutions the bulb lights up and in which solutions the
bulb does not light up.
We will observe that bulb lights up in case of tap water, common salt solution, vinegar solution, lemon juice solution and dilute hydrochloric acid solution. Thus, these liquids conduct electricity. We will also observe that bulb does not light up in case of distilled water, alcohol, petrol, kerosene oil and mustard oil. Thus, these liquids do not conduct electricity.
ACTIVITY
To show chemical reaction takes place when electric current is passed through common salt solution in water.
Materials required : • A cup shaped voltameter with platinum electrodes. • common salt solution in distilled water. • a matchbox. • 6 volt battery • a switch.
Method : Take the given voltameter. It consists of a cup-shaped glass vessel from the bottom of which arise two platinum electrodes. These electrodes are connected to brass terminals fixed on the wooden base.
Fill 3/4 of the voltameter with water containing dissolved common salt. The dissolved common salt makes the water electrically conducting.
Fill each of the test tube of the voltameter with common salt solution and then invert them over the platinum electrodes as shown in Fig., taking care that no water flows out of them. This can be achieved by placing the thumb on, the mouth of test tubes and then removing the thumb under the common salt solution in the voltameter.
Put the switch in off position and then connect the terminals of 6-volt battery to the voltmeter as shown in Fig.. Now put the switch in on position.
We will observe that tiny bubbles of colourless gases arise from both the electrodes and collect in the test tubes. Furthermore, the gas collected at the platinum terminal connected to the negative terminal of the battery is twice in volume as compared to the gas collected at the platinum terminal connected to the positive terminal of the battery.
The gas collected on the platinum terminal connected to the negative terminal of the battery is hydrogen gas. This gas can be easily tested by bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of test tube. The gas
catches fire with a loud pop sound and the matchstick goes off.
The gas collected on the platinum terminal connected to the positive terminal of the battery is oxygen gas. This gas can be easily tested by introducing the glowing end of the matchstick in the test tube, when the matchstick bursts into flame.
Water ⎯⎯elec⎯tric⎯cu⎯rren⎯t → Hydrogen gas + Oxygen gas
B. Fill In The Blanks :
(i) Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of ......................... and .........................
(ii) Distilled water is a ......................... conductor of electricity.
(iii) Tap water is a ......................... conductor of electricity.
(iv) The passage of an electric current through a solution causes chemical .........................
(v) Copper gets deposited on the plate connected to ......................... terminal of the battery.
(vi) The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another metallic object, by means of electricity, is called .........................
C. Write True Or False For The Following Statements :
(a) Distilled water is a good conductor of electricity.
(b) Iron is used for electroplating.
(c) EPNS is written on objects plated with silver.
(d) Chromium is used for electroplating because it is a cheap metal.
D. Select The Odd One Out Giving Reason :
(a) Gold, silver, iron.
(b) Distilled water, salt solution, acid.
(c) Sulphuric acid, sodium hydro oxide, distilled water
E. Tick The Correct Option :
1. A bad conductor of electricity is
(a) Distilled water
(b) copper sulphate
(c) silver nitrate
(d) sulphuric acid.
2. Electroplating is not done with
(a) Silver
(b) zinc
(c) gold
(d) iron.
3. Artificial jewellery is usually coated with
(a) Gold
(b) zinc
(c) chromium
(d) copper.
4. Chromium plating is done because, chromium
(a) Is expensive
(b) has a shiny appearance
(c) gets corroded
(d) does not resist scratches.
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
Materials that allow electricity to flow through them easily are called conductors. Materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them easily are called insulators.
Examples of conductors:
Metals, graphite (a form of carbon)
Examples of insulators:
Rubber, plastic, wood, glass
The difference between conductors and insulators is explained by a term called electrical conductivity.
Electrical conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to carry electric current.
Substances that are good conductors of electricity have high electrical conductivity as compared to substances that are poor electrical conductors (also called insulators). Some liquids, but not all, are also good conductors of electricity.
Semi conductor : Those substance whose conductivity lies between the conductor and insulators are called semi conductor. e.g. Silicon, germanium are semi conductors, semi conductor may become conductor by increasing its temperature.
CONDUCTIVITY OF WATER
We are often advised to avoid handling electrical appliances with wet hands. Do you know why?
By itself, pure water is a poor conductor of electricity. But the water that we use in our houses is not pure water. Generally, water (tap water, pond water, well water, etc.) contains a lot of impurities, most of which are usually dissolved salts. The presence of even a small amount of impurity makes water a good conductor of electricity.
Touching an electrical appliance with wet hands could, therefore, be dangerous. We are more likely to get an electric shock if you touch an electric appliance with wet hands than with dry hands because wet skin has many times more conductivity than dry skin. Remember, getting an electric shock can be a very serious matter. Should an electric current pass through our body, it could result in very serious consequences, even death. So, always take care while handling electrical plugs and gadgets.
LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED)
An electric bulb is used in the electric circuit to confirm the flow of current in the circuit. However, the electric bulb may not glow if the electric curent is weak. We use an LED in place of the electric bulb in case of weak electric current. In other words, LED glows even when a weak electric current flows through it. An LED has two wires attached to it. These wires are called leads. One lead is slightly longer than the other. It must be kept in mind that while connecting to a circuit the shorter lead is always connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the longer lead is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. It must be ensured that the free ends of the LEd do not touch each other. LEDs are available in many colours such as red, green, yellow, blue, white and are increasingly being used for many applications. LEDs are increasingly being used for lighting.
ACTIVITY
ELECTRICITY CONDUCTS THROUGH LEMON JUICE
Take an old used cell. Tear off a piece of zinc strip and carbon rod from it. Wash the strip of zinc you tore from the cell and clean it with a sand paper. Connect a wire to one end of the zinc strip. Now take a juicy lemon, cut a slit in it and push the zinc strip in it. Cut another slit and push in the carbon rod. Your cell is ready. now test this cell with the tip of your tongue as shown in fig. What do you feel? You will feel a slight tickling because your tongue is conducting electricity. The activity suggests that electricity conducts through lemon juice, an acidic solution.
MAKING A TESTER USING THE MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT
We have learnt that an electric current produces a magnetic field. What happens to compass needle when it is kept near a wire carrying electric curent? The magnetic needle will show deflection. The deflection is observed even if the current is weak. Thus, we can make a tester using the magnetic effect of current.
Take the tray from inside a discarded matchbox. Now wrap an electric wire 4-5 times around the tray. Gently place a small compass needle inside it. Join one free end of the wire to the terminal of a battery and the other end of the wire is left free. Now take another wire and join it with the other terminal of the battery.
The free ends of the two wires P and Q are joined momentarily. The compass needle shows some deflection. We have prepared a tester which can be used to detect the current flowing through a circuit.
MAKING AN ELECTRIC PEN
Heve you even thought of writing with the help of electricity? Amazing,isn't it? let us perform the following activity. You would need potassium iodide solution, starch solution (both available in your school laboratory), filter paper or tissue paper, metal sheet (copper), a battery and two connecting wires. Mix potassium iodide and starch solution and soak the filter paper in it. Spread the filter paper on the metal sheet. Attach the connecting wires to the terminals of the battery. Connect the wire coming from the positive terminal of the battery, to the metal plate (as shown in the fig.) and leave the othre wire (connected with the negative terminal) free.
Now write a word on the filter paper with the free end. You can see blue colour ink will appear at the places where it has been written. This is because the circuit is completed only when the wire touches the filter paper. This touching leads to the dissociation of KI (potassium iodide) which produces iodine. On reaction with starch, iodine forms blue-black colour. The electric pen was developed during Edison's research into telegraphy.
ELECTRICITY THROUGH DIFFERENT SUBSTANCES
All substances are made up of atoms, which have charged particles called electrons and protons. We know that electricity in all forms is due to the charges on these particles. When charged particles move in an orderly fashion, we get an electric current.
CONDUCTION IN SOLIDS
Among solids, metals are good conductors of electricity. In metals, some electrons are not very tightly bound to the atoms. They move about randomly in different directions within the metal. When a voltage is applied across a piece of a metal, these electrons move in an orderly fashion in one direction. This flow of electrons is the current in the metal. In most other solids, electrons are tightly bound to the atoms and are not easily available to flow. So, they do not conduct electricity well.
The randomly moving electrons in a metal bar start moving in an orderly fashion in one direction when a voltage is applied.
CONDUCTION IN LIQUIDS
Molten metals and mercury (a liquid metal) conduct electricity. The current through them is constituted by the flow of electrons. Other liquids conduct electricity because they have ions.
Under some conditions, an atom may lose one or more electrons, which get added to another atom. The atom that loses an electron (or electrons) has more protons than electrons. So, it becomes positively charged. And the atom that gains the electrons has more electrons than protons. So, it becomes negatively charged.
An atom or a radical that becomes charged by losing or gaining one or more electrons is called an ion.
K – e– → K+ (positively charged potassium ion)
(loses electron)
I + e– → I– (negatively charged iodide ion)
(gains electron)
Ca – 2e– → Ca2+ (positively charged calcium ion)
O + 2e– → O2– (negatively charged oxide ion)
Ions carrying opposite charges tend to attract and hold on to each other. This may lead to the formation of compounds called ionic compounds. For example, a sodium atom may lose an electron, which is gained by a chlorine atom. Thus, a positively charged sodium ion (Na+) and a negatively charged chloride ion (CI–) are formed. These come together to form the ionic compound NaCI.
Na – e– → Na+
CI + e– → CI –
Na+ + Cl– ⎯→ NaCI
Similarly, potassium iodide and calcium oxide are formed when their oppositely charged ions come together.
K+ + I– → KI
Ca2+ + O2– → CaO
Some more examples of ions and the compounds they form are given in Table.
IONS AND SOME COMPOUNDS THEY FORM
When an ionic compound is dissolved in water, it splits into its component ions. A liquid or a moist paste that has ions in it is called an electrolyte. When common salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it splits into Na+ and CI – ions.A solution of common salt is therefore an example of an electrolyte. In general, acids and solutions of salts and bases are electrolytes.
NaCl ⎯⎯ in water → Na+ + Cl –
The ions are free to move about in an electrolyte. When a voltage is applied across electrodes placed in the electrolyte,the ions start moving in an orderly fashion. The positive ions move towards the cathode (negative electrode) and the negative ions move towards the anode (positive electrode). Their flow constitutes a current through the electrolyte.
That is why liquids that have ions, such as acids and solutions of salts and bases, conduct electricity.
HOW THE ELECTRIC CURRENT BRINGS ABOUT CHEMICAL CHANGE IN WATER
A very, very small amount of water decomposes on its own to form positively charged hydrogen (H+) ions and negatively charged hydroxyl (OH–) ions. However, there number remains same and hence the water remains electrically neutral.
When electric current is passed through water, the hydrogen (H+) ions are attracted towards negatively charged platinum terminal. Here, they gain electric charges to form neutral hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen atoms subsequently join to form hydrogen molecule.
Conversely, on the passage of electric current, the hydroxyl (OH–) ions are attracted towards positively charged platinum terminal. Here, they lose electric charges to form neutral hydroxyl ions, which unite to form oxygen gas.
GENERAL TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE PASSAGE OF CURRENT THROUGH SOLUTIONS
1. Electrolyte : A solution of a chemical compound which conducts electric current and at the same time undergoes a chemical change is called electrolyte.
Examples :
(i) Aqueous solutions of all acids, such as HCI, HNO3, H2SO4 etc.
(ii) Aqueous solutions of all alkalis,. such as NaOH, KOH, etc.
(iii) Aqueous solution of salts, such as common salt, copper sulpate, sodium nitrate, zinc chloride, etc.
2. Non-electrolyte : A solution of a chemical compound which does not conduct electric current and hence does not undergo any chemical change is called non-electrolyte.
Examples : Petrol, kerosene oil, diesel oil, vegetable oils, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, alcohol, ether, benzene, distilled water, etc.
3. Electrolysis : The process due to which a solution of a chemical compound conducts electric current and at the same time undergoes a chemical change is called electrolysis.
4. Electrodes : The metal wires/plates/rods through which the current enters or leaves an electrolyte are called electrodes.
5. Cathode : The electrode connected to the negative terminal of a cell/battery is called cathode.
6. Anode : The electrode connected to the positive terminal of a cell/battery is called anode.
7. Ions : The electrically charged atoms/group of atoms formed when a chemical compound is dissolved in water are called ions.
8. Cations : The positively charged ions formed when a chemical compound dissolves in water are called cations.
During electrolysis, the cations are discharged at cathode by taking electric charges from it.
9. Anions : The negatively charged ions formed, when a chemical compound dissolves in water are called anions.
During electrolysis, the anions are discharged at anode by losing electric charges to it.
10. Voltameter : An apparatus in which electrolysis is carried out, such that it consists a vessel, two electrodes and electrolyte is called voltameter.
ELECTROPLATING
One of the uses of chemical effect of an electric current is electroplating. During electroplating the metal surface of a given article is coated with a thin layer of superior metal with the help of electric current.
Let us perform the following activity in order to show electroplating of an iron object.
ACTIVITY
To electroplate an article of iron with copper.
Materials required : • A glass container or 500 cc beaker. • copper sulphate crystals. • distilled water
• concentrated sulphuric acid • a copper plate • a 6 volt battery. • a switch
• three insulated copper wires with bare ends. • a glass rod. • an iron object.
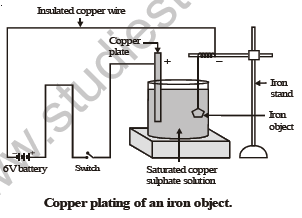
M E T H O D
(i) Half fill the given glass vessel with distilled water. To the distilled water add copper sulphate crystals and stir with glass rod, till the crystals stop dissolving. The solution so obtained is saturated copper sulphate solution.
(ii) In the above solution place a copper plate connected to an insulated copper wire through a switch. Tie the bare end of another copper wire to iron object and then immerse it in copper sulph…
(iii) Switch on the current and wait for 5-15 minutes.
(iv) Switch off the current and take the iron object out from copper sulphate solution.
You will notice that its surface is coated with a thin layer of copper which is reddish in colour.
HOW IS THIN LAYER OF COPPER METAL DEPOSITED ON THE GIVEN OBJECT?
The saturated copper sulphate solution contains the following cations and anions.
Cations : The positively charged cations are copper ions (Cu2+) from copper sulphate and hydrogen ions (H+) from water.
Anions : The negatively charged anions are hydroxyl ions (OH–) from water and sulphate ions (SO42–) from
copper sulphate.
When the electrical current is switched on, the cations start migrating towards the cathode and the anions towards the anode.
At the cathode the positively charged copper ions gain electrical charges to form copper atoms which deposit themselves on the surface of iron object. Thus, a thin layer of copper is deposited on iron objects.
The hydrogen ion do not discharge. Why? You will learn more about it in higher classes.
At anode, none of the negatively charged anions (hydroxyl and sulphate ions) discharge. Instead, the copper atoms on the copper plate lose their charges to form copper ions (Cu2+) which enter in the copper sulphate solution.
Thus, on the whole the anode loses copper atoms to form copper ions and the cathode gains same number of copper ions to form copper atoms,
ELECTROLYSIS AND ELECTROLYTIC CELL
It was found by Sir Humphry Davy that when electric current was passed through certain substances, they underwent a chemical change to give new substances. This is called electrolysis.
Thus, the production of a chemical reaction by passing an electric current through an electrolyte is called electrolysis.
Let us now understand the mechanism by which electric current passes through an electrolytic cell and how electrolysis occurs.
Figure shows how an electrolytic cell works. We dip two plates or rods made of a conducting material (like graphite, copper, ete.) in the liquid (called the electrolyte). These plates are called electrodes. One of them is called the cathode (connected to the negative terminal of the cell), and the other one is called the anode (connected to the positive terminal of the cell). The ends of the two electrodes are connected to a cell/battery.
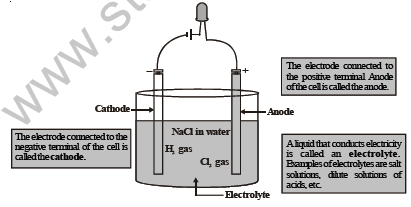
When we switch on the electric current, the electrolyte dissociates into positive ions and negative ions. The positive ions, called the cations, move towards the cathode and the negative ions, called the anions, move towards the anode.
At the cathode, the cations take up electrons and become neutral. The anions move to the anode and give up electrons.
USES OF ELECTROPLATING
1. Decoration purposes : Some metals give better look and finish. Therefore, the objects of not so expensive metals are generally electroplated with expensive metals such that they look more attractive and beautiful. For example, a flower vase of brass if electroplated with silver looks more decorative.
2. Protection against corrosion : More reactive metals tend to get rusted often. To protect the objects made of such reactive metals, they are electroplated with less reactive metals. For example, iron can be protected against rusting by electroplating it with nickel and zinc. Brass objects are protected against corrosion by chromium electroplating.
3. Repairing Finer Machine parts : Finer (small and precisely made) parts of certain machines cannot be repaired to ordinary methods involving welding, etc. Such like parts are repaired by depositing the desired metal at the proper location electrolytically.

LET US SUMMARIES
• Materials are classified as good or poor conductors of electricity.
• Distilled water does not conduct electricity.
• Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of acids, bases and salts.
• When two metal rods, called electrodes, are placed in a solution–called electrolyte–and current is passed through it, the current is conducted through the solution and the phenomenon is called electrolysis.
• The positive electrode through which current enters is called ano0de the negative electrode is called cathode.
• The phenonmen of causing chemical changes by passing electricity is called chemical effects of current.
• The method of purifying metals by using electricity is called electrorefining. metals such as zinc, copper, silver, gold, nickel, aluminium, etc. are refined by electrical method.
• The process of depositing a thin layer of a metal on any conducting substance by the process of electrolysis is known as electroplating.
EXERCISE - 1
CHOOSE THE CORRECT OPTION IN EACH OF THE FOLLOWING
Question. When electric current is passed through acidulated water, the gases produced are :
(A) Hydrogen and oxygen
(B) Hydrogen and ozone
(C) Oxygen and hydrogen peroxide
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. The object to be electroplated is made :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Cathode or anode
(D) Anode only
Answer : A
Question. The method of purifying metals by passing electricity is called :
(A) Electrolysis
(B) Electroplating
(C) Electrorefining
(D) None of these
Answer : C
Question. During purification of metals, the refined metal is obtained at the :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Surface of electrolyte
(D) Both (A) & (B)
Answer : B
Question. During electrolysis, the electrolyte undergoes :
(A) A physical change
(B) A chemical change
(C) Either (A) or (B)
(D) None of these
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is a non-electrolyte?
(A) Salt solution
(B) Lemon juice
(C) Distilled water
(D) Tap water
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is an electrolyte?
(A) Alcohol
(B) Benzene
(C) Sulphuric acid
(D) Kerosene oil
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is used to carry out electrolysis?
(A) Voltmeter
(B) Ammeter
(C) Voltameter
(D) All of these
Answer : C
Question. In an electrolytic cell, the electrode that is connected to the positive terminal of the battery is called :
(A) Cation
(B) Cathode
(C) Anion
(D) Anode
Answer : D
Question. The process by which a chemical change takes place in a substance when electric current is passed through it is called :
(A) Electrolysis
(B) Electroplating
(C) Electrodes
(D) Thermionic conduction
Answer : A
Question. Adding a soluble metallic salt to water :
(A) Increases its electrical conductivity
(B) Decreases its electrical conductivity
(C) Never produces any change in the conductivity
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. Electroplating is a method of :
(A) Making plates using electricity
(B) Plating a metal with another metal
(C) Coating any object with an electrically conducting plate
(D) Coating a metal with another metal by passing an electric current
Answer : D
Question. An electrolyte is :
(A) A light electric cell
(B) A liquid that conducts electricity
(C) A metal
(D) None of these
Answer : B
Question. A bad conductor of electricity is :
(A) Distilled water
(B) Copper sulphate
(C) Silver nitrate
(D) Sulphuric acid
Answer : A
Question. Electroplating is not done with :
(A) Silver
(B) Zinc
(C) Gold
(D) Iron
Answer : D
Question. Artifical jewellery is usually coated with
(A) Gold
(B) Zinc
(C) Chromium
(D) Copper
Answer : A
Question. Chromium plating is done because, chromium :
(A) Is expensive
(B) Has a shiny appearance
(C) Gets corroded
(D) Does not resist scratches
Answer : B
Question. When common salt is added to distilled water, the water becomes a :
(A) Good conductor
(B) Bad conductor
(C) Moderate conductor
(D) Both (A) & (B)
Answer : A
Question. Which of the following does not involve any chemical effects of current?
(A) Electroplating
(B) Electrorefining
(C) Dispersion
(D) None of these
Answer : C
Question. The process by which an electrolyte is decomposed with the help of electrcity is :
(A) Electroplating
(B) Electrorefining
(C) Electrolysis
(D) None of these
Answer : C
Question. The object to be electroplated is made :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Cathode or anode
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. The method of purifying metals by passing electricity is called :
(A) Electrolysis
(B) Electroplating
(C) Electrorefining
(D) Voltameter
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is used to test the flow of weak electric current through a circuit?
(A) LED
(B) Battery
(C) Voltameter
(D) Cathode
Answer : A
Question. Negatively charged electrode is known as :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Insulator
(D) Cathode or insulator
Answer : A
Question. During purification of metals, the refined metal is obtained at the :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Surface of electrolyte
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. How many leads does an LED have?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 8
Answer : A
Question. The longer end of LED is always connected to the ................ of the battery?
(A) Positive terminal
(B) Negative terminal
(C) Centre
(D) Insulator
Answer : A
Question. An LED is a type of :
(A) Resistor
(B) Tester
(C) Battery
(D) Bulb
Answer : B
Question. Jewellers electroplate silver and gold on :
(A) Expensive metals
(B) Less expensive metals
(C) All alkali metals
(D) All of these
Answer : B
Question. Tin cans, used for storing food, are made by electroplating tin onto :
(A) Lead
(B) Gold
(C) Iron
(D) Chromium
Answer : C
Question. Current is the flow of :
(A) Matter
(B) Electrons
(C) Protons
(D) Charge
Answer : D
Question. In electrolytic solutions, carier of charge is :
(A) Proton
(B) Electron
(C) Neutron
(D) Ion
Answer : D
Question. Insulators :
(A) Conduct electricity
(B) Do not conduct electricity
(C) Conduct electricity only at low temperature
(D) Conduct electricity at room temperature
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is an insulator?
(A) Wood
(B) Iron
(C) Carbon
(D) Silver
Answer : A
Question. In a cell, electrons move from :
(A) Positive electrode to negative electrode
(B) negative electrode to positive electrode
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Electrons do not move and only negative charge moves from on place to another place
Answer : B
Question. When an electron moves from negative electrode to positive electrode :
(A) Negative charge moves from negative electrode to positive electrode.
(B) Positive charge moves from positive electrode to negative electrode.
(C) No charge flows from either electrode to other electrode.
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer : D
Question. When the ends of metal wire are not connected to a battery :
(A) Electrons move from positive electrode to negative electrode.
(B) Electrons move from negative electrode to positive electrode.
(C) Electrons move in random directions
(D) Protons move in random direction in such a way that their net movement in a unit volume is zero.
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following statements are true ?
(A) During electrolysis, charge flows through electrolyte solution via electrons.
(B) The randomly moving electrons in a metal wire will start moving in a particular direction when a potential eifference is applied across it.
(C) A negatively charged particle has higher electric potential than a positively charged particle
(D) Charge flows only through negative charge carriers like electrons.
Answer : B
Question. A cell converts :
(A) Electrical energy into chemical energy.
(B) Chemical energy into electrical energy.
(C) Magnetic energy into electrical energy.
(D) Electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Answer : B
Question. An electrolyte :
(A) Has positive charge
(B) Has negative charge
(C) Should be able to conduct charge without dissociating
(D) Should able to form positive and negative ions.
Answer : D
Question. ____present in the lemon juice acts as electrolyte :
(A) Sulphuric acid
(B) Nitric acid
(C) Hydrochloric acid
(D) Critic acid
Answer : D
Question. Anode is :
(A) Positively charged electrode
(B) Negatively charged electrode
(C) Wire used to connect the electrodes
(D) Electrolyte which conducts electricity
Answer : A
Question. Cathode is :
(A) Positively charged electrode
(B) negatively charged electrode
(C) A positively charged ion formed in the electrolyte
(D) A negatively charged ion formed in the electgrolyte
Answer : B
Question. Copper electrode :
(A) Donates electrons to hydrogen ions
(B) Accepts electrons from hydrogen ions
(C) Denotes electrons to sulphate ions
(D) Accepts electrons from sulphate ions
Answer : A
Question. When coper rod donates electrons to hydrogen ions, it gains___charge.
(A) Positive
(B) Negative
(C) No charge
(D) Can't say
Answer : A
Question. The electrolyte in dry cell is :
(A) Copper sulphate
(B) Zinc sulphate
(C) Sulphuric acid
(D) Ammonium chloride
Answer : D
Question. In dry cell____acts as positive terminal.
(A) Carbon rod
(B) Manganese dioxide
(C) Manganese dioxide and powdered carbon
(D) Metal cap on the carbon rod
Answer : D
Question. The common dry cell produces a voltage of :
(A) 1.5 V
(B) 30 V
(C) 60 V
(D) 3 V
Answer : A
Question. When electric current is flown through a conductor, some amount of :
(A) Electrical energy is converted into heat energy
(B) Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy
(C) Mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy
(D) Heat energy is converted into electrical energy
Answer : A
Question. Nichrome is an alloy made of :
(A) Nickel and chromium
(B) Nitrogen and chromium
(C) Nitrogen, chlorine and chromium
(D) Nickel, chromium and manganese
Answer : A
Question. When current is passed through molten sodium chloride :
(A) Sodium is deposited at the positive electrode and chlorine gas is formed at the negative electrode
(B) Sodium is evaporated and chloride ions are formed at the negative electrode.
(C) Sodium is deposite at the positive electrode and chlorine is deposited at the negative electrode
(D) Sodium is deposited at the negative electrode and the chlorine gas is formed at the positive electrode.
Answer : D
Question. Splitting a compound using electricity is called :
(A) Electrolysis
(B) Electrolyte
(C) Electrokinesis
(D) None of these
Answer : A
Question. A bulb in an electric circuit glows due to :
(A) Magnetic effect of current
(B) Heating effect of current
(C) Chemical effect
(D) Conduction of current
Answer : B
Question. LEDs are extensively used to replace bulbs because :
(A) It consumes less electricity
(B) Have longer life
(C) Has more power
(D) All of the above
Answer : D
Question. Which of the following is a good conductor of electricity?
(A) Tap water
(B) Distilled water
(C) Sea water
(D) Rain water
Answer : C
Question. A compass placed in an electric field wil be deflected due to :
(A) Heating effect of current
(B) Magnetic effect of current
(C) Conducting effect
(D) Resistance of the needle to the electric field
Answer : B
Question. The most common industrial application of chemical effect of electric current is :
(A) Electroplating
(B) Galvanising
(C) Anodising
(D) Electrolysis
Answer : A
Question. The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by passing electric current is called :
(A) Electrolysis
(B) Electroplating
(C) Chromium plating
(D) Galvanising
Answer : B
Question. Tin cans, used for storing food are made by electroplating :
(A) Chrome onto tin
(B) Iron onto tin
(C) Tin onto iron
(D) Chrome onto iron
Answer : C
Question. To protect iron from corrosion and rust, it is coated by :
(A) Tin
(B) Copper
(C) Zinc
(D) Mercury
Answer : C
FILL IN THE BLANKS
Question. Water mixed with salts is a .................. conductor of electricity.
Answer : Good
Question. For electricity to flow in a medium, we need .................. charges in the medium.
Answer : Free
Question. Impurities in water generally .................. its conductivity.
Answer : Increase
Question. In liquids, electrical conductivity is generally due to ...................
Answer : Irons
Question. Cations carry .................. charge.
Answer : Positive
Question. Anions are attracted to the ...................
Answer : Cathode
Question. Na+ is a ...................
Answer : Cation
Question. The branch of science that deals with the interrelation between chemical phenomena and electricity is called...................
Answer : Electrochemistry
Question. The method of coating a metal with a layer of another metal using electric current is called ...................
Answer : Electroplating
Question. .................. is a measure of the ability of a substance to carry electric current.
Answer : Electrical conductivity
Question. Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of .................., .................. and ..................
Answer : acids, bases, salts
Question. Distilled water is a .................. conductor of electricity.
Answer : Bad
Question. Tap water is a .................. conductor of electricity.
Answer : Good
Question. The passage of an electric current through a solution causes chemical ...................
Answer : reactions
Question. Copper gets deposited on the plate connected to .................. terminal of the battery.
Answer : Negative
Question. The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another metallic object, by means of electricity, is called ...................
Answer : Electroplating
Question. The chemical effects of current involve transformation of .................. energy into .................. energy.
Answer : Electrical, Thermal
Question. During electrolysis, an electrolyte undergoes a .................. change.
Answer : Chemical
Question. .................. is used for making artifical jewellery.
Answer : Gold sliver chromium
Question. Liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of acids, bases and ...................
Answer : Salts
Question. .................. is the process by which an electrolyte is decomposed with the help of electricity.
Answer : Electrolysis
Question. Salt makes distilled water a .................. conductor of electricity.
Answer : Good
Question. Liquid that conducts electricity is called a/an ...................
Answer : Electrolysis
Question. The process by which an electrolyte is decomposed with the help of electricity is known as ...................
Answer : Electrolysis
Question. The electrode connected to the negative terminal is known as ...................
Answer : Cathode
WRITE TRUE OR FALSE THE FOLLOWING STATEMENTS
Question. Electrolysis is carried out in an electrolytic cell.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Cathode is a negative terminal.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Acidulated water conducts electricity.
Answer : TRUE
Question. The chemical effects of current involve transformation of electrical energy into thermal energy.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Addition of sodium hydroxide in distilled water makes it non-electrolyte.
Answer : FALSE
Question. Lemon juice cannot conduct electricity.
Answer : FALSE
Question. Distilled water is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer : FALSE
Question. Iron is used for electroplating.
Answer : FALSE
Question. EPNS is written on objects plated with silver.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Chromium is used for electroplating because it is a cheap metal.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Acids, bases and salts do not conduct electricity.
Answer : FALSE
Question. Electrode connected to positive terminal is called anode.
Answer : FALSE
Question. Items to be electroplated from the cathode.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Electrorefining is based on chemical effects of current.
Answer : TRUE
Question. Lemon juice is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer : TRUE
MATCH THE ITEMS IN COLUMN-A WITH THE ITEMS IN COLUMN-B
Column-A Column-B
1. (A) Corrosion (i) Positive electrode
(B) Anode (ii) Good conductor of electricity
(C) Aluminium (iii) Negative electrode
(D) Distilled water (iv) Electroplating
(E) Cathode (v) Electroplating
Column-A Column-B
2. (A) Negative electrode (i) Electrolyte
(B) Positive electrode (ii) Artifical jewellery
(C) CuSO4 (aq) (iii) Non-electrolyte
(D) Electroplating (iv) Cathode
(E) Kerosene (iv) Anode
Column-A Column-B
3. (A) Distilled water (i) Good conductor
(B) Tap water (ii) Chromium
(C) Electroplating (iii) Electroplating with silver
(D) EPNS (iv) Bad conductor
Answer :
MATCH THE FOLLOWING :
(A) (A) → iv ; (B) → i ; (C) → ii ; (D) → v ; (E) → iii; (B) (A) → iv ; (B) → v ; (C) → i ; (D) → ii ; (E) → iii;
(C) (A) → iv ; (B) → i ; (C) → ii ; (D) → iii
Please click the link below to download pdf file for CBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effect of Current Chapter Notes.
Q5. Identify the following solutions as good or bad conductors of electricity:
Ans.a) Vinegar Good conductor
b) Soap solution Good conductor
c) Mustard oil Bad conductor
d) Honey Bad conductor
e) Petrol Bad conductor
f) Sugar solution Bad conductor
g) Copper Sulphate solution Good conductor
Q6. Why should not we join the two free ends of a tester when it is not in use?
Ans. We should not join the two free ends of a tester when it is not in use so as to avoid the wastage of battery.
Q7. Suggest the possible alternatives to test the conductivity of a weakly conducting solution.
Ans. To test the conductivity of a weakly conducting solution:
a) We can replace the bulb of a tester with an LED.
b) We can use a magnetic compass.
Q8. Why does not pure water conduct electricity? How can we make it conducting?
Ans. Pure water does not conduct electricity because of the absence of charged particles called ions in it.It can be made conducting by adding a salt, an acid or a base in it.
Q9. a) What is the full form of LED?
b) Why is it preferred over a bulb while making a tester?
Ans. a) Light emitting diode.
b) An LED is preferred as it can glow even when the current passing through a circuit is weak.
Q1O. Why should we not touch the electrical equipment with wet hands?
Ans. We should not touch the electrical equipment with wet hands as tap water and human body are good conductors of electricity, so we can get an electric shock.
Part II
Q1. What changes are seen when an electric current is passed through a conducting solution ?
Ans. i. Bubbles of gas may be formed.
ii. Deposits of metals may be seen over electrodes.
iii. Change in colour of solution my occur.
Q2. What products are formed during the electrolysis of water?
Ans. Decomposition of water by the passage of electric current is known as electrolysis of water. Electrolysis of water leads to formation of Hydrogen gas at the cathode and Oxygen at the anode.
Q3. What is electroplating?
Ans. Deposition of a layer of metal over another by means of electricity is called electroplating.
Q4. What is an electrolyte ? Give some examples.
Ans. Any solution that conducts electricity is known as an electrolyte. Acids, Bases and Salt solutions are some electrolytes.
Q5. Explain how electroplating of one metal can be done over another metal by taking a suitable example.
Ans. In electroplating of Gold over Copper, Copper is made as cathode by connecting to the negative terminal of the battery. Gold which has to be deposited over the Copper is made as anode by connecting to the positive terminal of the battery.
Electrolyte is the salt solution of Gold. When the circuit is complete, Gold from the anode will go into the solution and an equivalent amount of Gold from the solution will be deposited over Copper (Cathode) thus causing its electroplating over Copper.
| CBSE Class 8 Science Crop Production And Management Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Microorganism Friend Or Foe Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Synthetic Fibres And Plastics Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Metal And Non Metals Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Coal And Petroleum Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Combustion and Flame Chapter Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Conservation Of Plants And Animals Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Cell Structure And Functions Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Cell and Tissue Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Reproduction And Cloning Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Reproduction in Animals Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Force And Pressure Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Friction Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Sound Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Chemical Effects of Electric Current Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Some Natural Phenomena Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Light Notes |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Stars and the Solar System |
| CBSE Class 8 Science Pollution of Air and Water Notes |
More Study Material
CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Notes
We hope you liked the above notes for topic Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 8 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 8 should download and practice the above notes for Class 8 Science regularly. All revision notes have been designed for Science by referring to the most important topics which the students should learn to get better marks in examinations. Studiestoday is the best website for Class 8 students to download all latest study material.
Notes for Science CBSE Class 8 Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
Our team of expert teachers have referred to the NCERT book for Class 8 Science to design the Science Class 8 notes. If you read the concepts and revision notes for one chapter daily, students will get higher marks in Class 8 exams this year. Daily revision of Science course notes and related study material will help you to have a better understanding of all concepts and also clear all your doubts. You can download all Revision notes for Class 8 Science also from www.studiestoday.com absolutely free of cost in Pdf format. After reading the notes which have been developed as per the latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science provided by our teachers
Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Notes for Science CBSE Class 8
All revision class notes given above for Class 8 Science have been developed as per the latest curriculum and books issued for the current academic year. The students of Class 8 can rest assured that the best teachers have designed the notes of Science so that you are able to revise the entire syllabus if you download and read them carefully. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 8 Science in the notes so that you can learn the concepts and also solve questions relating to the topics. All study material for Class 8 Science students have been given on studiestoday.
Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current CBSE Class 8 Science Notes
Regular notes reading helps to build a more comprehensive understanding of Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current concepts. notes play a crucial role in understanding Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current in CBSE Class 8. Students can download all the notes, worksheets, assignments, and practice papers of the same chapter in Class 8 Science in Pdf format. You can print them or read them online on your computer or mobile.
Notes for CBSE Science Class 8 Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
CBSE Class 8 Science latest books have been used for writing the above notes. If you have exams then you should revise all concepts relating to Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current by taking out a print and keeping them with you. We have also provided a lot of Worksheets for Class 8 Science which you can use to further make yourself stronger in Science
You can download notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the link above and download notes PDFs for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current which you can use for daily revision
Yes, the notes issued for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current have been made available here for latest CBSE session
You can easily access the link above and download the Class 8 Notes for Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current for each topic in Pdf
There is no charge for the notes for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current, you can download everything free of charge
www.studiestoday.com is the best website from which you can download latest notes for Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Science Class 8
Come to StudiesToday.com to get best quality topic wise notes for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
We have provided all notes for each topic of Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current as per latest CBSE syllabus

