Download CBSE Class 11 Biology Excretory Products And Their Elimination Notes in PDF format. All Revision notes for Class 11 Biology have been designed as per the latest syllabus and updated chapters given in your textbook for Biology in Class 11. Our teachers have designed these concept notes for the benefit of Class 11 students. You should use these chapter wise notes for revision on daily basis. These study notes can also be used for learning each chapter and its important and difficult topics or revision just before your exams to help you get better scores in upcoming examinations, You can also use Printable notes for Class 11 Biology for faster revision of difficult topics and get higher rank. After reading these notes also refer to MCQ questions for Class 11 Biology given on studiestoday
Revision Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination
Class 11 Biology students should refer to the following concepts and notes for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination in Class 11. These exam notes for Class 11 Biology will be very useful for upcoming class tests and examinations and help you to score good marks
Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Notes Class 11 Biology
Excretory Products and Their Elimination
POINTS TO REMEMBER :
• Ammonotelic: elimination of nitrogenous waste in the form of ammonia.(fish)
• Ureotelic: elimination of nitrogenous waste in the form of urea.(Amphibia and mammalian)
• Uricotelic: elimination nitrogenous waste in the form of uric acid. (Reptilia, bird and insects)
Excretory organs :
• Protonephridia or flame cells – Platyhelminthes (Planaria), rotifers, some annelids and cephalochordates (Amphioxus)
• Nephridia: annelid.
• Malpighian tubules – insects
• Antennal gland or green glands – crustacean like prawn.
HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM :
o Human excretory system consists of
• A pair of kidney
• A pair of ureters
• A urinary bladder
• A urethra
o Kidney is reddish brown, bean shaped structure situated between the levels of last thoracic vertebra close to dorsal inner wall of the abdominal cavity.
o Each kidney measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width, 2-3 cm in thickness.
o Towards the centre of inner concave surface is a notch, called hilum through which ureters, blood vessel and nerves enter into the kidney.
o Inner to hilum is a broad funnel shaped space called renal pelvis with projections called calyces.
o The outer wall of kidney is a tough capsule.
o Internally the kidney is differentiated into outer cortex and inner medulla.
o The medulla is divided into a few conical masses called medullary pyramids.
o Pyramids projected into the calyces.
o The cortex extended in-between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called columns of Bertini.
o Each kidney has nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephrons.
o Structural and functional unit of kidney is called nephron or uriniferous tubule.
o Each nephron has two parts:
• Glomerulus
• Renal tubule.
o Glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries formed by the afferent renal arteriole (a branch of renal artery).
o Blood from the Glomerulus is collected by efferent renal arteriole.
o The renal tubule begins with a double walled cup-like structure called Bowman’s capsule, which encloses the Glomerulus.
o Glomerulus along with Bowman’s capsule is called Malpighian body or renal corpuscles.
o Bowman’s capsule followed by highly coiled proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
o PCT followed by hairpin shaped Henle’s loop with ascending and descending limb.
o The ascending limb followed by another coiled tubular region called distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
o DCT of many nephron opens into a straight tube called collecting duct.
o All the collecting duct converges and opens into renal pelvis through medullary pyramids in the calyces.
o The malpighian corpuscles, PCT and DCT of the nephron are located in the cortex but the loop of Henle dips into the upper medulla.
o In some of the nephron, the loop of the Henle is very long and runs deep into the inner medulla. These nephrons are called juxta medullary nephrons.
o The efferent renal arteriole emerging from the Glomerulus forms a fine capillary network around the renal tubule called the peritubular capillaries.
o A minute vessel of this network runs parallel to the loop of Henle forming‘U’ shaped vasa recta.
o Vasa recta are absent or reduced in cortical nephron.
o The juxta medullary nephron has juxta-glomerular apparatus, in which the DCT run close to the afferent renal arteriole.
MECHANISM OF URINE FORMATION :
o Urine formation involves three main processes –
• Glomerular filtration
• Selective reabsorption
• Tubular secretion.
Glomerular filtration or ultra filtration :
o On an average 1120-1200 ml blood is filtered by the kidneys per minute.
o The glomerular capillary blood pressure caused filtration of through filtration membrane.
o The filtration membrane is formed by –
• Endothelium of glomerular blood vessel.
• The epithelium of Bowman’s capsule (podocytes)
• Basement membrane of these two layers.
o The epithelial cells of Bowman’s capsule called podocytes are arranged in an intricate manner so as to leave some minute spaces called filtration slit or slit pores.
o All constituent of plasma pass the filtration membrane except protein, hence it is called ultra filtration.
o The amount of filtrate formed by the kidneys per minute is called glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
o GFR is about 125 ml/min. i.e. 180 liters per day.
Selective reabsorption :
• Out of 180 liters of filtrate formed every day 178.5 liters along with useful materials reabsorbed into the blood through peritubular capillaries leaving 1.5 liters excreted in the form of urine.
• The tubular epithelial cells of different segments of nephron perform these either active or passive mechanisms.
• Substance like glucose, amino acids Na+ absorbed actively.
• Nitrogenous wastes are absorbed by passive transport.
• Reabsorption of water also occurs passively in the initial segments of the nephron.
Tubular secretion :
• The tubular cells adds substances like H+ , K+ and ammonia to the filtrate from the peritubular capillaries.
• Tubular secretion maintains ionic and acid base balance of the body fluids.
FUNCTION OF THE TUBULES :
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) :
• PCT is lined by simple Cuboidal brush border epithelium which increases the surface area for absorption.
• All essential nutrients and 70-80% of the electrolytes and water are reabsorbed by this segment.
• PCT also maintain the pH and ionic balance of the body fluids by selective secretion of H+, K+ and ammonia into the filtrate and by absorption of HCO3-.
Henle’s Loop :
o This region plays important role in maintenance of high osmolarity of medullary interstitial fluid.
o The descending limb is permeable to water but impermeable to electrolytes. This concentrates the filtrates as it moves down.
o The ascending limb is permeable to electrolytes but impermeable to electrolytes. Therefore as the concentrated filtrate pass upward, it gets diluted due to active or passive transport of electrolytes to the medullary fluid.
Distal convoluted tubules :
o Selectable reabsorption of Na+ and water takes place in this segment.
o DCT also capable of reabsorption of HCO3- and selective secretion of H+, K+, and NH3 to maintain the pH and sodium-potassium level in blood.
Collecting duct :
o This duct extends from cortex to inner part of the medulla.
o Large amount of water could be reabsorbed from this region to produce concentrated urine.
o This segment allow small amount of urea into the medullary interstitium to keep up the osmolarity.
MECHANISM OF CONCENTRATION OF FILTRATE :
o Mammals have the ability to produce concentrated urine.
o The Henle’s loop and vasa recta plays significant role in concentrating urine.
o The flow of filtrate in two limb of Henle’s loop and blood flow in two limbs of vasa recta are in opposite direction hence form counter current.
o The proximity between the Henle’s loop and vasa recta, as well as the counter current in them help in maintain an increasing osmolarity towards the inner medullary interstitium, i.e. from 300 mOsmolL-1 in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmolL-1 in the inner medulla.
o The gradient is mainly due to NaCl and urea.
o The NaCl actively transported from the ascending limb of Henle’s loop is exchanged by the ascending portion of the vasa recta.
o NaCl is returned to the interstitium by the ascending portion of vasa recta.
o Small amount of urea enters the thin segment of ascending limb of Henle’s loop which is transported back to the interstitium by the collecting tubule.
o This above described transport of substances facilitated by the special arrangement of Henle’s loop and vasa recta is called the counter current mechanism.
o This mechanism helps to maintain a concentration gradient in the medullary interstitium, that promote easy passage of water from the collecting duct, leads to formation of concentrated urine.
REGULATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION :
Regulation by ADH :
• Osmoreceptors present in the hypothalamus are activated by the change of blood volume, body fluid volume and ionic concentration.
• An excessive loss of body fluid activates the Osmoreceptors of hypothalamus to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) orvasopressin from the neurohypophysis.
• ADH facilitates active reabsorption of water from the DCT, preventing dieresis.
• An increase in body fluid volume can switch off the Osmoreceptors and suppress the release of ADH, promoting dilute urine formation.
• ADH also constricts the afferent renal arteriole in increase the blood pressure in the other hand to maintain the GFR.
Regulation by JGA (Juxta Glomerular Apparatus) :
• A fall in glomerular blood flow/glomerular blood pressure/GFR can activate the Juxta Glomerular cells to releaserenin.
• Renin converts angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin I and further to angiotensin II.
• Angiotensin II constricts afferent renal arteriole to increase glomerular blood pressure and thereby GFR.
• Angiotensin II also stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
• Aldosterone cause active reabsorption of Na+ and water from the distal part of the tubule, this increase in blood volume and GFR.
• This complex mechanism is called RAAS (Renin angiotensin aldosterone system).
Regulation by ANF :
• An increase in blood flow to the atria of the heart due RAAS cause the release of Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF).
• ANF can cause vasodilation (afferent renal arteriole) and thereby decrease the blood pressure.
• ANF also stop the release of renin hence stops RAAS.
MICTURITION :
• The expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder. It is a reflex process but can be controlled voluntarily to some extent in grown up children and adults.
• The CNS (Central Nervous System) sends the signal which causes the stretching of the urinary bladder when it gets filled with urine.
• In response, the stretch receptors on the walls of the bladder send signals to the CNS. The CNS passes on motor massage to initiate the contraction of smooth muscles of the bladder and simultaneous relaxation of the urethral sphincter causing the release of urine.
• An adult human excretes on an average 1 to 1.5 liters of urine per day.
• On an average 25-30 gram of urea is excreted out per day.
• Presence of Glucose is called Glycosuria.
• Presence of Ketone bodies in urine called Ketoneuria.
• Glycosuria and Ketoneuria are the indication of Diabetes mellitus.
Role of other organs in excretion :
• Lungs - removes CO2 (18L/day) and water.
• Liver - secretes bilirubin, biliverdin etc. helps to eliminate these substances along with cholesterol, vitamins, drugs and degraded steroid hormones through digestive wastes.
• Sweat and sebaceous glands - These glands of skin help to eliminate small amount of urea, NaCl and lactic acid etc. through sweat while sebaceous glands help to eliminate some substances like steroids, hydrocarbons and waxes through sebum.
• Saliva - It can help to eliminate small amount of nitrogenous wastes.
Disorders of Excretory system :
o Uremia - The accumulation of urea in blood due to malfunctioning of kidney.
o Hemodialysis - The process of removal of urea from the blood artificially. In this process the blood from an artery is passed into dialysing unit after adding an anticoagulant like heparin. The blood passes through coiled cellophane tube surrounding by dialysing fluid. The nitrogenous wastes from the concentration gradient and the blood become clear. This blood is pumped back to the body through vein after adding anti-heparin to it.
o Renal calculi - The formation of insoluble mass of crystallised salts (oxalates or phosphates of calcium.
o Glomerulonephritis - Inflammation of glomeruli of kidney.
Diabetes Insipidus
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is one of the hormones that efficiently monitors and regulates the functioning of the kidneys. Can you recall the other hormones involved? Why is ADH so called? (Diuresis is urine production). Antidiuretic hormone released from the posterior pituitary, prevents wide swings in water balance, helping to avoid dehydration or water overload. Try to recollect how ADH facilitates reabsorption of water by the distal parts of the kidney tubules and thereby prevents diuresis. Deficiency of ADH leads to diabetes insipedus, a condition marked by the output of huge amounts of urine and intense thirst. The name itself (diabetes =overflow; insipidus = tasteless) distinguishes it from diabetes mellitus (mel = honey), in which insulin deficiency causes large amounts of blood sugar to be lost in the urine.
Artificial kidney
You have studied about various disorders of the excretory system. Hemodialysis is an artificial process of removing toxic substances from the blood in patients of kidney failure. The hemodialysis machine is therefore also known as the artificial kidney.
MCQ Questions for NCERT Class 11 Biology Excretory Products and Their Elimination
Ques. A decrease in blood pressure/volume will not cause the release of
(a) atrial natriuretic factor
(b) aldosterone
(c) ADH
(d) renin.
Answer: A
Question. Sebaceous glands eliminate
(a) sterols and hydrocarbons
(b) heavy metals
(c) glucose and amino acids
(d) none of these.
Answer. A
Question. What is not true about uricotelic animals?
(a) They are exemplify by reptiles, birds and insects, etc.
(b) They spend least amount of water for elimination of the excretory product.
(c) It is a most toxic excretory product needing prompt removal.
(d) Uric acid is almost insoluble and can be eliminated in solid state.
Answer. C
Question. The location of kidney normally is between _________ thoracic vertebra and _________ lumbar vertebra.
(a) 8th and 1st, respectively
(b) 6th and 1st, respectively
(c) 10th and 2nd, respectively
(d) 12th and 3rd, respectively
Answer. D
Question. Podocytes are the cells present in
(a) cortex of nephron
(b) inner wall of Bowman’s capsule
(c) outer wall of Bowman’s capsule
(d) wall of glomerular capillaries.
Answer. B
Question. Identify the labelled parts A to D in the given figure of the Malpighian body and select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) Efferent Afferent Bowman’s Proximal arteriole arteriole capsule convoluted tubule
(b) Afferent Efferent Renal Proximal arteriole arteriole corpuscle convoluted tubule
(c) Afferent Efferent Bowman’s Proximal arteriole arteriole capsule convoluted tubule
(d) Afferent Efferent Bowman’s Distal arteriole arteriole capsule convoluted tubule
Answer. C
Question. Condition which result from renal failure of kidney is known as
(a) uremia
(b) enuresis
(c) diurea
(d) haematuria.
Answer. A
Question. Refer to the following diagram and identify the parts of a kidney indicated.
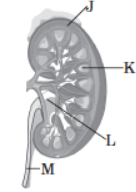
(a) J = nephron, K = pelvis, L = renal papilla, M = hilum
(b) J = medulla, K = nephron, L = pelvis, M = ureter
(c) J = cortex, K = medulla, L = calyx, M = pelvis
(d) J = cortex, K = medulla, L = pelvis, M = ureter
Answer. D
Question. Proximal convoluted tubule is lined by ________ cells.
(a) flattened
(b) columnar
(c) cuboidal with brush border
(d) simple rectangular
Answer. C
Question. Consider the following statements each with one or two blanks.
(i) The ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to (1) but allows transport of (2) .
(ii) (3) and (4) play a significant role in producing a concentrated urine.
(iii) A fall in glomerular blood flow/glomerular blood pressure/GFR can activate the JG cells to release (5) .
Which one of the following options correctly fills the blanks in any two of the statements?
(a) (1)-water, (2)-electrolytes, (5)-renin
(b) (3)-Henle’s loop, (4)-vasa recta,
(5)-angiotensin
(c) (1)-electrolytes, (2)-water, (3)-PCT, (4)-DCT
(d) (3)-Henle’s loop, (4)-vasa recta,
(5)-angiotensinogen
Answer. A
Question. Identify P, Q, R, S and select the correct option.
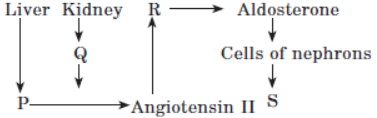
P Q R S
(a) Angiotensin I Renin Adrenal Increased Na+
cortex reabsorption
(b) Angiotensinogen Renin Adrenal Increased Na+
cortex reabsorption
(c) Angiotensinogen Renin Adrenal Decreased Na+
medulla reabsorption
(d) Angiotensin I Renin Adrenal Decreased Na+
cortex reabsorption
Answer. B
Question. The kidney is expected to carry out all the functions except
(a) removal of excretory products
(b) maintenance of proper pH of body fluids
(c) blood pressure regulation
(d) production of antibodies and sustain immune system.
Answer. D
Question. Excretion of nitrogenous waste product in a form of semi-solid paste occur in
(a) amniotes
(b) desert animals
(c) ureotelic animals
(d) uricotelic animals.
Answer. D
Question. A person diagnosed with inflammation of renal pelvis and the medullary tissue of the kidney, is suffering from
(a) renal calculi
(b) renal tubular acidosis
(c) renal failure
(d) pyelonephritis.
Answer. D
Question. The given figure represents a single nephron from a mammalian kidney. Identify the labelled parts, match them with the functions (i-iv) and select the correct option.
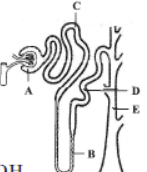
(i) The site of ultrafiltration.
(ii) Particularly sensitive to ADH.
(iii) The main site for the reabsorption of glucose and amino acids.
(iv) Responsible for the maintenance of blood pH.
(a) (i)-A, (ii)-E, (iii)-C, (iv)-D
(b) (i)-A, (ii)-B, (iii)-C, (iv)-D
(c) (i)-B, (ii)-A, (iii)-C, (iv)-E
(d) (i)-E, (ii)-B, (iii)-D, (iv)-A
Answer. D
Ques. Which of the following causes an increase in sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule?
(a) Increase in aldosterone levels
(b) Increase in antidiuretic hormone levels
(c) Decrease in aldosterone levels
(d) Decrease in antidiuretic hormone levels
Answer: A
Ques. A fall in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) activates
(a) juxtaglomerular cells to release renin
(b) adrenal cortex to release aldosterone
(c) adrenal medulla to release adrenaline
(d) posterior pituitary to release vasopressin.
Answer: A
Ques. Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to kidney function regulation?
(a) When someone drinks lot of water, ADH release is suppressed.
(b) Exposure to cold temperature stimulates ADH release.
(c) An increase in glomerular blood flow stimulates formation of angiotensin II.
(d) During summer when body loses lot of water by evaporation, the release of ADH is suppressed.
Answer: A
Ques. Angiotensinogen is a protein produced and secreted by
(a) juxtaglomerular (JG) cells
(b) macula densa cells
(c) endothelial cells (cells lining the blood vessels)
(d) liver cells.
Answer: D
Ques. If excess water passes out from the tissue without being restored by the kidneys, the cells would
(a) burst open and die
(b) take water from the plasma
(c) not be affected at all
(d) shrivel and die.
Answer: D
Ques. Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below.
Column I Column II
(Function) (Part of excretory system)
A. Ultrafiltration (i) Henle’s loop
B. Concentration of urine (ii) Ureter
C. Transport of urine (iii) Urinary bladder
D. Storage of urine (iv) Malpighian corpuscle
(v) Proximal convoluted tubule
A B C D
(a) (iv) (v) (ii) (iii)
(b) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
(c) (v) (iv) (i) (ii)
(d) (v) (iv) (i) (iii)
Answer: B
Ques. Human urine is usually acidic because
(a) potassium and sodium exchange generates acidity
(b) hydrogen ions are actively secreted into the filtrate
(c) the sodium transporter exchanges one hydrogen ion for each sodium ion, in peritubular capillaries
(d) excreted plasma proteins are acidic.
Answer: B
Ques. Which of the following does not favour the formation of large quantities of dilute urine?
(a) Renin
(b) Atrial-natriuretic factor
(c) Alcohol
(d) Caffeine
Answer: A
Ques. What will happen if the stretch receptors of the urinary bladder wall are totally removed?
(a) Micturition will continue.
(b) Urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder.
(c) There will be no micturition.
(d) Urine will not collect in the bladder.
Answer: A
Ques. A person who is on a long hunger strike and is surviving only on water, will have
(a) less amino acids in his urine
(b) more glucose in his blood
(c) less urea in his urine
(d) more sodium in his urine.
Answer: C
Ques. A person is undergoing prolonged fasting. His urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of
(a) fats
(b) amino acids
(c) glucose
(d) ketones.
Answer: D
Ques. Use of an artificial kidney during hemodialysis may result in
(A) Nitrogenous waste build-up in the body
(B) Non-elimination of excess potassium ions
(C) Reduced absorption of calcium ions from gastro-intestinal tract
(D) Reduced RBC production.
Which of the following options is the most appropriate ?
(a) (A) and (D) are correct.
(b) (A) and (B) are correct.
(c) (B) and (C) are correct.
(d) (C) and (D) are correct.
Answer: D
Ques. Match the items given in column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below.
Column I Column II
A. Glycosuria (i) Accumulation of uric acid in joints
B. Gout (ii) Mass of crystallised salts within the kidney
C. Renal calculi (iii) Inflammation in glomeruli
D. Glomerular nephritis (iv) Presence of glucose in urine
A B C D
(a) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(c) (ii) (iii) (i) (iv)
(d) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
Answer: D
Ques. A condition of failure of kidney to form urine is called
(a) anuria
(b) deamination
(c) uremia
(d) none of these.
Answer: A
Ques. Presence of RBC in urine is
(a) alkaptonuria
(b) urothiasis
(c) hematuria
(d) proteinuria.
Answer: C
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the mode of excretion and form of nitrogenous wastes excreted in the following organisms?
(a) Ascaris
(b) Pila
(c) Crocodiles
(d) Asterias
Answer. (a) Ascaris - Dual excretion, i.e., both ureotelic and ammonotelic. Wastes are ammonia (in water) and urea (on land). (b) Pila - Ammonotelic, waste product is ammonia. (c) Crocodiles - Ammonotelic, waste product is ammonia. (d) Asterias - Aminotelic, excretes amino acids.
Question. What role sweat plays in our body?
Answer. Sweat provides a cooling effect to our body when it gets evaporated. It also helps in excretion of NaCl, small amounts of urea, lactic acid, etc.
Question. What are the functions of collecting duct?
Answer. The collecting duct has important functions in regulating the composition of urine, as water, ions and nutrients are reabsorbed from the filtrate in the nephron tubules and collecting ducts. This reabsorption prevents the loss of useful nutrients, ions, and water, and provides an opportunity for tubule cells to regulate the composition of blood and the body fluids by maintaining their pH and ionic balance due to selective secretion of H+ and K+ ions.
Question. (a) What is meant by reabsorption in urine formation?
(b) Name the two modes of reabsorption.
Answer. (a) Reabsorption is the process by which most of the substances from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed by the nephron. (b) Active and passive mechanism.
Question. What is the role played by NaCl and urea in the counter current mechanism?
Answer. NaCl and urea help to maintain the gradient for osmolarity of 300 mOsmolL–1 in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmolL–1 in the inner medulla. The increased concentration of NaCl and urea in the interstitial fluid draws out water by osmosis thus concentrating the urine.
Question. What is the role played by renin in increasing the blood volume?
Answer. Renin initiates a series of chemical reactions that ultimately result in the formation of angiotensin II. It increases blood volume in two ways : Firstly, it induces the proximal convoluted tubules to reabsorb more NaCl and water and secondly it stimulates the adrenal glands to release a hormone, called aldosterone that induces the distal convoluted tubule to absorb more Na+ and water.
Question. Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone can cause diabetes. Justify.
Answer. Antidiuretic hormone facilitates absorption of water from distal part of tubules. Its deficiency may cause passing of excessive dilute urine and intense thirst. This condition is known as diabetes insipidus.
Question. Give a brief description of
(a) Podocytes (b) Glomerulus
Answer. (a) Podocytes are specialised cells found in the epithelium of visceral layer of glomerular membrane. They have foot like processes called the pedicels, hence called so. The space between the pedicels are called slit pores through which filtration occurs. (b) Glomerulus is a capillary network within the Bowman’s capsules. Blood enters glomerular capillaries through afferent arterioles and leaves through efferent arterioles. The diameter of afferent arteriole is much more than that of efferent arteriole.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Describe the structure of a human kidney with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer. Human excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Kidneys are reddish brown, bean shaped structures, situated between the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebra close to the dorsal inner wall of abdominal cavity. The kidneys are covered by a layer of fibrous connective tissue, the renal capsule. Outside the capsule, is a layer of fat, the adipose capsule, followed by a fibrous membrane, the renal fascia. The renal capsule, adipose capsule and renal fascia constitute the protective coats of kidneys. Towards the centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney, is a notch called hilus or hilum. Blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves and ureters enter or leave the kidney through hilus. There are two distinct zones in kidney–an outer, darker, renal cortex and an inner, lighter renal medulla which is made of 15-16 conical subdivisions called renal pyramids. The cortex extends in between medullary pyramids as renal columns, called columns of Bertini. Ureters are narrow, tubular structures composed of transitional epithelium, about 25-30 cm long and run backward along the abdominal wall to open into urinary bladder. Ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is muscular, pear shaped, sac-like structure lying in the pelvic cavity. Its inner lining is formed of transitional epithelium and muscular layer is called detrusor muscle. Urinary bladder stores urine temporarily. Urethra in males carries both urine and semen but, in females it carries only urine. Diagrammatic representation of human kidney is as follows: (IMG 160)
Please click the link below to download pdf file for CBSE Class 11 Biology Excretory Products And Their Elimination Notes.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biological Classification Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology Of Flowering Plants Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation In Animals Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell The Unit Of Life Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle And Cell Division Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Transport In Plants Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Mineral Nutrition Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration In Plants Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth And Development Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Digestion and Absorption Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids And Circulation Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Excretory Products And Their Elimination Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Locomotion And Movement Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control And Coordination Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set A |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology OTBA Guidance Document Set B |
More Study Material
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Notes
We hope you liked the above notes for topic Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 11 should download and practice the above notes for Class 11 Biology regularly. All revision notes have been designed for Biology by referring to the most important topics which the students should learn to get better marks in examinations. Studiestoday is the best website for Class 11 students to download all latest study material.
Notes for Biology CBSE Class 11 Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination
Our team of expert teachers have referred to the NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to design the Biology Class 11 notes. If you read the concepts and revision notes for one chapter daily, students will get higher marks in Class 11 exams this year. Daily revision of Biology course notes and related study material will help you to have a better understanding of all concepts and also clear all your doubts. You can download all Revision notes for Class 11 Biology also from www.studiestoday.com absolutely free of cost in Pdf format. After reading the notes which have been developed as per the latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology provided by our teachers
Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Notes for Biology CBSE Class 11
All revision class notes given above for Class 11 Biology have been developed as per the latest curriculum and books issued for the current academic year. The students of Class 11 can rest assured that the best teachers have designed the notes of Biology so that you are able to revise the entire syllabus if you download and read them carefully. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 11 Biology in the notes so that you can learn the concepts and also solve questions relating to the topics. All study material for Class 11 Biology students have been given on studiestoday.
Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination CBSE Class 11 Biology Notes
Regular notes reading helps to build a more comprehensive understanding of Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination concepts. notes play a crucial role in understanding Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination in CBSE Class 11. Students can download all the notes, worksheets, assignments, and practice papers of the same chapter in Class 11 Biology in Pdf format. You can print them or read them online on your computer or mobile.
Notes for CBSE Biology Class 11 Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination
CBSE Class 11 Biology latest books have been used for writing the above notes. If you have exams then you should revise all concepts relating to Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination by taking out a print and keeping them with you. We have also provided a lot of Worksheets for Class 11 Biology which you can use to further make yourself stronger in Biology
You can download notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, you can click on the link above and download notes PDFs for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination which you can use for daily revision
Yes, the notes issued for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination have been made available here for latest CBSE session
You can easily access the link above and download the Class 11 Notes for Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination for each topic in Pdf
There is no charge for the notes for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination, you can download everything free of charge
www.studiestoday.com is the best website from which you can download latest notes for Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Class 11
Come to StudiesToday.com to get best quality topic wise notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination
We have provided all notes for each topic of Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination as per latest CBSE syllabus

